7 2/9 As An Improper Fraction
Next Genwave
Mar 10, 2025 · 5 min read
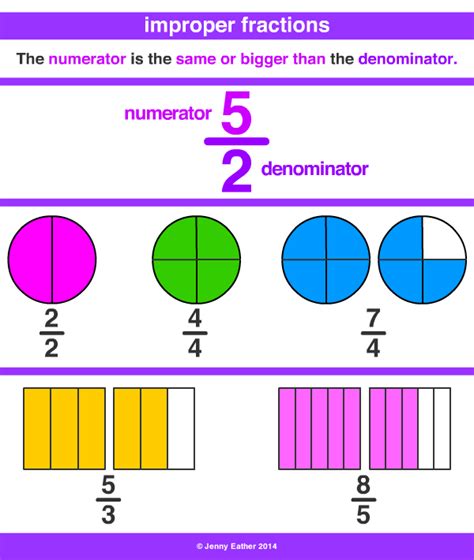
Table of Contents
7 2/9 as an Improper Fraction: A Comprehensive Guide
Converting mixed numbers to improper fractions is a fundamental skill in mathematics, crucial for various applications from basic arithmetic to advanced calculus. This comprehensive guide will delve deep into the process of converting the mixed number 7 2/9 into its improper fraction equivalent, explaining the underlying concepts and providing numerous examples to solidify your understanding. We'll also explore the practical applications of this conversion and address common misconceptions.
Understanding Mixed Numbers and Improper Fractions
Before diving into the conversion, let's clarify the definitions:
-
Mixed Number: A mixed number combines a whole number and a proper fraction. A proper fraction has a numerator (top number) smaller than the denominator (bottom number). For example, 7 2/9 is a mixed number; 7 is the whole number, and 2/9 is the proper fraction.
-
Improper Fraction: An improper fraction has a numerator equal to or greater than its denominator. For instance, 65/9 is an improper fraction.
Converting a mixed number to an improper fraction involves representing the entire quantity using a single fraction. This is essential for performing operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division involving fractions efficiently.
Converting 7 2/9 to an Improper Fraction: Step-by-Step Guide
The conversion of 7 2/9 to an improper fraction follows a simple, two-step process:
Step 1: Multiply the whole number by the denominator.
In our example, the whole number is 7, and the denominator is 9. Therefore, we calculate 7 * 9 = 63.
Step 2: Add the numerator to the result from Step 1.
The numerator of our fraction is 2. We add this to the result from Step 1: 63 + 2 = 65.
Step 3: Keep the original denominator.
The denominator remains unchanged. It's still 9.
Therefore, the improper fraction equivalent of 7 2/9 is 65/9.
Visualizing the Conversion
Imagine you have seven whole pizzas, each cut into nine slices. The mixed number 7 2/9 represents seven whole pizzas and two additional slices from a ninth pizza. To convert this to an improper fraction, we count the total number of slices. Since each pizza has 9 slices, seven pizzas have 7 * 9 = 63 slices. Adding the two extra slices gives us a total of 63 + 2 = 65 slices. As each slice represents 1/9 of a pizza, we have 65/9 slices in total.
Practical Applications of Improper Fractions
The conversion of mixed numbers to improper fractions is vital in numerous mathematical contexts:
-
Addition and Subtraction of Mixed Numbers: Adding or subtracting mixed numbers directly can be cumbersome. Converting them to improper fractions simplifies the process, allowing for straightforward addition or subtraction of the numerators while keeping the denominator consistent.
-
Multiplication and Division of Mixed Numbers: Directly multiplying or dividing mixed numbers can lead to errors. Converting them to improper fractions significantly simplifies these operations. Multiplying fractions involves multiplying the numerators and denominators separately, while dividing involves multiplying by the reciprocal of the second fraction.
-
Solving Equations: Many algebraic equations involve fractions. Converting mixed numbers to improper fractions streamlines the solution process.
-
Real-World Applications: Improper fractions are prevalent in various real-world scenarios. For example, in cooking, you might need to use 11/4 cups of flour. This improper fraction is a more precise representation than its mixed number equivalent, 2 ¾ cups. Similarly, in construction or engineering, precise measurements often necessitate using improper fractions.
Further Examples
Let's explore a few more examples to strengthen your understanding:
-
Converting 3 1/5 to an improper fraction:
- Multiply the whole number by the denominator: 3 * 5 = 15
- Add the numerator: 15 + 1 = 16
- Keep the denominator: 5
- Result: 16/5
-
Converting 12 3/7 to an improper fraction:
- Multiply the whole number by the denominator: 12 * 7 = 84
- Add the numerator: 84 + 3 = 87
- Keep the denominator: 7
- Result: 87/7
-
Converting 5 0/11 to an improper fraction: Note that even though the fractional part is 0/11, the process remains the same.
- Multiply the whole number by the denominator: 5 * 11 = 55
- Add the numerator: 55 + 0 = 55
- Keep the denominator: 11
- Result: 55/11 (This simplifies to 5)
Addressing Common Misconceptions
A common mistake is forgetting to add the numerator after multiplying the whole number by the denominator. Always remember that the numerator represents a portion of the whole, and it must be included in the final improper fraction.
Beyond the Basics: Simplifying Improper Fractions
Sometimes, the resulting improper fraction can be simplified. This means reducing the fraction to its lowest terms by dividing both the numerator and the denominator by their greatest common divisor (GCD). For example, while 65/9 is a correct improper fraction equivalent of 7 2/9, it cannot be simplified further as the GCD of 65 and 9 is 1.
However, let's consider the improper fraction 16/4. The GCD of 16 and 4 is 4. Dividing both the numerator and the denominator by 4 gives us 4/1, which simplifies to 4. This demonstrates that simplification can sometimes result in a whole number.
Conclusion
Converting a mixed number like 7 2/9 into its improper fraction equivalent, 65/9, is a fundamental skill in mathematics. Mastering this conversion is crucial for efficient manipulation of fractions and solving various mathematical problems in diverse fields. Understanding the process, applying it through practice, and recognizing potential simplification opportunities will enable you to confidently handle fractions in any mathematical context. Remember the simple steps: multiply, add, and keep the denominator. With practice, you'll master this essential skill and confidently navigate the world of fractions.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How To Factor X 3 2x 2 X 2
Mar 11, 2025
-
Write Equation Of Parabola Given Focus And Directrix Calculator
Mar 11, 2025
-
Y Ln X Solve For X
Mar 11, 2025
-
7 12 Divided By 5 9
Mar 11, 2025
-
2 A 4 4a 2a 4
Mar 11, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 7 2/9 As An Improper Fraction . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
