How Do I Graph X 1
Next Genwave
Mar 10, 2025 · 5 min read
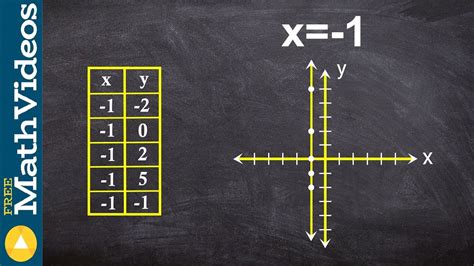
Table of Contents
How Do I Graph x = 1? A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding how to graph simple equations is fundamental to grasping more complex mathematical concepts. This guide will delve into the specifics of graphing the equation x = 1, explaining the process, the underlying principles, and its implications in various mathematical contexts. We'll explore different approaches, providing a clear and comprehensive understanding suitable for students of all levels.
Understanding the Equation x = 1
The equation x = 1 represents a vertical line on a Cartesian coordinate system. Unlike equations like y = mx + c (where 'm' is the slope and 'c' is the y-intercept), which represent lines with a defined slope, x = 1 signifies a line with an undefined slope. This is because the value of x remains constant regardless of the value of y. This means that for every possible y-coordinate, the corresponding x-coordinate will always be 1.
Graphing x = 1: A Step-by-Step Guide
Graphing x = 1 is remarkably straightforward. Here's a step-by-step approach:
-
Draw the Coordinate Plane: Begin by drawing a standard Cartesian coordinate system with an x-axis (horizontal) and a y-axis (vertical). Clearly label both axes with numerical values.
-
Locate the Point (1, 0): The equation x = 1 dictates that the x-coordinate is always 1. Therefore, we start by locating the point where x = 1 and y = 0. This point lies on the x-axis.
-
Extend the Vertical Line: Since the value of x remains constant (1) irrespective of the value of y, draw a vertical line passing through the point (1, 0). This line extends infinitely in both the positive and negative y-directions.
-
Label the Line: Finally, label the line as x = 1 to clearly identify the equation it represents.
Why is the Slope Undefined?
The slope of a line is defined as the change in y divided by the change in x (Δy/Δx). In the equation x = 1, the change in x (Δx) is always zero because x remains constant. Division by zero is undefined in mathematics, hence the slope of the line x = 1 is undefined. This is a crucial characteristic that distinguishes vertical lines from other lines on the coordinate plane.
Contrasting with Horizontal Lines (y = c)
It’s helpful to compare the equation x = 1 with horizontal lines represented by equations of the form y = c, where 'c' is a constant. For example, y = 2 represents a horizontal line passing through all points with a y-coordinate of 2. Unlike x = 1, the line y = 2 has a defined slope of zero (Δy/Δx = 0/Δx = 0), as the change in y is zero.
Key Differences:
| Feature | x = 1 (Vertical Line) | y = c (Horizontal Line) |
|---|---|---|
| Slope | Undefined | 0 |
| Orientation | Vertical | Horizontal |
| x-coordinate | Constant (1) | Varies |
| y-coordinate | Varies | Constant (c) |
Applications of Vertical Lines
While seemingly simple, the equation x = 1, and vertical lines in general, have significant applications in various mathematical and real-world contexts:
-
Domain Restrictions: In functions, vertical lines often define the boundaries of a function's domain. A vertical asymptote of a function, for instance, indicates a value of x where the function is undefined. Understanding vertical lines is crucial for analyzing function behavior and identifying discontinuities.
-
Systems of Equations: Solving systems of equations involving both vertical and other lines helps determine the point of intersection, or lack thereof. For instance, a system of equations with one equation x=1 and another y = 2x +1 would have a single solution (1,3).
-
Geometry: Vertical lines play a significant role in geometry, particularly in defining perpendicular lines, right angles, and specific geometric shapes and constructions. In coordinate geometry, they're used to calculate distances, areas, and other geometric properties.
-
Real-World Applications: Vertical lines can represent various real-world phenomena. For example, the height of a building might be modeled with a vertical line, where the x-coordinate represents a fixed location and the y-coordinate represents the height.
Advanced Concepts and Extensions
The simple equation x = 1 provides a stepping stone towards understanding more complex mathematical concepts:
-
Functions: While x = 1 itself isn't a function (it fails the vertical line test), understanding it contributes to analyzing functions and their properties.
-
Linear Algebra: In linear algebra, the concept of vectors and their representation is related to lines and coordinate systems. Understanding vertical lines contributes to a better grasp of vectors and their operations.
-
Calculus: Vertical lines can help illustrate limits, continuity, and other important calculus concepts. Understanding the behavior of functions near vertical asymptotes is a crucial aspect of calculus.
-
Three-Dimensional Space: Extending this concept to three-dimensional space, the equation x = 1 represents a plane that is parallel to the yz-plane and intersects the x-axis at x = 1.
Practical Exercises
To solidify your understanding, try these practice exercises:
-
Graph the following equations: y = 3, x = -2, y = -1, x = 5. Describe the orientation and slope of each line.
-
Find the intersection point(s) (if any) of the following systems of equations:
- x = 2 and y = x + 1
- x = -1 and y = 2x -3
- x = 0 and y = 0
-
Describe how the equation x = 1 might be used to represent a real-world scenario.
-
Explain why the slope of x = 1 is undefined, while the slope of y = 1 is 0.
Conclusion: Mastering the Basics
The equation x = 1, though seemingly simple, provides a foundational understanding of lines, slopes, and coordinate systems. Mastering this concept lays a solid groundwork for tackling more advanced mathematical topics. By understanding the fundamental principles involved and practicing the techniques explained in this guide, you'll develop a deeper comprehension of this core element of mathematics and its diverse applications. Through continued practice and exploration, you’ll build confidence and proficiency in graphing and interpreting mathematical equations. Remember that a strong grasp of fundamental concepts is crucial for success in higher-level mathematics and related fields.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
2 2 9 As An Improper Fraction
Mar 10, 2025
-
Write 6 75 As A Mixed Number
Mar 10, 2025
-
23 Is What Percent Of 25
Mar 10, 2025
-
3 2d 8 11d 18 D 3
Mar 10, 2025
-
2143 57 Rounded To The Nearest Hundredth
Mar 10, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Do I Graph X 1 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
