4 1/7 As An Improper Fraction
Next Genwave
Mar 07, 2025 · 5 min read
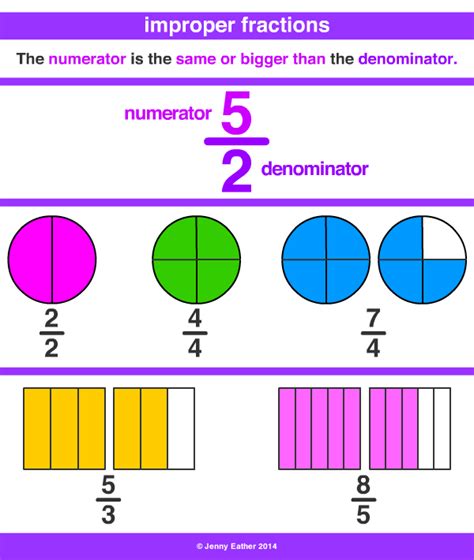
Table of Contents
4 1/7 as an Improper Fraction: A Comprehensive Guide
Converting mixed numbers to improper fractions is a fundamental skill in mathematics. This comprehensive guide will delve into the process of converting the mixed number 4 1/7 into an improper fraction, explaining the underlying concepts, providing step-by-step instructions, and exploring practical applications. We'll also touch upon related concepts and offer tips for mastering this essential skill.
Understanding Mixed Numbers and Improper Fractions
Before we begin converting 4 1/7, let's clarify the definitions of mixed numbers and improper fractions.
Mixed Number: A mixed number combines a whole number and a proper fraction. A proper fraction has a numerator (top number) smaller than its denominator (bottom number). For example, 4 1/7 is a mixed number: 4 represents the whole number, and 1/7 is the proper fraction.
Improper Fraction: An improper fraction has a numerator that is equal to or greater than its denominator. For example, 22/7 is an improper fraction because the numerator (22) is greater than the denominator (7).
Converting 4 1/7 to an Improper Fraction: A Step-by-Step Guide
The conversion process involves two main steps:
Step 1: Multiply the whole number by the denominator.
In our example, the whole number is 4, and the denominator of the fraction is 7. Multiplying these together gives us 4 * 7 = 28.
Step 2: Add the numerator to the result from Step 1.
The numerator of our fraction is 1. Adding this to the result from Step 1 (28) gives us 28 + 1 = 29.
Step 3: Keep the same denominator.
The denominator remains unchanged throughout the conversion process. Therefore, the denominator of our improper fraction will still be 7.
Step 4: Write the final improper fraction.
Combining the results from Steps 2 and 3, we get the improper fraction 29/7. Therefore, 4 1/7 is equivalent to 29/7.
Visualizing the Conversion
Imagine you have four whole pizzas, each cut into seven equal slices. The mixed number 4 1/7 represents four whole pizzas and one additional slice from a fifth pizza. To express this as an improper fraction, we need to determine the total number of slices.
Since each pizza has seven slices, four pizzas have 4 * 7 = 28 slices. Adding the extra slice gives us a total of 28 + 1 = 29 slices. Since each slice represents 1/7 of a pizza, we have 29/7 slices in total, confirming our conversion.
Practical Applications of Improper Fractions
Improper fractions are crucial in various mathematical applications, including:
-
Adding and Subtracting Fractions: It's often easier to add or subtract fractions when they're in improper form. For example, adding 2 1/2 and 1 1/4 becomes simpler after converting both mixed numbers into improper fractions.
-
Multiplication and Division of Fractions: While you can multiply and divide mixed numbers directly, converting them to improper fractions often streamlines the process, especially when dealing with more complex mixed numbers.
-
Algebra: In algebra, improper fractions are commonly used in equation solving and simplifying expressions.
-
Real-World Problems: Many real-world scenarios involve fractional quantities, making the ability to convert between mixed numbers and improper fractions essential for accurate calculations. Imagine dividing a piece of land, calculating ingredients for a recipe using fractional measurements, or determining the total cost of items priced fractionally.
Understanding the Relationship Between Mixed Numbers and Improper Fractions
Mixed numbers and improper fractions are simply different ways of representing the same quantity. They are interchangeable; you can always convert a mixed number to an improper fraction and vice versa. Choosing between using a mixed number or an improper fraction depends on the context and the specific mathematical operation being performed. Sometimes, an improper fraction is more convenient for calculations, while other times, a mixed number offers a clearer representation of the quantity.
Further Practice and Advanced Concepts
To solidify your understanding of converting mixed numbers to improper fractions, consider practicing with different mixed numbers. Start with simpler numbers and gradually move towards more complex examples. You could create your own practice problems, utilize online resources, or consult textbooks for additional exercises.
More advanced concepts related to fractions include:
-
Simplifying Fractions: Once you have an improper fraction, you might need to simplify it to its lowest terms by finding the greatest common divisor (GCD) of the numerator and denominator and dividing both by the GCD. For example, 14/21 simplifies to 2/3 because the GCD of 14 and 21 is 7.
-
Converting Improper Fractions to Mixed Numbers: This is the reverse process of what we've covered, and it involves dividing the numerator by the denominator. The quotient becomes the whole number, and the remainder becomes the numerator of the proper fraction, keeping the same denominator.
-
Operations with Fractions: Mastering addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division of fractions (including improper fractions and mixed numbers) is essential for more advanced mathematical concepts.
Troubleshooting Common Mistakes
While the process of converting 4 1/7 to an improper fraction is relatively straightforward, some common mistakes can occur:
-
Incorrect Multiplication: Ensure you accurately multiply the whole number by the denominator in Step 1.
-
Incorrect Addition: Double-check your addition in Step 2 to avoid errors.
-
Forgetting the Denominator: Remember that the denominator remains the same throughout the conversion process.
-
Misunderstanding the Concepts: If you're struggling, review the definitions of mixed numbers and improper fractions to ensure a clear understanding of the underlying principles.
Conclusion: Mastering Fraction Conversions
Converting mixed numbers, like 4 1/7, to improper fractions is a fundamental mathematical skill. Understanding the process, practicing regularly, and being aware of common errors will help you master this essential skill. This newfound proficiency will greatly enhance your ability to solve various mathematical problems and tackle more advanced concepts. By understanding the relationship between mixed numbers and improper fractions, and their practical applications, you will be well-equipped to navigate the world of fractions with confidence. Remember, practice makes perfect! Continue to practice converting mixed numbers to improper fractions and vice versa to improve your fluency and accuracy.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 1 5th Of 15
Mar 09, 2025
-
What Is 3 375 As A Fraction
Mar 09, 2025
-
What Is The Simplified Form Of The Expression
Mar 09, 2025
-
What Percent Of 60 Is 21
Mar 09, 2025
-
2 3a 1 6 1 3
Mar 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 4 1/7 As An Improper Fraction . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
