Find The Area Between The Curves Calculator
Next Genwave
Mar 10, 2025 · 6 min read
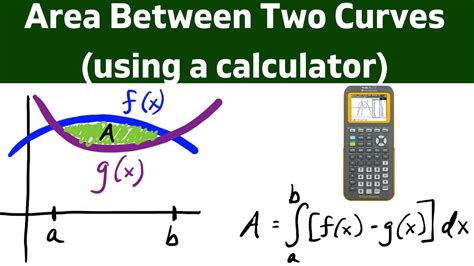
Table of Contents
Find the Area Between the Curves Calculator: A Comprehensive Guide
Finding the area between curves is a fundamental concept in integral calculus with applications spanning various fields, from physics and engineering to economics and statistics. While the underlying mathematical principles might seem daunting, numerous online calculators simplify this process, providing a user-friendly interface to calculate these areas accurately and efficiently. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of area calculation between curves, explaining the mathematical foundation, exploring different approaches, and highlighting the practical benefits of using an area between curves calculator.
Understanding the Concept: Area Between Curves
The area between two curves, f(x) and g(x), within a specified interval [a, b], represents the region bounded by these curves and the vertical lines x = a and x = b. This area isn't simply the difference between the areas under each curve individually; it's a more nuanced calculation.
To find this area, we rely on the power of definite integration. The formula for the area (A) is given by:
A = ∫<sub>a</sub><sup>b</sup> |f(x) - g(x)| dx
This formula indicates that we integrate the absolute difference between the two functions over the specified interval. The absolute value is crucial because the area must always be positive, regardless of which function has a larger value within a given sub-interval.
Key Considerations:
-
Intersection Points: Determining the points where the curves intersect (i.e., where f(x) = g(x)) is essential for defining the limits of integration (a and b). These intersection points delineate the boundaries of the area we're calculating. If the curves don't intersect within the given interval, you're calculating the area under a single curve, which is a simpler integration problem.
-
Function Dominance: Identifying which function is greater than the other within the interval is vital. The function with the larger value determines which function is subtracted from the other in the integral. Incorrectly identifying the dominant function will lead to an incorrect, possibly negative, area.
-
Interval Selection: The specified interval [a, b] defines the region for which you're calculating the area. Choosing the correct interval is critical for accuracy. If multiple intersection points exist, you might need to break the integration into multiple sub-intervals to account for changes in function dominance.
-
Types of Functions: The types of functions involved (polynomial, trigonometric, exponential, etc.) impact the complexity of the integration process. While simple polynomial functions might be easily integrated manually, more complex functions might require advanced integration techniques or the aid of a calculator or software.
The Role of an Area Between Curves Calculator
An area between the curves calculator acts as an invaluable tool for simplifying this process. It streamlines the calculations, especially when dealing with complex functions or multiple intersection points.
Benefits of Using a Calculator:
-
Time Savings: Manual calculation of integrals, particularly for intricate functions, can be incredibly time-consuming and prone to errors. Calculators eliminate this bottleneck, providing near-instantaneous results.
-
Accuracy: Manual calculations are inherently susceptible to human errors, especially during complex integration steps. Calculators significantly reduce this risk, offering highly precise results.
-
Accessibility: Calculators make this mathematical concept accessible to a wider audience. Even those without advanced calculus knowledge can readily utilize them to calculate the area between curves.
-
Visualization: Many online calculators provide graphical representations of the functions and the calculated area, offering a visual understanding of the problem. This visual aid improves comprehension and facilitates learning.
-
Handling Complex Functions: Calculators can efficiently handle complex functions that might be challenging to integrate manually.
Step-by-Step Guide to Using an Area Between Curves Calculator
While the specific interface might differ slightly between calculators, the general steps remain consistent:
-
Input Functions: Enter the equations of the two functions, f(x) and g(x), using the correct mathematical notation (e.g., x^2 for x squared, sin(x) for sine of x). Ensure you’re using a consistent notation for mathematical operations.
-
Specify Interval: Define the interval [a, b] over which you want to calculate the area. This can often be done by providing the lower and upper limits of integration. If the calculator doesn't directly allow you to input interval limits, you may need to solve for the intersection points yourself, and input those as the limits.
-
Select Calculation Type: Some calculators offer different calculation methods (numerical vs. symbolic integration), allowing you to choose the level of precision or type of output you need.
-
Execute Calculation: Click the "Calculate" or equivalent button to initiate the process. The calculator will compute the definite integral and display the result, representing the area between the curves.
-
Interpret Results: Carefully interpret the calculator’s output. The answer should be a numerical value representing the area. Pay attention to units if specified in the problem.
Advanced Applications and Considerations
The concept of finding the area between curves extends beyond simple integration problems. It's applicable in numerous advanced scenarios:
1. Finding Areas Bounded by More Than Two Curves:
The basic principle can be extended to scenarios involving three or more curves. In such cases, the area is calculated by integrating the difference between the upper and lower functions within each sub-interval. You'll likely need to break the integration into multiple segments, based on which curve is dominant in which region.
2. Applications Involving Parametric Equations:
If your curves are defined using parametric equations (x = f(t), y = g(t)), you need to employ a slightly modified approach involving the parameter 't' for integration. This involves calculating the area using the formula ∫<sub>t1</sub><sup>t2</sup> |g(t) * f'(t)| dt, where t1 and t2 are the parameter values defining the interval. Many advanced calculators can directly handle parametric equations.
3. Areas in Polar Coordinates:
For curves defined in polar coordinates (r = f(θ)), the area calculation involves a different integral formula. Advanced calculators capable of handling polar coordinates are required for such calculations.
4. Applications in Economics and Statistics:
Area between curves finds applications in economic models (e.g., consumer surplus and producer surplus) and statistical analysis (e.g., calculating the area under a probability density function).
Choosing the Right Area Between Curves Calculator
Many excellent online calculators are available; selecting the best one depends on individual needs and preferences. Consider the following factors:
-
Ease of Use: Opt for a calculator with a user-friendly interface and clear instructions. Intuitive input methods and readily understandable outputs are essential.
-
Function Support: Ensure the calculator supports the types of functions you intend to use (polynomial, trigonometric, exponential, etc.).
-
Accuracy: Look for calculators known for their accuracy and reliability, preferably those that use robust numerical integration techniques.
-
Visualization Capabilities: A graphical representation of the area is highly beneficial for understanding the problem and verifying the results.
-
Additional Features: Some calculators may offer additional features like step-by-step solutions or the ability to handle more complex functions.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Calculators
Finding the area between curves is a powerful mathematical tool with wide-ranging applications. While the underlying mathematical principles are important to understand, the use of area between curves calculators significantly simplifies the process, eliminating the tediousness of manual calculations and enhancing the accuracy of results. By understanding the principles involved and leveraging the power of these tools, users can efficiently and accurately solve problems across various disciplines, fostering a deeper understanding of this fundamental concept of integral calculus. With the appropriate calculator and a solid understanding of the theory, tackling these problems becomes both straightforward and rewarding.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
2 2 9 As An Improper Fraction
Mar 10, 2025
-
Write 6 75 As A Mixed Number
Mar 10, 2025
-
23 Is What Percent Of 25
Mar 10, 2025
-
3 2d 8 11d 18 D 3
Mar 10, 2025
-
2143 57 Rounded To The Nearest Hundredth
Mar 10, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Find The Area Between The Curves Calculator . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
