3 Times The Square Root Of 2
Next Genwave
Mar 06, 2025 · 6 min read
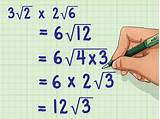
Table of Contents
3 Times the Square Root of 2: Unveiling the Mysteries of this Mathematical Constant
The seemingly simple expression "3 times the square root of 2" (3√2) hides a surprising depth of mathematical significance and practical applications. While it might not hold the same immediate recognition as π (pi) or e (Euler's number), its presence weaves throughout various fields, from geometry and physics to computer science and engineering. This exploration delves into the fascinating world of 3√2, examining its properties, calculations, applications, and its intriguing place within the broader landscape of mathematics.
Understanding the Square Root of 2
Before we dive into 3√2, it's crucial to grasp the fundamental concept of the square root of 2 (√2). This irrational number, approximately equal to 1.41421356, represents the length of the hypotenuse of a right-angled isosceles triangle with legs of length 1. Its irrationality means it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction – its decimal representation continues infinitely without repeating. The discovery of the square root of 2 is often credited to the Pythagorean school of ancient Greece, and its irrationality presented a significant challenge to their then-current understanding of numbers.
The Significance of Irrational Numbers
The irrationality of √2, and by extension 3√2, highlights the richness and complexity of the number system. Irrational numbers, alongside rational numbers (fractions), form the real numbers, providing a complete framework for mathematical operations and measurements. These numbers are not merely abstract concepts; they represent quantities found in real-world phenomena, underscoring the interconnectedness of theoretical mathematics and physical reality.
Calculating 3√2
Calculating 3√2 is straightforward. We simply multiply the approximate value of √2 (1.41421356...) by 3. This yields an approximate value of 4.242640687... Again, this is an irrational number, meaning its decimal expansion is infinite and non-repeating. Different levels of precision are required depending on the application. For many practical purposes, a rounded-off value such as 4.24 or 4.2426 is sufficient.
Methods for Approximation
While calculators provide readily available approximations, understanding alternative methods enhances our understanding of the number. One method involves using iterative techniques like the Babylonian method (also known as Heron's method) to progressively refine the approximation of √2 and then multiplying by 3. Another approach involves using continued fractions, providing a sequence of increasingly accurate rational approximations to √2.
Applications of 3√2 in Geometry and Physics
The appearance of 3√2 transcends pure mathematical curiosity; it finds practical applications in various fields.
Geometry: Constructing Geometric Figures
In geometry, 3√2 arises in the construction of certain shapes and figures. For example, consider a square with side length of 1. Its diagonal has a length of √2. A larger square, with the original square's diagonal as its side, has a diagonal of 2√2. This type of construction, which builds upon square roots of 2, is used in building geometric patterns and analyzing complex shapes.
Physics: Vector Calculations and Mechanics
In physics, particularly in mechanics and vector analysis, 3√2 frequently appears in calculations involving forces, velocities, and displacements. For example, in scenarios where a resultant force is derived from three mutually perpendicular vectors of equal magnitude, its magnitude might include this constant.
3√2 in Computer Science and Engineering
The constant 3√2 also plays a role in computer science and engineering, often appearing in optimization problems and algorithms.
Optimization Problems
In optimization problems, finding the minimum or maximum of a function often involves solving equations containing square roots. The appearance of 3√2 in such equations is not uncommon, particularly in problems related to geometry, resource allocation, or path finding.
Algorithm Design and Analysis
In algorithm design and analysis, the constant 3√2 may appear in expressions for the time or space complexity of certain algorithms. Understanding the behavior of such constants is crucial for determining the efficiency and scalability of algorithms. As an example, consider algorithms that need to analyze data structures with dimensions closely tied to the geometry discussed earlier. The time it takes to process such a structure might include terms dependent on 3√2.
3√2 in Everyday Life (Surprising Applications)
While less obvious than its use in scientific fields, 3√2 surprisingly has implications in areas many wouldn't anticipate.
Construction and Architecture: Precise Measurements
The construction and architecture industry, relying on precise measurements, may encounter situations where 3√2 becomes relevant. For example, calculating the diagonal of a rectangular structure or determining the exact length of a support beam in a unique configuration can lead to calculations involving this constant.
Graphic Design and Digital Art: Creating Specific Proportions
Graphic designers and digital artists often work with specific proportions and ratios to achieve aesthetically pleasing and balanced compositions. The need for precise ratios, especially involving irrational numbers like √2, can lead to calculations involving multiples such as 3√2.
Exploring the Mathematical Properties of 3√2
Beyond its practical applications, 3√2 possesses intriguing mathematical properties worth exploring.
Irrationality and Transcendence
As a multiple of an irrational number, 3√2 is itself irrational. This means it cannot be expressed as a fraction of two integers. Furthermore, because √2 is a transcendental number (not the root of any non-zero polynomial with rational coefficients), 3√2 also shares this property of transcendence, making it a member of an exclusive class of numbers.
Relationships with Other Mathematical Constants
While not as widely known as π or e, 3√2 shares mathematical relationships with other constants. These connections can often be discovered through exploring trigonometric identities, geometric constructions, or advanced mathematical concepts.
Continued Fraction Representation
Like all irrational numbers, 3√2 can be represented as a continued fraction. This representation provides a unique and insightful way to approximate the value of the constant using rational numbers. The continued fraction can be used to generate progressively more accurate approximations.
Conclusion: The Enduring Relevance of 3√2
While 3 times the square root of 2 might appear initially as a straightforward mathematical expression, its significance extends far beyond its simple calculation. From its role in fundamental geometric constructions and physical calculations to its appearances in computer algorithms and even in design applications, 3√2 demonstrates the pervasive influence of seemingly simple mathematical constants in diverse fields. Its exploration provides a glimpse into the interconnectedness of mathematics and the real world, showcasing the beauty and elegance of mathematical structures and their practical implications. Further investigation into its properties, relationships with other constants, and applications in various fields promises to unearth even more fascinating insights. The seemingly simple "3√2" is, in reality, a rich and multifaceted mathematical concept with enduring relevance.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
X 4 5x 2 4 0
Mar 07, 2025
-
1 2 X 2 3 X 3 4
Mar 07, 2025
-
Cual Es La Raiz Cuadrada De 1
Mar 07, 2025
-
2x 4y 8 In Slope Intercept Form
Mar 07, 2025
-
9 9 Rounded To The Nearest Tenth
Mar 07, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 3 Times The Square Root Of 2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
