A B C Solve For B
Next Genwave
Mar 09, 2025 · 5 min read
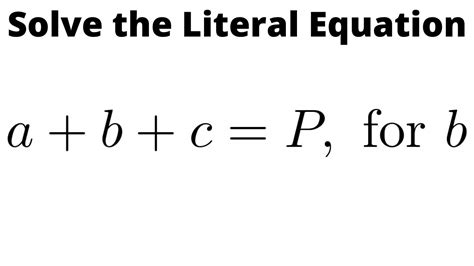
Table of Contents
Solving for 'b': A Comprehensive Guide to Algebraic Manipulation
The seemingly simple equation "a + b + c = x" often hides a crucial skill in algebra: solving for a specific variable. This article delves into the intricacies of isolating 'b' in various scenarios, from basic linear equations to more complex situations involving exponents, fractions, and even systems of equations. We'll explore the fundamental principles and provide numerous examples to build your understanding and confidence in algebraic manipulation.
Understanding the Fundamentals: Isolating Variables
At the heart of solving for 'b' (or any variable) lies the principle of balancing the equation. Whatever operation you perform on one side of the equals sign, you must perform the same operation on the other side to maintain equality. This principle is fundamental to all algebraic manipulations. Think of an equation as a perfectly balanced scale; if you add weight to one side, you need to add the same weight to the other side to keep it balanced.
The Golden Rule of Algebra: Maintaining Equality
The key to successfully solving for 'b' is to systematically undo the operations performed on 'b', working backward step-by-step. This involves using inverse operations:
- Addition and Subtraction: These are inverse operations. To undo addition, subtract; to undo subtraction, add.
- Multiplication and Division: These are also inverse operations. To undo multiplication, divide; to undo division, multiply.
- Exponents and Roots: Raising to a power and taking a root are inverse operations. To undo a square, take the square root; to undo a cube, take the cube root, and so on.
Solving for 'b' in Simple Linear Equations
Let's start with the simplest case: solving for 'b' in a linear equation of the form a + b + c = x, where a, c, and x are known constants.
Example 1: Solve for 'b' in the equation 5 + b + 3 = 12.
-
Combine like terms: The equation simplifies to 8 + b = 12.
-
Isolate 'b': Subtract 8 from both sides: 8 + b - 8 = 12 - 8.
-
Simplify: This leaves us with b = 4.
Example 2: Solve for 'b' in the equation 2a + b - 5c = 10, where a = 2 and c = 1.
-
Substitute known values: Substitute a = 2 and c = 1 into the equation: 2(2) + b - 5(1) = 10.
-
Simplify: This gives us 4 + b - 5 = 10.
-
Combine like terms: Simplify to b - 1 = 10.
-
Isolate 'b': Add 1 to both sides: b - 1 + 1 = 10 + 1.
-
Simplify: The solution is b = 11.
Solving for 'b' in Equations with Fractions
Equations involving fractions require an extra step: eliminating the fractions by finding a common denominator.
Example 3: Solve for 'b' in the equation (b/2) + 3 = 7.
-
Isolate the term with 'b': Subtract 3 from both sides: (b/2) = 4.
-
Eliminate the fraction: Multiply both sides by 2: 2 * (b/2) = 4 * 2.
-
Simplify: This simplifies to b = 8.
Example 4: Solve for 'b' in the equation (a + b)/c = x.
-
Eliminate the fraction: Multiply both sides by 'c': c * (a + b)/c = x * c.
-
Simplify: This gives us a + b = cx.
-
Isolate 'b': Subtract 'a' from both sides: b = cx - a.
Solving for 'b' in Equations with Exponents
Equations involving exponents require the use of roots to isolate 'b'.
Example 5: Solve for 'b' in the equation b² = 25.
-
Take the square root: Take the square root of both sides: √b² = ±√25. Remember that both positive and negative square roots are possible solutions.
-
Simplify: This gives us b = ±5.
Example 6: Solve for 'b' in the equation 2b³ + 5 = 13.
-
Isolate the term with 'b': Subtract 5 from both sides: 2b³ = 8.
-
Isolate 'b³': Divide both sides by 2: b³ = 4.
-
Take the cube root: Take the cube root of both sides: ³√b³ = ³√4.
-
Simplify: b = ³√4.
Solving for 'b' in Systems of Equations
Solving for 'b' within a system of equations requires using techniques like substitution or elimination to reduce the system to a single equation solvable for 'b'.
Example 7: Solve for 'b' in the following system of equations:
a + b = 7 a - b = 1
-
Use elimination: Add the two equations together. Notice that the 'a' terms cancel out, leaving 2b = 8.
-
Solve for 'b': Divide both sides by 2: b = 4.
Example 8: Solve for 'b' using substitution.
a + 2b = 10 a = b + 2
-
Substitute: Substitute the second equation (a = b + 2) into the first equation: (b + 2) + 2b = 10.
-
Simplify: Combine like terms: 3b + 2 = 10.
-
Isolate 'b': Subtract 2 from both sides: 3b = 8.
-
Solve for 'b': Divide both sides by 3: b = 8/3.
Advanced Techniques and Considerations
Solving for 'b' can become significantly more complex when dealing with more advanced mathematical concepts, such as:
-
Logarithmic equations: These equations require the use of logarithmic properties and inverse functions to isolate 'b'.
-
Trigonometric equations: These equations often necessitate trigonometric identities and inverse trigonometric functions to solve for 'b'.
-
Differential equations: Solving for 'b' within a differential equation involves techniques like separation of variables, integrating factors, and other advanced calculus methods.
-
Inequalities: Solving for 'b' in inequalities involves considering the impact of the inequality sign on the solution set.
Real-World Applications
The ability to solve for 'b' (or any variable) is not just a theoretical exercise. It's a fundamental skill with countless applications in various fields:
-
Physics: Solving for unknown variables in physical equations related to motion, energy, and forces.
-
Engineering: Designing structures, calculating loads, and analyzing systems.
-
Finance: Modeling financial growth, calculating interest rates, and analyzing investments.
-
Computer science: Developing algorithms, solving optimization problems, and building models.
-
Economics: Building economic models, analyzing market behavior, and forecasting trends.
Conclusion: Mastering Algebraic Manipulation
Mastering the skill of solving for 'b' is a crucial step towards proficiency in algebra and other mathematical disciplines. By understanding the fundamental principles of balancing equations and applying the appropriate inverse operations, you can confidently tackle a wide range of algebraic problems. Remember to practice regularly, work through diverse examples, and don't hesitate to consult additional resources when needed. The ability to isolate variables effectively will open doors to a deeper understanding of mathematical concepts and enhance your problem-solving capabilities across multiple fields. The journey to becoming proficient in algebra is iterative; embrace the challenge and enjoy the process of unlocking the power of algebraic manipulation.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Derivative Of 6
Mar 09, 2025
-
28 Divided By 8 With Remainder
Mar 09, 2025
-
3 7 Rounded To The Nearest Tenth
Mar 09, 2025
-
Find Equation Of Parallel Line Given Original Line And Point
Mar 09, 2025
-
4 2n 3 5n 3 2
Mar 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about A B C Solve For B . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
