How Do You Find The Slope Of A Line Perpendicular
Next Genwave
Mar 10, 2025 · 4 min read
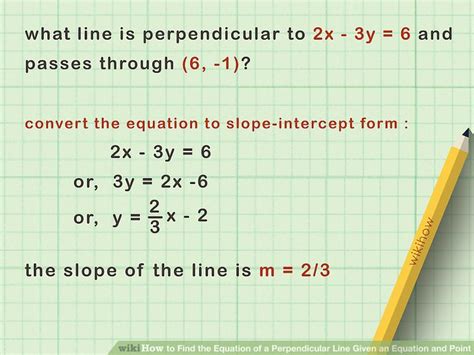
Table of Contents
How Do You Find the Slope of a Perpendicular Line? A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the relationship between lines, particularly perpendicular lines, is fundamental in geometry and various applications of mathematics. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of finding the slope of a perpendicular line, providing a step-by-step approach suitable for all levels of mathematical understanding. We'll cover definitions, formulas, examples, and even address common misconceptions. By the end, you'll confidently determine the slope of any perpendicular line given sufficient information.
Understanding Slope and its Significance
Before diving into perpendicular lines, let's solidify our understanding of slope. The slope of a line, often denoted by m, represents the steepness and direction of the line. It's calculated as the ratio of the vertical change (rise) to the horizontal change (run) between any two distinct points on the line. Formally, if we have two points (x₁, y₁) and (x₂, y₂), the slope is given by:
m = (y₂ - y₁) / (x₂ - x₁)
A positive slope indicates a line that rises from left to right, while a negative slope indicates a line that falls from left to right. A slope of zero represents a horizontal line, and an undefined slope represents a vertical line.
The Concept of Perpendicular Lines
Two lines are perpendicular if they intersect at a right angle (90°). This geometric relationship has a significant impact on their slopes. The slopes of perpendicular lines are inversely related and exhibit a specific mathematical relationship that we'll explore in detail.
The Relationship Between Slopes of Perpendicular Lines
The crucial relationship between the slopes of two perpendicular lines is that they are negative reciprocals of each other. In simpler terms:
- If the slope of one line is m, then the slope of a line perpendicular to it is -1/m.
Let's break this down:
-
Negative: The sign of the slope is reversed. If the original slope is positive, the perpendicular slope is negative, and vice versa.
-
Reciprocal: The numerator and denominator are switched. For example, if the slope is 2 (which can be written as 2/1), the reciprocal is 1/2.
Finding the Slope of a Perpendicular Line: A Step-by-Step Approach
Let's illustrate the process with several examples, progressing from simpler to more complex scenarios.
Example 1: Given the slope of one line.
Problem: Find the slope of a line perpendicular to a line with a slope of 3.
Solution:
-
Identify the given slope: m = 3
-
Find the negative reciprocal: -1/m = -1/3
Therefore, the slope of the perpendicular line is -1/3.
Example 2: Given two points on one line.
Problem: Find the slope of a line perpendicular to the line passing through the points (2, 4) and (6, 8).
Solution:
-
Calculate the slope of the given line:
m = (8 - 4) / (6 - 2) = 4 / 4 = 1
-
Find the negative reciprocal: -1/m = -1/1 = -1
Therefore, the slope of the perpendicular line is -1.
Example 3: Given the equation of one line.
Problem: Find the slope of a line perpendicular to the line represented by the equation y = 2x + 5.
Solution:
-
Identify the slope of the given line: The equation is in slope-intercept form (y = mx + b), where m is the slope. Therefore, the slope of the given line is 2.
-
Find the negative reciprocal: -1/m = -1/2
Therefore, the slope of the perpendicular line is -1/2.
Example 4: Dealing with horizontal and vertical lines.
-
Horizontal Line: A horizontal line has a slope of 0. A line perpendicular to a horizontal line is a vertical line, which has an undefined slope.
-
Vertical Line: A vertical line has an undefined slope. A line perpendicular to a vertical line is a horizontal line, which has a slope of 0.
Advanced Applications and Considerations
The concept of perpendicular lines and their slopes extends beyond basic geometry. It finds applications in:
-
Vector Analysis: Determining the orthogonality (perpendicularity) of vectors.
-
Calculus: Finding tangent and normal lines to curves.
-
Computer Graphics: Creating perpendicular lines for various visual effects and geometric constructions.
-
Physics and Engineering: Modeling perpendicular forces and movements.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
-
Forgetting the negative sign: Remember that the negative reciprocal involves changing the sign.
-
Incorrectly calculating the reciprocal: Ensure you correctly switch the numerator and denominator.
-
Confusing parallel and perpendicular lines: Parallel lines have the same slope, while perpendicular lines have negative reciprocal slopes.
Conclusion: Mastering Perpendicular Line Slopes
Finding the slope of a perpendicular line is a fundamental skill in mathematics. By understanding the concept of negative reciprocals and following the step-by-step approach outlined in this guide, you can confidently tackle various problems involving perpendicular lines. Remember to practice regularly, and don't hesitate to review the examples to reinforce your understanding. Mastering this concept opens doors to more advanced mathematical topics and applications in various fields. The more you practice, the more comfortable and proficient you will become in handling these types of problems. Always double-check your calculations to ensure accuracy. Remember that a strong foundation in understanding slope and its properties is crucial for successfully navigating more complex mathematical concepts.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
5 4 3 2 1 Math Term
Mar 10, 2025
-
4 1 2 As A Mixed Number
Mar 10, 2025
-
12 As A Percentage Of 40
Mar 10, 2025
-
How To Simplify To A Bi Form
Mar 10, 2025
-
Find A Line Perpendicular To Another Line
Mar 10, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Do You Find The Slope Of A Line Perpendicular . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
