32 7 As A Mixed Number
Next Genwave
Mar 10, 2025 · 6 min read
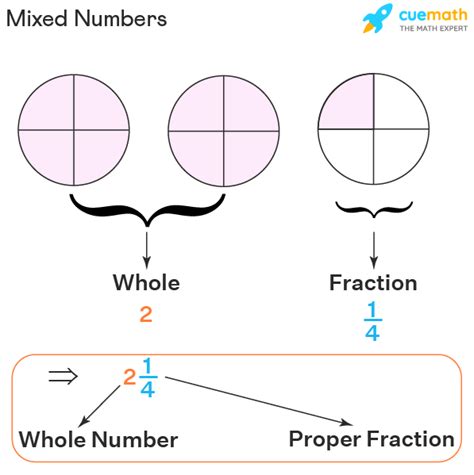
Table of Contents
32/7 as a Mixed Number: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding fractions and how to convert them into mixed numbers is a fundamental skill in mathematics. This comprehensive guide delves deep into the process of converting the improper fraction 32/7 into a mixed number, explaining the concept thoroughly and providing various approaches to solve similar problems. We'll also explore the practical applications of this conversion and touch upon related mathematical concepts.
What is a Mixed Number?
A mixed number is a combination of a whole number and a proper fraction. A proper fraction is one where the numerator (the top number) is smaller than the denominator (the bottom number). For instance, 2 ¾ is a mixed number; 2 is the whole number, and ¾ is the proper fraction. Mixed numbers are often used to represent quantities that are more than one whole unit but not a complete number of units.
Converting Improper Fractions to Mixed Numbers
An improper fraction is a fraction where the numerator is greater than or equal to the denominator. The fraction 32/7 is an improper fraction because 32 (numerator) is larger than 7 (denominator). To convert an improper fraction to a mixed number, we need to determine how many times the denominator goes into the numerator and what the remainder is.
Step-by-Step Conversion of 32/7
Here's how to convert 32/7 into a mixed number:
-
Division: Divide the numerator (32) by the denominator (7). 32 ÷ 7 = 4 with a remainder of 4.
-
Whole Number: The quotient (the result of the division) becomes the whole number part of the mixed number. In this case, the quotient is 4.
-
Fractional Part: The remainder (4) becomes the numerator of the fractional part, and the denominator remains the same (7). This gives us the fraction 4/7.
-
Mixed Number: Combine the whole number and the fraction to form the mixed number. Therefore, 32/7 as a mixed number is 4 ⁴⁄₇.
Alternative Methods and Visual Representations
While the long division method is the most common, let's explore alternative approaches to understanding this conversion:
Repeated Subtraction
Imagine you have 32 items, and you want to group them into sets of 7. You can repeatedly subtract 7 until you have fewer than 7 items left:
- 32 - 7 = 25
- 25 - 7 = 18
- 18 - 7 = 11
- 11 - 7 = 4
You performed the subtraction 4 times, which represents the whole number part (4). The remaining 4 items represent the numerator of the fraction, and 7 remains the denominator. This leads us back to the mixed number 4 ⁴⁄₇.
Visual Representation using a Number Line
A number line can visually demonstrate the conversion. Imagine a number line marked in increments of 7/7 (which equals 1). Counting in increments of 7/7 four times brings you to 28/7 (4). The remaining distance to 32/7 is 4/7, resulting in the mixed number 4 ⁴⁄₇.
Practical Applications of Mixed Numbers
Mixed numbers are frequently encountered in real-world scenarios:
- Measurement: When measuring length, weight, or volume, you might obtain measurements that aren't whole numbers. For example, a piece of wood might be 4 ⁴⁄₇ feet long.
- Cooking: Recipes often use mixed numbers for ingredient quantities, such as 2 ½ cups of flour or 1 ⅓ teaspoons of baking powder.
- Time: We commonly use mixed numbers to represent time, for instance, 2 ½ hours or 1 ¼ minutes.
- Construction: In construction, dimensions often involve mixed numbers to represent precise measurements.
- Data Analysis: Mixed numbers can appear in data sets when dealing with averages or measurements.
Converting Mixed Numbers Back to Improper Fractions
It's equally important to understand the reverse process: converting a mixed number back to an improper fraction. This is useful for simplifying calculations involving mixed numbers. Let's convert 4 ⁴⁄₇ back to an improper fraction:
-
Multiply and Add: Multiply the whole number (4) by the denominator (7): 4 x 7 = 28. Add this result to the numerator (4): 28 + 4 = 32.
-
New Numerator: This sum (32) becomes the new numerator of the improper fraction.
-
Denominator Remains the Same: The denominator remains the same (7).
-
Improper Fraction: Therefore, the improper fraction is 32/7.
Expanding on Fractions: Understanding Equivalent Fractions
Understanding equivalent fractions is crucial for working with mixed numbers and other fractional calculations. Equivalent fractions represent the same value but have different numerators and denominators. For example, 4/7, 8/14, and 12/21 are all equivalent fractions. Finding equivalent fractions involves multiplying or dividing both the numerator and denominator by the same number. This principle is essential for simplifying fractions and performing addition and subtraction with fractions having different denominators.
Simplifying Fractions
Simplifying a fraction means reducing it to its lowest terms. This involves dividing both the numerator and denominator by their greatest common divisor (GCD). For example, the fraction 12/18 can be simplified by dividing both the numerator and denominator by 6, resulting in the simplified fraction 2/3. Simplifying fractions makes them easier to work with and interpret. In the case of 4 ⁴⁄₇, the fraction ⁴⁄₇ is already in its simplest form as 4 and 7 share no common divisors other than 1.
Adding and Subtracting Mixed Numbers
Adding and subtracting mixed numbers often requires converting them to improper fractions first for easier calculation. Once the calculation is complete, the result can be converted back to a mixed number if necessary. For instance, adding 2 ½ and 1 ⅓ would first involve converting them to improper fractions (5/2 and 4/3 respectively). Finding a common denominator (6), we get 15/6 and 8/6. Adding them yields 23/6, which can then be converted to the mixed number 3 ⁵⁄₆.
Multiplying and Dividing Mixed Numbers
Similar to addition and subtraction, multiplying and dividing mixed numbers frequently involves converting them into improper fractions. Multiplication of improper fractions is straightforward: multiply the numerators and multiply the denominators. Division involves inverting the second fraction and multiplying. The result can then be simplified and converted back to a mixed number if necessary.
Conclusion
Converting 32/7 to the mixed number 4 ⁴⁄₇ is a fundamental skill in mathematics with wide-ranging applications. This guide not only detailed the steps involved but also explored alternative methods, visual representations, and practical applications, emphasizing the importance of understanding fractions and their various forms. Furthermore, it provided a foundation for more complex fractional calculations, reinforcing the interconnectedness of various mathematical concepts. By mastering the conversion of improper fractions to mixed numbers, and vice versa, one gains a robust understanding of fractions and their significance in numerical problem-solving.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Domain And Range For X 2
Mar 10, 2025
-
6 1 4 3 5 8
Mar 10, 2025
-
How To Solve X 1 X 3
Mar 10, 2025
-
P 144p Y Solve For P
Mar 10, 2025
-
Cual Es La Raiz Cuadrada De 117
Mar 10, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 32 7 As A Mixed Number . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
