How To Factor X 3 2
Next Genwave
Mar 06, 2025 · 5 min read
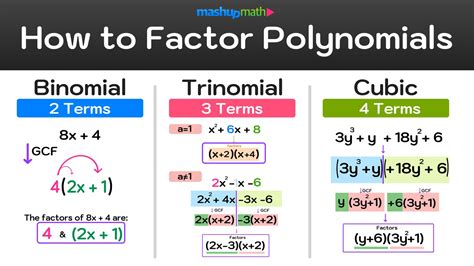
Table of Contents
How to Factor x³ + 2
Factoring cubic polynomials can seem daunting, but with a systematic approach, even seemingly complex expressions like x³ + 2 can be tackled effectively. This comprehensive guide will walk you through various methods, focusing on understanding the underlying principles rather than just memorizing formulas. We'll explore different scenarios and strategies, equipping you with the skills to factor a wide range of cubic expressions.
Understanding the Basics of Factoring
Before diving into the specifics of factoring x³ + 2, let's refresh some fundamental concepts. Factoring, in essence, is the process of expressing a polynomial as a product of simpler polynomials. It's the reverse of expanding brackets using the distributive property (also known as FOIL).
For example, factoring the quadratic expression x² - 4 involves finding two binomials whose product equals x² - 4. In this case, the factors are (x - 2) and (x + 2), since (x - 2)(x + 2) = x² - 4.
Cubic polynomials, like our target x³ + 2, are slightly more complex, but the underlying principle remains the same: we aim to break down the expression into simpler factors.
Approaches to Factoring x³ + 2
Unfortunately, x³ + 2 doesn't easily factor using common techniques like grouping or simple binomial factoring. The key lies in recognizing that it's a sum of cubes. The general formula for the sum of cubes is:
a³ + b³ = (a + b)(a² - ab + b²)
Let's apply this to our expression:
-
Identify 'a' and 'b': In x³ + 2, a = x and b = ∛2 (the cube root of 2). Note that b is not a whole number; this is typical for sum of cubes that aren't easily apparent.
-
Substitute into the formula: Substituting a = x and b = ∛2 into the sum of cubes formula gives us:
x³ + 2 = (x + ∛2)(x² - x∛2 + (∛2)²)
This is the factored form of x³ + 2. While it might not look as "clean" as factoring a simple quadratic, it is indeed the fully factored form over the real numbers.
Exploring Other Cubic Factoring Techniques
While the sum of cubes formula perfectly handles x³ + 2, let's explore other methods that are valuable for factoring different types of cubic polynomials. These techniques will broaden your understanding and help you tackle a wider range of problems.
1. Factoring by Grouping
This method is effective when a cubic polynomial can be grouped into pairs of terms that share common factors. For example, consider the polynomial:
x³ + 2x² - x - 2
We can group it as follows:
(x³ + 2x²) + (-x - 2)
Now factor out common factors from each group:
x²(x + 2) - 1(x + 2)
Notice that (x + 2) is a common factor, so we can factor it out:
(x + 2)(x² - 1)
The resulting expression can be further factored (x² - 1 is a difference of squares):
(x + 2)(x - 1)(x + 1)
2. Using the Rational Root Theorem
The Rational Root Theorem helps identify potential rational roots (roots that are fractions) of a polynomial. It states that if a polynomial has rational roots, they will be of the form p/q, where p is a factor of the constant term and q is a factor of the leading coefficient.
Let's consider the polynomial:
x³ - 3x² - 4x + 12
The constant term is 12, and the leading coefficient is 1. Potential rational roots are factors of 12: ±1, ±2, ±3, ±4, ±6, ±12.
We can test these values by substituting them into the polynomial. If a value makes the polynomial equal to zero, it's a root. Let's try x = 2:
2³ - 3(2)² - 4(2) + 12 = 8 - 12 - 8 + 12 = 0
Since x = 2 is a root, (x - 2) is a factor. We can perform polynomial long division or synthetic division to find the other factor. The result is (x - 2)(x² - x - 6). This quadratic can be further factored: (x - 2)(x - 3)(x + 2).
3. Using the Cubic Formula
For the most general cases, the cubic formula can be used to find the roots of a cubic polynomial. However, it's quite complex and often leads to messy expressions, especially when dealing with irrational or complex roots. It's generally not recommended unless other methods fail.
Advanced Considerations and Applications
While x³ + 2's factorization is relatively straightforward using the sum of cubes formula, understanding these additional techniques is crucial for tackling more complex cubic equations. Here are some advanced considerations:
-
Complex Roots: Cubic equations can have complex roots (involving the imaginary unit 'i'). When dealing with such roots, the factored form might involve complex numbers.
-
Repeated Roots: A cubic polynomial can have repeated roots. For example, x³ - 3x² + 3x - 1 = (x - 1)³ has a repeated root of x = 1.
-
Applications in Calculus: Factoring cubic polynomials is fundamental in calculus, particularly in finding critical points, inflection points, and analyzing the behavior of functions.
-
Applications in Physics and Engineering: Cubic equations frequently appear in models describing physical phenomena and engineering problems, from projectile motion to circuit analysis.
Practical Tips and Strategies
-
Start with the simplest methods: Always attempt simple factoring techniques (like grouping or common factors) before resorting to more advanced methods.
-
Utilize technology strategically: Computer algebra systems (CAS) or online calculators can assist with polynomial long division or finding roots, but understanding the underlying principles is essential. Don't rely solely on technology; use it as a tool to confirm your work or handle computationally intensive tasks.
-
Practice regularly: Mastering cubic factoring requires consistent practice. Work through numerous examples, gradually increasing the complexity of the polynomials.
-
Break down complex problems: When confronted with a complicated cubic expression, try to simplify it by substituting or manipulating it before attempting to factor.
Conclusion
Factoring x³ + 2, using the sum of cubes formula, reveals the relatively simple factorization (x + ∛2)(x² - x∛2 + (∛2)²). However, the journey to mastering cubic factoring extends beyond this specific example. By understanding various methods like grouping, the rational root theorem, and appreciating the limitations of the cubic formula, you'll develop the skills to confidently tackle a wide range of cubic polynomial factoring problems. Remember that practice and a systematic approach are key to success. This understanding will not only benefit your algebra skills but will also lay a strong foundation for more advanced mathematical concepts in calculus and beyond.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Greatest Common Factor Of 10 And 8
Mar 06, 2025
-
What Is The Percent Of 8 15
Mar 06, 2025
-
What Is 2 1 2 As A Decimal
Mar 06, 2025
-
How Many Yards Are In 24 Feet
Mar 06, 2025
-
What Percentage Of 25 Is 15
Mar 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How To Factor X 3 2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
