16 To The Power Of 2
Next Genwave
Mar 06, 2025 · 5 min read
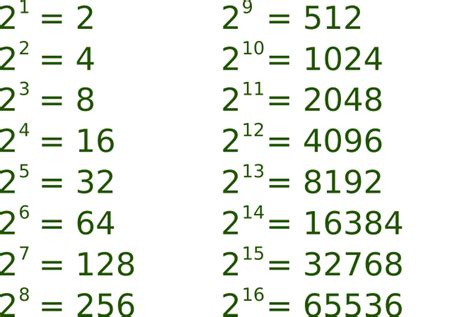
Table of Contents
16 to the Power of 2: Unpacking the Math and Exploring its Applications
The seemingly simple mathematical expression, 16², often gets overlooked. However, understanding this calculation – and its broader implications – opens doors to a deeper appreciation of exponential functions and their practical applications across diverse fields. This article will delve into the intricacies of 16 to the power of 2, exploring its calculation, its significance within various mathematical contexts, and its surprising real-world applications.
Calculating 16²: The Basics
At its core, 16² (16 to the power of 2) represents 16 multiplied by itself: 16 x 16. This straightforward calculation yields the result: 256. This seemingly simple operation forms the foundation for more complex mathematical concepts.
Understanding Exponents
The exponent (the small '2' in 16²) indicates the number of times the base (16) is multiplied by itself. Therefore, 16² means 16 multiplied by itself twice. This concept extends to higher exponents; for example, 16³ would be 16 x 16 x 16 = 4096. Understanding exponents is crucial for grasping exponential growth and decay, prevalent in various scientific and financial models.
Alternative Calculation Methods
While direct multiplication is the most straightforward method, alternative approaches exist. For example, recognizing that 16 is 2⁴ (2 to the power of 4), we can rewrite 16² as (2⁴)². Using the power of a power rule in algebra, this simplifies to 2<sup>4x2</sup> = 2⁸. Calculating 2⁸ (2 multiplied by itself eight times) also yields 256. This demonstrates the power of algebraic manipulation to simplify calculations.
The Significance of 256 in Different Contexts
The number 256, the result of 16², holds significant meaning across various disciplines:
Computer Science and Binary Systems
In computer science, 256 plays a crucial role due to its relationship with binary numbers. Since computers operate on binary code (a system with only two digits: 0 and 1), powers of 2 are fundamental. 256 (2⁸) represents 2<sup>8</sup> bits, equating to one byte. A byte is a fundamental unit of computer memory and data storage. Understanding this relationship is essential for comprehending data structures, memory management, and network protocols.
Bytes, Kilobytes, and Beyond
The prevalence of 256 in computer science extends beyond bytes. Kilobytes (KB), megabytes (MB), gigabytes (GB), and terabytes (TB) are all based on powers of 2, often approximated for human understanding. While strictly speaking a kilobyte is 1024 bytes (2<sup>10</sup>), it's often rounded to 1000 bytes for simplicity. However, understanding the underlying binary basis is critical for accurate data calculations and system performance analysis.
Color Representation in Digital Media
The number 256 also appears prominently in digital image representation. In many color models (like RGB), each color channel (red, green, blue) uses 8 bits, or one byte, to represent the intensity of the color. This means 2<sup>8</sup> = 256 possible intensity levels for each color, creating a rich palette of 16,777,216 (256³) unique colors. This impacts image quality, file size, and color accuracy in digital media.
Other Applications of 256
Beyond computer science and digital media, 256 appears in various mathematical and scientific contexts. It’s a significant number in cryptography, playing a role in certain encryption algorithms and hash functions. It also features in various mathematical sequences and patterns, often relating to modulo operations and prime factorization.
Exploring Exponential Growth and Decay
The concept of 16² directly relates to exponential growth and decay, fundamental principles in various fields:
Compound Interest
In finance, compound interest demonstrates exponential growth. If an initial investment grows at a fixed rate compounded annually, the final amount after a certain period can be calculated using exponential functions. While not directly related to 16², the underlying principle is analogous. Understanding exponential growth is crucial for financial planning, investment strategies, and economic modeling.
Population Growth Models
Exponential functions are frequently used to model population growth in biology and ecology. Under ideal conditions, populations can grow exponentially. However, factors like resource limitations and environmental constraints often lead to a more complex growth pattern. Nevertheless, the initial phases of population growth often exhibit exponential characteristics.
Radioactive Decay
Radioactive decay, on the other hand, demonstrates exponential decay. The rate at which a radioactive substance decays is constant, and the amount remaining after a certain time can be modeled using an exponential function. This concept is crucial in various applications, including carbon dating (used to determine the age of artifacts), nuclear medicine, and environmental monitoring.
16² in Advanced Mathematical Contexts
The seemingly simple calculation of 16² touches upon more complex mathematical concepts:
Number Theory
Within number theory, 256 (and its factors) could be analyzed for its properties, such as divisibility, primality, and relationships with other numbers. The study of numbers and their properties is a vast field with applications in cryptography and computer science.
Abstract Algebra
In abstract algebra, the concept of powers and exponents extends to groups and rings, which are abstract algebraic structures. The properties of exponentiation in these structures are essential for understanding various mathematical concepts.
Advanced Calculus
Derivatives and integrals of exponential functions are essential in calculus and its applications. Understanding the behavior of exponential functions is crucial for solving differential equations, modeling physical phenomena, and optimizing various processes.
Conclusion: The Unsung Power of 16²
While 16² may seem a simple mathematical problem, its solution, 256, reveals a wealth of connections across different disciplines. From its foundational role in computer science and digital media to its applications in exponential growth models and advanced mathematical concepts, 256 demonstrates the far-reaching implications of seemingly basic mathematical calculations. By understanding this seemingly simple equation, we gain a broader perspective on the power of mathematics and its essential role in shaping our world. The seemingly mundane 16² serves as a gateway to appreciating the elegance and practicality of mathematics in its various forms. It's a reminder that even the simplest concepts can unveil a surprising depth of understanding and application. Further exploring these connections can lead to a richer understanding of mathematics and its impact on various fields.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is A 13 Out Of 20
Mar 06, 2025
-
What Percent Is 45 Out Of 60
Mar 06, 2025
-
What Is 1 3 9 3
Mar 06, 2025
-
Whats The Square Root Of 10
Mar 06, 2025
-
What Is A 32 Out Of 40
Mar 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 16 To The Power Of 2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
