Factors Of X 2 2x 4
Next Genwave
Mar 07, 2025 · 5 min read
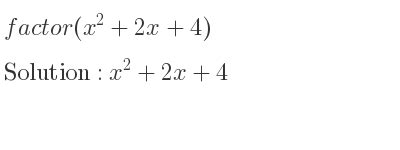
Table of Contents
Unraveling the Factors of x² + 2x + 4: A Deep Dive into Quadratic Expressions
Understanding quadratic expressions and their factorization is a cornerstone of algebra. This article will delve deep into the process of finding the factors of the quadratic expression x² + 2x + 4, exploring various methods and highlighting the significance of this seemingly simple equation within a broader mathematical context. We’ll cover topics including the discriminant, complex numbers, and the relationship between factoring and finding roots.
Understanding Quadratic Equations: A Quick Refresher
Before we dive into the specifics of x² + 2x + 4, let's review the fundamental structure of a quadratic equation. A general quadratic equation takes the form:
ax² + bx + c = 0
where 'a', 'b', and 'c' are constants, and 'x' is the variable. Our target expression, x² + 2x + 4, is a quadratic expression (note that it's not equal to zero, making it an expression, not an equation). In this case, a = 1, b = 2, and c = 4.
Attempting Traditional Factoring Methods
The most common approach to factoring quadratic expressions involves finding two numbers that add up to 'b' (the coefficient of x) and multiply to 'c' (the constant term). Let's try this method with x² + 2x + 4:
We need two numbers that add up to 2 and multiply to 4. Let's list the factor pairs of 4:
- 1 and 4
- 2 and 2
- -1 and -4
- -2 and -2
None of these pairs add up to 2. This indicates that the expression x² + 2x + 4 cannot be factored using real numbers. This doesn't mean it's prime or unfactorable; it simply means its factors involve complex numbers.
The Discriminant: A Key to Understanding Factorability
The discriminant (Δ) of a quadratic equation is a crucial tool that tells us about the nature of the roots (solutions) of the equation. It's calculated as:
Δ = b² - 4ac
For our expression (remember, we’re treating it as an equation set to zero for the discriminant calculation), a = 1, b = 2, and c = 4. Let's calculate the discriminant:
Δ = (2)² - 4(1)(4) = 4 - 16 = -12
A negative discriminant indicates that the quadratic equation has two complex roots (roots involving the imaginary unit 'i', where i² = -1). This confirms our earlier observation that the expression cannot be factored using only real numbers.
Introducing Complex Numbers
Complex numbers are numbers of the form a + bi, where 'a' and 'b' are real numbers, and 'i' is the imaginary unit (√-1). Since our discriminant is negative, the factors of x² + 2x + 4 will involve complex numbers.
Factoring Using the Quadratic Formula
The quadratic formula provides a direct method for finding the roots of a quadratic equation, even when those roots are complex. The formula is:
x = [-b ± √(b² - 4ac)] / 2a
Plugging in our values (a = 1, b = 2, c = 4), we get:
x = [-2 ± √(-12)] / 2
Since √(-12) = √(12)√(-1) = 2√3i, the roots are:
x = -1 + √3i and x = -1 - √3i
Connecting Roots to Factors
The relationship between the roots of a quadratic equation and its factors is as follows: if α and β are the roots, then the quadratic expression can be factored as:
(x - α)(x - β)
Therefore, the factors of x² + 2x + 4 are:
(x - (-1 + √3i))(x - (-1 - √3i))
Simplifying this gives us:
(x + 1 - √3i)(x + 1 + √3i)
Graphical Representation and Significance
While we can't easily visualize the roots on a standard Cartesian coordinate system (as they are complex numbers), the original expression x² + 2x + 4 represents a parabola. The fact that it doesn't intersect the x-axis (where y=0) visually confirms that it has no real roots. This parabola opens upwards (since the coefficient of x² is positive) and lies entirely above the x-axis, reflecting the absence of real solutions.
Applications of Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations
The seemingly abstract concept of complex numbers and factoring quadratic expressions with complex roots has significant applications across various fields:
-
Electrical Engineering: Complex numbers are crucial in analyzing alternating current circuits. Impedance, a measure of opposition to current flow, is often represented as a complex number.
-
Quantum Mechanics: Complex numbers play a fundamental role in the mathematical formalism of quantum mechanics, describing wave functions and other quantum phenomena.
-
Signal Processing: Complex numbers are used extensively in signal processing techniques for analyzing and manipulating signals, such as in audio and image processing.
-
Fluid Dynamics: Complex analysis is used in certain fluid dynamics problems, particularly those involving potential flow.
Further Exploration: Beyond x² + 2x + 4
While we've focused on a specific expression, the principles discussed here are applicable to a broad range of quadratic equations. The discriminant remains a powerful tool for determining the nature of roots, and the quadratic formula is universally applicable. Understanding the relationship between roots and factors is essential for solving quadratic equations and manipulating related algebraic expressions. Exploring more complex quadratic equations and their factoring using similar methods will solidify your understanding of these fundamental algebraic concepts. Consider investigating cubic and higher-order polynomial equations to expand your knowledge further.
Conclusion: Mastering Quadratic Expressions
Factoring x² + 2x + 4, even though it involves complex numbers, provides a valuable insight into the intricacies of quadratic expressions and the broader world of algebra. Mastering these techniques is not just about memorizing formulas; it's about developing a deep understanding of the relationships between coefficients, roots, and factors, and appreciating the powerful applications of complex numbers in various scientific and engineering disciplines. The journey from simple real-number factorization to embracing complex roots expands the scope of your mathematical knowledge significantly.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Gcf Of 28 And 24
Mar 09, 2025
-
100 Out Of 150 As A Percentage
Mar 09, 2025
-
What Is 4 20 As A Percent
Mar 09, 2025
-
What Is A Half Of 150
Mar 09, 2025
-
What Percent Is 13 Out Of 15
Mar 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Factors Of X 2 2x 4 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
