1 4/7 As An Improper Fraction
Next Genwave
Mar 09, 2025 · 5 min read
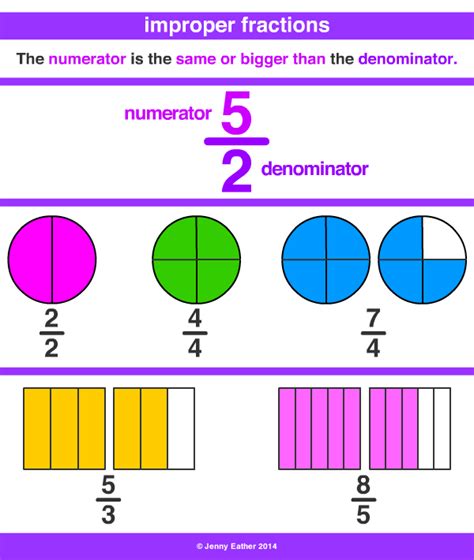
Table of Contents
1 4/7 as an Improper Fraction: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding fractions is a fundamental aspect of mathematics, crucial for various applications in everyday life and advanced studies. This article delves into the conversion of mixed numbers, like 1 4/7, into improper fractions, explaining the process step-by-step and exploring related concepts. We’ll cover not just the mechanics of the conversion but also its practical significance and applications.
Understanding Mixed Numbers and Improper Fractions
Before diving into the conversion, let's clarify the terms:
-
Mixed Number: A mixed number combines a whole number and a proper fraction. A proper fraction has a numerator (top number) smaller than the denominator (bottom number). For example, 1 4/7 is a mixed number: 1 is the whole number, and 4/7 is the proper fraction.
-
Improper Fraction: An improper fraction has a numerator that is greater than or equal to its denominator. For instance, 11/7 is an improper fraction. The numerator (11) is larger than the denominator (7).
Converting between these forms is essential for various mathematical operations, particularly addition and subtraction of fractions.
Converting 1 4/7 to an Improper Fraction: The Step-by-Step Process
The conversion of 1 4/7 to an improper fraction involves a straightforward two-step process:
Step 1: Multiply the whole number by the denominator.
In our example, the whole number is 1, and the denominator of the fraction is 7. Multiplying these together gives us: 1 * 7 = 7
Step 2: Add the numerator to the result from Step 1.
The numerator of our fraction is 4. Adding this to the result from Step 1 (7), we get: 7 + 4 = 11
Step 3: Keep the same denominator.
The denominator of the original fraction remains unchanged. Therefore, the denominator of our improper fraction is still 7.
Result: Combining the results from Steps 2 and 3, we arrive at the improper fraction: 11/7
Visualizing the Conversion: A Pictorial Representation
Imagine a pizza cut into 7 equal slices. The mixed number 1 4/7 represents one whole pizza (7/7) plus 4 additional slices (4/7). If we combine all the slices, we have a total of 11 slices out of the 7 slices that constitute a whole pizza. This visually represents the improper fraction 11/7.
Why is this Conversion Important?
Converting mixed numbers to improper fractions is crucial for several reasons:
-
Simplifying Calculations: Adding, subtracting, multiplying, and dividing fractions becomes much easier when all the fractions involved are in the same form – either all mixed numbers or all improper fractions. Trying to perform these operations directly with a mix of mixed numbers and improper fractions can be confusing and prone to errors.
-
Solving Equations: Many algebraic equations involving fractions require that you work with improper fractions for consistent and accurate solutions.
-
Real-World Applications: This conversion is applied in various fields, including:
-
Baking and Cooking: Recipes often require precise measurements, and converting mixed numbers to improper fractions simplifies calculations involving fractional quantities of ingredients.
-
Construction and Engineering: Precise measurements are paramount, and converting between mixed numbers and improper fractions aids in accurate calculations for building structures and designing systems.
-
Finance: Working with fractions of currency values requires accurate conversions to avoid errors in financial transactions and calculations.
-
Further Exploring Improper Fractions: Key Concepts and Examples
Let's delve into some related concepts and examples to reinforce understanding:
1. Converting Improper Fractions Back to Mixed Numbers:
The reverse process is equally important. To convert an improper fraction to a mixed number, divide the numerator by the denominator. The quotient becomes the whole number, the remainder becomes the numerator, and the denominator stays the same.
For example, to convert 11/7 back to a mixed number:
11 ÷ 7 = 1 with a remainder of 4. Therefore, 11/7 = 1 4/7
2. Simplifying Improper Fractions:
Sometimes, an improper fraction can be simplified. This involves finding the greatest common divisor (GCD) of the numerator and the denominator and dividing both by the GCD. For example, consider the improper fraction 12/6. The GCD of 12 and 6 is 6. Dividing both numerator and denominator by 6 gives us 2/1, which simplifies to 2.
3. Comparing Improper Fractions:
Comparing improper fractions involves comparing their numerical values. One easy method is to convert them to decimals. For instance, to compare 11/7 and 13/8, convert them to decimals: 11/7 ≈ 1.57 and 13/8 = 1.625. Therefore, 13/8 > 11/7.
4. Working with Improper Fractions in Calculations:
Let's illustrate the ease of working with improper fractions in calculations. Consider adding 1 4/7 and 2 3/7:
First, convert both mixed numbers to improper fractions:
1 4/7 = 11/7 2 3/7 = 17/7
Now, add the improper fractions:
11/7 + 17/7 = 28/7 = 4
This is much simpler than trying to add the mixed numbers directly.
Advanced Applications and Real-World Scenarios
The conversion between mixed numbers and improper fractions extends beyond basic arithmetic. It's a fundamental concept in:
-
Calculus: Dealing with limits and derivatives often involves manipulating fractions, where converting between mixed numbers and improper fractions is necessary for simplification and accurate calculations.
-
Probability and Statistics: Calculating probabilities and statistical measures frequently involves working with fractions, where converting between mixed numbers and improper fractions streamlines the process.
-
Computer Programming: Many programming languages require numerical representations of fractions, which often use improper fractions for greater computational efficiency and consistency.
Conclusion: Mastering the Conversion and its Implications
Understanding how to convert 1 4/7 (and other mixed numbers) to improper fractions is a fundamental skill that extends far beyond basic arithmetic. It simplifies complex calculations, ensures accuracy in various fields, and enhances understanding of more advanced mathematical concepts. Mastering this conversion is crucial for anyone looking to develop a solid foundation in mathematics and its numerous applications in daily life and specialized fields. The process itself is straightforward, but its implications are wide-ranging and impactful. This comprehensive guide aims to provide you with not only the 'how' but also the 'why' behind this essential mathematical transformation. Regular practice and application will solidify your understanding and build confidence in handling fractions efficiently and accurately.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
3 N 4 1 2 6n 4
Mar 09, 2025
-
What Is 1 3 Divided By 2
Mar 09, 2025
-
0 996 Rounded To The Nearest Hundredth
Mar 09, 2025
-
1 2 Times 1 2 Times 1 2
Mar 09, 2025
-
What Percent Of 9 Is 7
Mar 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 1 4/7 As An Improper Fraction . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
