Factor X 3 3x 2 3
Next Genwave
Mar 08, 2025 · 4 min read
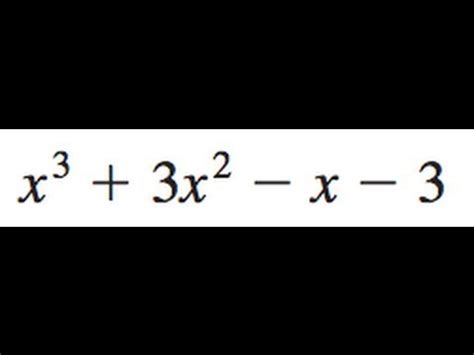
Table of Contents
Decomposing and Solving the Cubic Equation: x³ + 3x² + 3x + 1 = 0
The cubic equation x³ + 3x² + 3x + 1 = 0 might seem deceptively simple at first glance. However, understanding its solution involves exploring several key mathematical concepts, including factoring, the binomial theorem, and the nature of cubic equations. This article delves deep into the process of solving this specific equation, offering a comprehensive explanation accessible to a wide audience, from high school students to those revisiting their algebra skills.
Recognizing the Pattern: A Binomial Expansion
The key to unlocking the solution to x³ + 3x² + 3x + 1 = 0 lies in recognizing a familiar pattern. This equation is not just a random collection of terms; it's the expansion of a binomial raised to the power of three. Recall the binomial theorem:
(a + b)ⁿ = Σ (nCk) * aⁿ⁻ᵏ * bᵏ
Where:
- n is the power
- k ranges from 0 to n
- nCk is the binomial coefficient (n! / (k! * (n-k)!))
Applying the binomial theorem to (a + b)³:
(a + b)³ = (3C0)a³b⁰ + (3C1)a²b¹ + (3C2)a¹b² + (3C3)a⁰b³ = a³ + 3a²b + 3ab² + b³
Comparing this expansion to our equation, x³ + 3x² + 3x + 1 = 0, we can see a clear correspondence:
- If we let a = x and b = 1, the expansion perfectly matches our cubic equation.
Factoring the Cubic Equation
Now that we've identified the binomial expansion, factoring becomes straightforward. We can rewrite the equation as:
(x + 1)³ = 0
This factored form significantly simplifies the problem. To solve for x, we simply take the cube root of both sides:
∛[(x + 1)³] = ∛0
This gives us:
x + 1 = 0
Therefore, the solution to the cubic equation x³ + 3x² + 3x + 1 = 0 is:
x = -1
Understanding the Nature of Cubic Equations
Cubic equations, unlike quadratic equations, always have at least one real root. They can have one real root and two complex conjugate roots, or three real roots (some of which might be repeated, as in our case). The fundamental theorem of algebra guarantees that a polynomial of degree n has exactly n roots (counting multiplicity). In our case, the single real root, x = -1, has a multiplicity of three. This means the root x = -1 appears three times as a solution to the equation.
Graphical Representation and Root Multiplicity
Plotting the function f(x) = x³ + 3x² + 3x + 1 visually reinforces the concept of root multiplicity. The graph will intersect the x-axis at x = -1. Instead of simply crossing the x-axis, the graph will touch the x-axis at this point and then turn around, indicating a repeated root. This behavior is characteristic of roots with even multiplicity. For roots with odd multiplicity (like our case of multiplicity 3), the graph will flatten out around the root before continuing its ascent or descent.
Alternative Methods for Solving Cubic Equations
While the binomial expansion provided a direct and elegant solution in this specific case, other methods can be employed to solve more general cubic equations. These methods include:
- Rational Root Theorem: This theorem helps identify potential rational roots of a polynomial equation. It's particularly useful when dealing with cubic equations with integer coefficients.
- Cardano's Method: This is a more involved algebraic technique used to find the roots of a general cubic equation. It involves a series of substitutions and manipulations to reduce the cubic equation to a simpler form that can be solved.
- Numerical Methods: For cubic equations that lack neat algebraic solutions, numerical methods like the Newton-Raphson method provide approximate solutions to a desired level of accuracy.
Applications of Cubic Equations
Cubic equations, despite their apparent complexity, have numerous applications across various fields, including:
- Engineering: Cubic equations are used extensively in structural analysis, fluid dynamics, and other engineering disciplines to model complex systems and solve for critical parameters.
- Physics: They appear in physics problems involving motion, projectile trajectories, and oscillations.
- Chemistry: Cubic equations are often employed in chemical kinetics and equilibrium calculations.
- Economics: Certain economic models utilize cubic equations to represent relationships between variables.
Further Exploration: More Complex Cubic Equations
While x³ + 3x² + 3x + 1 = 0 offers a relatively simple illustration of a cubic equation and its solution, more complex cubic equations can require more sophisticated techniques. For instance, equations with irrational or complex coefficients demand a deeper understanding of number systems and advanced algebraic methods. The concepts explored in this article provide a solid foundation for tackling these more challenging problems.
Conclusion: A Foundation for Further Mathematical Exploration
Solving the cubic equation x³ + 3x² + 3x + 1 = 0 serves as a valuable exercise in algebraic manipulation and highlights the importance of recognizing patterns and applying fundamental mathematical principles. Understanding the binomial theorem, recognizing the inherent structure of the equation, and applying factorization techniques allows for a straightforward solution. This understanding lays a strong foundation for tackling more complex cubic equations and other polynomial problems, paving the way for further exploration into the fascinating world of higher-order equations and their applications in various fields. The simplicity of this particular equation, however, should not overshadow the underlying power and elegance of the mathematical tools used to solve it. Remember that even the most seemingly complex mathematical problems can often be reduced to simpler forms with careful observation and the application of appropriate techniques.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
13x 11y 12 In Slope Intercept Form
Mar 09, 2025
-
What Is 2 1 As A Decimal
Mar 09, 2025
-
Ax By C Solve For Y
Mar 09, 2025
-
Find The Direction Angle Of V For The Following Vector
Mar 09, 2025
-
How Many Yards Are In 24 Ft
Mar 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Factor X 3 3x 2 3 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
