Factor Of X 2 X 6
Next Genwave
Mar 06, 2025 · 5 min read
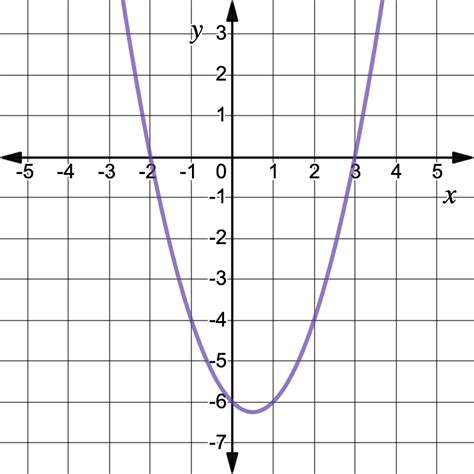
Table of Contents
Factoring x² + x - 6: A Comprehensive Guide
Factoring quadratic expressions is a fundamental skill in algebra. Understanding how to factor expressions like x² + x - 6 is crucial for solving quadratic equations, simplifying algebraic expressions, and progressing to more advanced mathematical concepts. This comprehensive guide will delve into the various methods for factoring x² + x - 6, explaining the underlying principles and providing practical examples. We'll also explore the broader context of factoring quadratic trinomials and highlight common pitfalls to avoid.
Understanding Quadratic Expressions
Before we tackle the specific factorization of x² + x - 6, let's establish a solid understanding of quadratic expressions. A quadratic expression is a polynomial of degree two, meaning the highest power of the variable (usually x) is 2. It generally takes the form ax² + bx + c, where a, b, and c are constants, and 'a' is not equal to zero.
In our case, x² + x - 6 fits this form perfectly, with a = 1, b = 1, and c = -6. The goal of factoring is to rewrite this expression as a product of two simpler expressions, usually binomials.
Method 1: The AC Method (for factoring ax² + bx + c)
The AC method, also known as the grouping method, is a systematic approach to factoring quadratic trinomials. It's particularly useful when the coefficient of x² (a) is not equal to 1. Even though our example has a = 1, understanding this method is valuable for more complex quadratic expressions.
Here's how the AC method works:
-
Find the product AC: In our case, A = 1 and C = -6, so AC = 1 * -6 = -6.
-
Find two numbers that add up to B and multiply to AC: We need two numbers that add up to 1 (our B value) and multiply to -6. These numbers are 3 and -2 (3 + (-2) = 1 and 3 * (-2) = -6).
-
Rewrite the middle term: Replace the middle term (bx) with the two numbers we found. This gives us: x² + 3x - 2x - 6
-
Factor by grouping: Group the terms in pairs and factor out the greatest common factor (GCF) from each pair: x(x + 3) - 2(x + 3)
-
Factor out the common binomial: Notice that (x + 3) is a common factor in both terms. Factor it out: (x + 3)(x - 2)
Therefore, the factored form of x² + x - 6 is (x + 3)(x - 2).
Method 2: The Trial and Error Method (Suitable for a = 1)
When the coefficient of x² (a) is 1, the trial and error method can be quicker. This method involves directly finding two binomials whose product equals the given quadratic expression.
Since our expression is x² + x - 6, we look for two numbers that add up to 1 (the coefficient of x) and multiply to -6 (the constant term). As we found earlier, these numbers are 3 and -2.
Therefore, we can write the factored form as (x + 3)(x - 2).
Method 3: Using the Quadratic Formula (for finding roots, then factoring)
While not a direct factoring method, the quadratic formula can help us find the roots of the quadratic equation x² + x - 6 = 0. These roots can then be used to factor the expression.
The quadratic formula is: x = [-b ± √(b² - 4ac)] / 2a
For our equation, a = 1, b = 1, and c = -6. Plugging these values into the formula gives us:
x = [-1 ± √(1² - 4 * 1 * -6)] / 2 * 1 x = [-1 ± √25] / 2 x = [-1 ± 5] / 2
This gives us two roots: x = 2 and x = -3.
If 'r' and 's' are the roots of a quadratic equation ax² + bx + c = 0, then the factored form is a(x - r)(x - s). In our case, a = 1, r = 2, and s = -3. Therefore, the factored form is (x - 2)(x + 3), which is equivalent to the result obtained by the other methods.
Checking Your Answer
It's always a good practice to check your factored answer by expanding it. Let's expand (x + 3)(x - 2):
(x + 3)(x - 2) = x² - 2x + 3x - 6 = x² + x - 6
This confirms that our factorization is correct.
Why Factoring is Important
Factoring quadratic expressions is not merely an algebraic exercise; it's a fundamental tool with broad applications:
-
Solving Quadratic Equations: Factoring allows us to solve quadratic equations easily. For example, to solve x² + x - 6 = 0, we can factor the expression as (x + 3)(x - 2) = 0. This means either x + 3 = 0 or x - 2 = 0, giving us the solutions x = -3 and x = 2.
-
Simplifying Algebraic Expressions: Factoring can simplify complex expressions, making them easier to manipulate and analyze.
-
Graphing Quadratic Functions: The factored form reveals the x-intercepts (roots) of the quadratic function, which are crucial for accurately graphing the parabola.
-
Calculus and Beyond: Factoring skills are essential for calculus, particularly in techniques like integration and differentiation.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
-
Incorrect Signs: Pay close attention to the signs of the constants in the binomial factors. A common mistake is misinterpreting the signs when finding the numbers that add to 'b' and multiply to 'ac'.
-
Missing Factors: Double-check to ensure that all factors have been accounted for. Carefully review your grouping and factoring steps.
-
Not Checking Your Answer: Always expand your factored expression to verify that it equals the original quadratic expression. This simple step can save you from many errors.
Expanding on Factoring: More Complex Quadratics
The methods described above can be extended to factor more complex quadratic expressions, even those with a coefficient of x² greater than 1. The AC method is particularly useful in these cases. However, some quadratics might not factor nicely using integer coefficients. In such cases, you might need to use the quadratic formula or other numerical techniques to find the roots and then express the quadratic in factored form.
Conclusion
Factoring x² + x - 6, and quadratic expressions in general, is a cornerstone of algebra. Mastering the various methods, understanding the underlying principles, and practicing regularly will greatly enhance your algebraic skills and provide a solid foundation for more advanced mathematical studies. Remember to check your work meticulously and don't be afraid to explore different approaches until you find the one that best suits your understanding. The journey to mastering factoring is iterative and rewarding, leading to a deeper appreciation of the elegance and power of algebra.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Square Root Of 63
Mar 06, 2025
-
X 3 3x 2 4x 12
Mar 06, 2025
-
What Percent Is 11 Out Of 20
Mar 06, 2025
-
35 Out Of 50 As A Percentage
Mar 06, 2025
-
75 Do F Bang Bao Nhieu Do C
Mar 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Factor Of X 2 X 6 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
