9 2/5 As An Improper Fraction
Next Genwave
Mar 06, 2025 · 5 min read
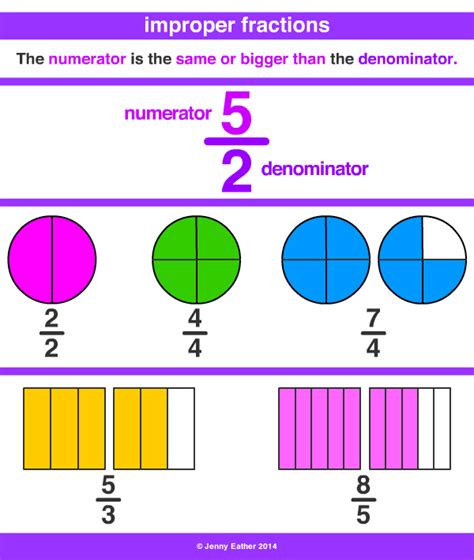
Table of Contents
9 2/5 as an Improper Fraction: A Comprehensive Guide
Converting mixed numbers to improper fractions is a fundamental skill in mathematics, crucial for various applications from simple arithmetic to complex calculus. This comprehensive guide will delve deep into the process of converting the mixed number 9 2/5 into an improper fraction, explaining the underlying principles and providing practical examples to solidify your understanding. We'll also explore the broader context of fractions, touching upon their importance and applications in various fields.
Understanding Mixed Numbers and Improper Fractions
Before we dive into the conversion, let's clarify the definitions:
-
Mixed Number: A mixed number combines a whole number and a proper fraction. For example, 9 2/5 is a mixed number; it represents 9 whole units and 2/5 of another unit.
-
Improper Fraction: An improper fraction has a numerator (the top number) that is greater than or equal to its denominator (the bottom number). For example, 47/5 is an improper fraction. Improper fractions represent a value greater than or equal to one.
The conversion between these two forms is essential for performing calculations involving fractions, especially when adding, subtracting, multiplying, or dividing them.
Converting 9 2/5 to an Improper Fraction: Step-by-Step Guide
The process of converting a mixed number to an improper fraction involves two simple steps:
Step 1: Multiply the whole number by the denominator.
In our case, the whole number is 9, and the denominator of the fraction is 5. Therefore, we multiply 9 * 5 = 45.
Step 2: Add the numerator to the result from Step 1.
The numerator of our fraction is 2. Adding this to the result from Step 1, we get 45 + 2 = 47.
Step 3: Keep the denominator the same.
The denominator of the original fraction remains unchanged. Therefore, the denominator stays as 5.
Step 4: Write the improper fraction.
Combining the results from Steps 2 and 3, we arrive at our improper fraction: 47/5. This represents the same quantity as the mixed number 9 2/5.
Visualizing the Conversion
Imagine you have 9 full pizzas and 2/5 of another pizza. To represent this as a single fraction, we need to determine the total number of slices. Assuming each pizza is cut into 5 slices, you have:
- 9 pizzas * 5 slices/pizza = 45 slices
- Plus the 2 extra slices from the remaining pizza, giving a total of 45 + 2 = 47 slices.
Since each pizza has 5 slices, our total number of slices (47) is expressed as 47/5, which is our improper fraction.
Practical Applications of Improper Fractions
Improper fractions are incredibly useful in various mathematical contexts and real-world scenarios:
-
Simplifying calculations: Adding and subtracting mixed numbers often involves converting them to improper fractions first, making the calculations significantly easier.
-
Division and ratios: Improper fractions provide a convenient way to represent quantities larger than one, making them ideal for expressing ratios and solving division problems. For instance, if you divide 47 cookies equally among 5 friends, each friend will receive 47/5 cookies, which is equal to 9 2/5 cookies.
-
Advanced mathematics: Improper fractions are fundamental to more advanced mathematical concepts like algebra, calculus, and linear algebra.
-
Real-world examples: Imagine a recipe calling for 9 2/5 cups of flour. This can be more easily handled as an improper fraction (47/5 cups) when performing calculations involving scaling the recipe.
Further Exploration of Fractions
This section delves into a deeper understanding of fractions and their properties.
Types of Fractions:
- Proper Fractions: These have a numerator smaller than the denominator (e.g., 2/5, 3/8). Their value is less than 1.
- Improper Fractions: As discussed above, these have a numerator greater than or equal to the denominator (e.g., 7/5, 47/5). Their value is greater than or equal to 1.
- Equivalent Fractions: These fractions have different numerators and denominators but represent the same value (e.g., 1/2, 2/4, 3/6).
Operations with Fractions:
-
Adding and Subtracting Fractions: When adding or subtracting fractions, a common denominator is essential. This is easily achieved by converting mixed numbers to improper fractions and then finding the least common multiple of the denominators.
-
Multiplying Fractions: Multiplication of fractions is straightforward. Multiply the numerators together to get the new numerator and the denominators to get the new denominator.
-
Dividing Fractions: To divide fractions, invert the second fraction (reciprocal) and multiply.
Simplifying Fractions:
Simplifying fractions involves reducing them to their lowest terms by dividing both the numerator and the denominator by their greatest common divisor (GCD). For example, the fraction 10/15 can be simplified to 2/3 by dividing both the numerator and the denominator by 5 (their GCD).
Troubleshooting Common Mistakes
When working with mixed numbers and improper fractions, some common mistakes can occur:
-
Incorrect multiplication/addition in conversion: Double-check your arithmetic when multiplying the whole number by the denominator and adding the numerator.
-
Forgetting to keep the denominator: Remember, only the numerator changes during conversion; the denominator remains the same.
-
Mistakes in simplification: Always simplify the improper fraction to its lowest terms to present the most concise and accurate representation.
Conclusion: Mastering Fractions for Mathematical Success
Converting 9 2/5 to the improper fraction 47/5 is a fundamental skill in mathematics. Understanding the process and the underlying concepts of mixed numbers and improper fractions is crucial for success in various mathematical applications. By mastering these techniques, you'll be well-equipped to tackle more complex mathematical challenges and confidently navigate various real-world scenarios involving fractions. Remember to practice regularly, and don't hesitate to review the steps if needed. The more you practice, the more comfortable and confident you'll become with working with fractions. From simple arithmetic to advanced calculus, fractions form the bedrock of numerical understanding. Mastering them opens up a world of mathematical possibilities!
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Greatest Common Factor Of 10 And 8
Mar 06, 2025
-
What Is The Percent Of 8 15
Mar 06, 2025
-
What Is 2 1 2 As A Decimal
Mar 06, 2025
-
How Many Yards Are In 24 Feet
Mar 06, 2025
-
What Percentage Of 25 Is 15
Mar 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 9 2/5 As An Improper Fraction . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
