5 4 As A Mixed Number
Next Genwave
Mar 10, 2025 · 5 min read
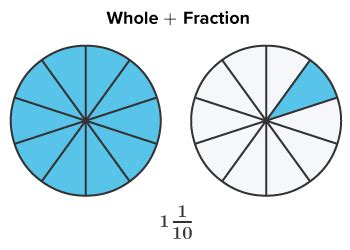
Table of Contents
5 4 as a Mixed Number: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding mixed numbers is fundamental in mathematics, particularly in fractions and their applications. This comprehensive guide delves deep into the concept of expressing improper fractions as mixed numbers, specifically focusing on how to represent 5 4 as a mixed number. We'll cover various methods, explain the underlying principles, and offer practical examples to solidify your understanding. This will equip you with the knowledge to confidently tackle similar fraction conversions.
Understanding Fractions: A Quick Recap
Before we dive into converting 5/4, let's briefly review the basics of fractions. A fraction represents a part of a whole. It's composed of two key parts:
- Numerator: The top number, indicating the number of parts we have.
- Denominator: The bottom number, indicating the total number of equal parts the whole is divided into.
For example, in the fraction 3/4, the numerator (3) represents three parts, and the denominator (4) indicates that the whole is divided into four equal parts.
What are Mixed Numbers?
A mixed number combines a whole number and a proper fraction. A proper fraction is one where the numerator is smaller than the denominator (e.g., 1/2, 3/4, 5/8). Mixed numbers are a convenient way to represent improper fractions, which are fractions where the numerator is greater than or equal to the denominator (e.g., 5/4, 7/3, 9/9).
Converting Improper Fractions to Mixed Numbers: The General Approach
The process of converting an improper fraction to a mixed number involves dividing the numerator by the denominator. The steps are as follows:
- Divide the numerator by the denominator: This gives you the whole number part of your mixed number.
- Determine the remainder: This remainder will become the numerator of the fractional part of your mixed number.
- Keep the original denominator: The denominator of the fraction in your mixed number remains the same as the denominator of the original improper fraction.
Let's illustrate this with an example before tackling 5/4:
Convert 7/3 to a mixed number.
- Divide 7 by 3: 7 ÷ 3 = 2 with a remainder of 1.
- The remainder is 1.
- The denominator remains 3.
Therefore, 7/3 as a mixed number is 2 1/3.
Converting 5/4 to a Mixed Number
Now, let's apply this process to the specific improper fraction 5/4:
- Divide the numerator (5) by the denominator (4): 5 ÷ 4 = 1 with a remainder of 1.
- The remainder is 1. This will be the numerator of our fraction.
- The denominator remains 4.
Therefore, 5/4 expressed as a mixed number is 1 1/4.
Visualizing 5/4
It's often helpful to visualize fractions to solidify your understanding. Imagine a pizza cut into four equal slices (denominator = 4). The fraction 5/4 represents having five of these slices. You can have one whole pizza (four slices) and one extra slice remaining, hence 1 1/4.
Alternative Methods for Conversion
While the division method is the most common, there are other approaches to convert improper fractions to mixed numbers. These methods can be helpful for building a more robust understanding and improving mental calculation skills.
Method 2: Subtracting the Denominator
This method involves repeatedly subtracting the denominator from the numerator until the result is less than the denominator. The number of times you subtract the denominator becomes the whole number part, and the remaining value becomes the numerator of the fractional part.
Let's convert 5/4 using this method:
- Subtract 4 from 5: 5 - 4 = 1
- We subtracted 4 once, so the whole number is 1.
- The remainder is 1, which is the numerator of the fraction.
- The denominator remains 4.
This again gives us the mixed number 1 1/4.
Method 3: Using Equivalent Fractions
This method relies on finding an equivalent fraction with a numerator that is a multiple of the denominator. While less efficient for simple fractions like 5/4, it's beneficial for understanding the concept of equivalent fractions. This method is less straightforward for 5/4 but is valuable for more complex scenarios.
Applications of Mixed Numbers
Mixed numbers are used extensively in various real-world applications, including:
- Measurement: Expressing lengths, weights, volumes, etc. For example, a piece of wood could measure 2 1/2 feet.
- Cooking and Baking: Following recipes often involves using mixed numbers for ingredient quantities.
- Construction and Engineering: Precise measurements are crucial, and mixed numbers facilitate accurate calculations.
- Everyday Life: Sharing items, calculating portions, and managing resources often involve fractional representation using mixed numbers.
Practicing Fraction Conversion
Mastering the conversion between improper fractions and mixed numbers requires consistent practice. Here are some practice problems:
- Convert 11/5 to a mixed number.
- Convert 9/2 to a mixed number.
- Convert 17/6 to a mixed number.
- Convert 23/8 to a mixed number.
- Convert 35/12 to a mixed number.
Answers:
- 2 1/5
- 4 1/2
- 2 5/6
- 2 7/8
- 2 11/12
By working through these problems and applying the methods discussed, you'll significantly improve your understanding and proficiency in converting improper fractions to mixed numbers. Remember, consistent practice is key!
Beyond 5/4: Expanding Your Knowledge
Understanding how to represent 5/4 as a mixed number is a stepping stone to tackling more complex fraction manipulations. Once you're comfortable with this basic conversion, you can explore more advanced topics such as:
- Adding and Subtracting Mixed Numbers: This involves converting mixed numbers to improper fractions for easier calculations.
- Multiplying and Dividing Mixed Numbers: Similar to addition and subtraction, conversion to improper fractions simplifies these operations.
- Converting Decimals to Fractions and Mixed Numbers: This expands your understanding of different number representations.
Conclusion: Mastering Mixed Numbers
Converting improper fractions like 5/4 to mixed numbers is a crucial skill in mathematics. This guide has provided a thorough explanation of the process, explored different methods, and highlighted the practical applications of mixed numbers. Remember that consistent practice is vital for mastering this fundamental concept. Through diligent effort, you'll build confidence and proficiency in working with fractions and mixed numbers, empowering you to tackle more complex mathematical challenges.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
3 2 7 As An Improper Fraction
Mar 10, 2025
-
4 24 Rounded To The Nearest Tenth
Mar 10, 2025
-
X 2 Xy Y 2 Factor
Mar 10, 2025
-
What Is 3 4 1 2
Mar 10, 2025
-
What Is The Derivative Of X 1 3
Mar 10, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 5 4 As A Mixed Number . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
