2 And 2/3 As An Improper Fraction
Next Genwave
Mar 10, 2025 · 5 min read
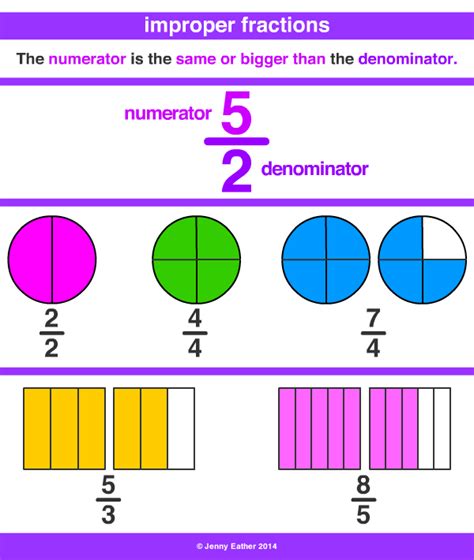
Table of Contents
2 and 2/3 as an Improper Fraction: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding fractions is fundamental to mathematics, and converting mixed numbers (like 2 and 2/3) into improper fractions is a crucial skill. This comprehensive guide will delve deep into the process, exploring various methods, providing practical examples, and offering valuable insights into why this conversion is important. We’ll also touch upon real-world applications and explore the broader context of fractions in mathematics.
Understanding Mixed Numbers and Improper Fractions
Before diving into the conversion, let's clarify the definitions:
-
Mixed Number: A mixed number combines a whole number and a fraction, such as 2 and 2/3. It represents a quantity greater than one.
-
Improper Fraction: An improper fraction has a numerator (the top number) that is greater than or equal to its denominator (the bottom number). For example, 8/3 is an improper fraction.
Converting a mixed number to an improper fraction is essentially expressing the same quantity in a different form. Both represent the same value, but the improper fraction format is often more convenient for calculations and certain mathematical operations.
Method 1: The Multiplication and Addition Method
This is the most common and straightforward method for converting a mixed number to an improper fraction. It involves two simple steps:
-
Multiply the whole number by the denominator: In our example (2 and 2/3), multiply 2 (the whole number) by 3 (the denominator). This gives us 6.
-
Add the numerator: Add the result from step 1 (6) to the numerator (2). 6 + 2 = 8. This becomes the new numerator of the improper fraction.
-
Retain the denominator: The denominator remains the same. In our case, it's 3.
Therefore, 2 and 2/3 converted to an improper fraction is 8/3.
Example 1: Convert 3 and 1/4 to an improper fraction.
- Multiply the whole number by the denominator: 3 * 4 = 12
- Add the numerator: 12 + 1 = 13
- Retain the denominator: 4
The improper fraction is 13/4.
Example 2: Convert 5 and 3/7 to an improper fraction.
- Multiply the whole number by the denominator: 5 * 7 = 35
- Add the numerator: 35 + 3 = 38
- Retain the denominator: 7
The improper fraction is 38/7.
Method 2: Visual Representation using Fraction Bars
This method is helpful for visualizing the concept and is particularly useful for beginners.
Imagine 2 and 2/3 as two whole bars divided into thirds, plus another bar with two-thirds shaded. If we divide each whole bar into thirds, we have a total of six thirds (2 * 3 = 6) from the two whole bars. Adding the two additional thirds gives us a total of eight thirds (6 + 2 = 8). This visually demonstrates that 2 and 2/3 is equivalent to 8/3.
Why Convert to Improper Fractions?
Converting mixed numbers to improper fractions is crucial for several mathematical operations:
-
Addition and Subtraction of Fractions: It's much easier to add or subtract fractions when they have a common denominator. Converting to improper fractions simplifies this process, especially when dealing with mixed numbers.
-
Multiplication and Division of Fractions: Multiplying and dividing mixed numbers directly can be cumbersome. Converting them to improper fractions makes these operations significantly easier and less prone to errors.
-
Solving Algebraic Equations: Many algebraic equations involve fractions. Converting mixed numbers to improper fractions is often a necessary first step in solving these equations.
-
Working with Ratios and Proportions: Improper fractions are frequently used when working with ratios and proportions, particularly in problems involving scaling or comparisons.
Real-World Applications
Understanding and using improper fractions is not limited to the classroom; it has practical applications in various real-world scenarios:
-
Cooking and Baking: Recipes often involve fractions of ingredients. Converting mixed numbers to improper fractions can help with accurate measurements and scaling recipes.
-
Construction and Engineering: Precise measurements are essential in construction and engineering. Converting between mixed numbers and improper fractions ensures accuracy in calculations and designs.
-
Finance and Accounting: Improper fractions can simplify calculations involving percentages, interest rates, and financial ratios.
-
Data Analysis: In data analysis, improper fractions might appear when working with proportions or representing data as fractions of a whole.
Advanced Concepts and Further Exploration
Beyond the basic conversion, understanding improper fractions opens doors to more advanced mathematical concepts:
-
Simplifying Improper Fractions: After converting a mixed number to an improper fraction, it's often possible to simplify the resulting improper fraction by finding a common factor for both the numerator and denominator. For example, 8/4 simplifies to 2/1 or simply 2.
-
Converting Improper Fractions back to Mixed Numbers: The reverse process is equally important. Knowing how to convert an improper fraction back to a mixed number allows you to present your answer in a more understandable and practical format. This involves dividing the numerator by the denominator; the quotient becomes the whole number, and the remainder becomes the numerator of the fraction, retaining the original denominator.
-
Operations with Improper Fractions: Mastering addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division with improper fractions is a cornerstone of further mathematical studies. This includes working with complex fractions and understanding the order of operations (PEMDAS/BODMAS).
Conclusion
Converting 2 and 2/3 to an improper fraction, resulting in 8/3, is a fundamental skill in mathematics. Understanding the process, exploring different methods, and recognizing its real-world applications are essential for building a solid mathematical foundation. This conversion simplifies various calculations and is a critical stepping stone towards mastering more advanced mathematical concepts. Whether you're a student, a professional, or simply someone curious about mathematics, grasping the concept of improper fractions and their relationship to mixed numbers is an invaluable asset. Continuously practicing conversions and applying them in various contexts will solidify your understanding and build confidence in your mathematical abilities. Remember, practice is key to mastering this essential skill.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 4 9 As A Percentage
Mar 10, 2025
-
Complex Number To Rectangular Form Calculator
Mar 10, 2025
-
What Is The Square Root Of 180
Mar 10, 2025
-
What Is The Square Root Of 58
Mar 10, 2025
-
Whats The Square Root Of 6400
Mar 10, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 2 And 2/3 As An Improper Fraction . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
