Integral 1 X 2 1 2
Next Genwave
Mar 06, 2025 · 5 min read
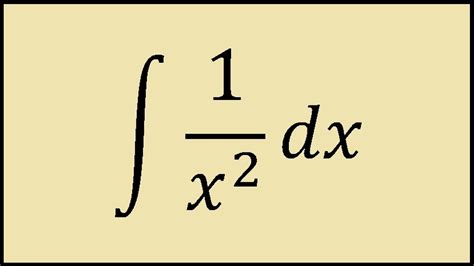
Table of Contents
Decoding the Integral: A Deep Dive into ∫(1/(x²+1))dx
The seemingly simple integral, ∫(1/(x²+1))dx, holds a significant place in calculus. While its solution might appear straightforward at first glance, understanding its derivation, applications, and broader implications within the realm of mathematics reveals a rich tapestry of mathematical concepts. This comprehensive exploration will delve into the intricacies of this integral, exploring its evaluation, significance, and connections to other mathematical areas.
Understanding the Integral: A Foundation
Before embarking on the solution, let's establish a firm understanding of the integral itself. The expression ∫(1/(x²+1))dx represents the indefinite integral of the function f(x) = 1/(x²+1). In simpler terms, we are searching for a function whose derivative is 1/(x²+1). This process is the reverse of differentiation, seeking the antiderivative.
Methods of Evaluation: Unveiling the Solution
Several approaches exist to solve this integral, each providing a valuable insight into different mathematical techniques.
1. Using Trigonometric Substitution: A Classical Approach
This method leverages the trigonometric identity 1 + tan²(θ) = sec²(θ). We substitute x = tan(θ), which implies dx = sec²(θ)dθ. Substituting these into the integral, we get:
∫(1/(x²+1))dx = ∫(1/(tan²(θ)+1))sec²(θ)dθ = ∫(1/sec²(θ))sec²(θ)dθ = ∫dθ = θ + C
Since x = tan(θ), we have θ = arctan(x). Therefore, the solution is:
∫(1/(x²+1))dx = arctan(x) + C
Where 'C' represents the constant of integration, crucial because the derivative of a constant is zero. This method elegantly demonstrates the connection between trigonometric functions and the integral.
2. Employing Partial Fraction Decomposition: An Alternate Perspective
While less intuitive for this specific integral, partial fraction decomposition provides a valuable alternative technique applicable to more complex rational functions. However, since 1/(x²+1) is already in its simplest form (irreducible quadratic denominator), this method isn't directly applicable here. Its inclusion serves to highlight the versatility of different integration techniques.
3. Recognizing the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus: A Conceptual Link
The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus establishes the profound relationship between differentiation and integration. It states that the derivative of the integral of a function is the function itself. Knowing that the derivative of arctan(x) is 1/(x²+1), we can directly conclude, using this theorem, that the integral of 1/(x²+1) is arctan(x) + C.
The Significance of arctan(x): Exploring its Properties and Applications
The arctangent function (arctan(x) or tan⁻¹(x)), resulting from the integral, possesses remarkable properties and finds wide-ranging applications in numerous fields.
-
Inverse Trigonometric Function: arctan(x) represents the inverse of the tangent function, providing the angle whose tangent is x. This inverse relationship is crucial in various geometric and trigonometric calculations.
-
Range and Domain: The range of arctan(x) is (-π/2, π/2), meaning the output values are confined to this interval. The domain is all real numbers, encompassing both positive and negative values of x.
-
Applications in Physics and Engineering: Arctan(x) appears extensively in physics and engineering applications, particularly in problems involving angles, vectors, and complex numbers. For instance, calculating the angle of a projectile's trajectory or determining phase shifts in electrical circuits often involve arctan(x).
-
Use in Complex Analysis: The arctangent function plays a vital role in complex analysis, helping to define complex logarithms and various complex functions.
Beyond the Basic Integral: Extending the Concept
While we've focused primarily on ∫(1/(x²+1))dx, exploring related integrals enhances our understanding and highlights the integral's broader context.
-
Integrals with a constant multiplier: Consider the integral ∫(a²/(x²+a²))dx, where 'a' is a constant. A simple u-substitution (u = x/a) transforms this integral into the form we've already solved. The solution becomes (1/a)arctan(x/a) + C. This generalization underscores the adaptability of the solution method.
-
Definite Integrals: Evaluating the definite integral ∫[a,b] (1/(x²+1))dx provides a numerical value representing the area under the curve of 1/(x²+1) from x = a to x = b. This involves substituting the limits of integration into the antiderivative, arctan(x), and calculating the difference. This calculation is crucial for various applications, particularly in probability and statistics.
-
Integrals involving more complex rational functions: While this specific integral deals with a simple rational function, techniques such as partial fraction decomposition and other advanced integration methods are essential for handling more complex rational functions, which frequently appear in applied mathematics and engineering problems.
The Integral in Context: Connections to Other Mathematical Fields
The seemingly simple integral ∫(1/(x²+1))dx is not isolated; it has profound connections to other areas of mathematics:
-
Probability and Statistics: The arctangent function is integral to various probability distributions, such as the Cauchy distribution, where it's crucial in calculating probabilities and statistical parameters.
-
Differential Equations: Solving differential equations frequently involves integrating functions, and this integral often emerges as a component of the solution to various types of differential equations.
-
Numerical Analysis: Numerical methods are used to approximate definite integrals when analytical solutions are unavailable or computationally intensive. Understanding this fundamental integral provides a basis for understanding more advanced numerical techniques.
Conclusion: A Journey of Discovery
This comprehensive exploration of the integral ∫(1/(x²+1))dx demonstrates that what appears initially as a straightforward problem reveals a wealth of mathematical insights. From its solution through various techniques to its wide-ranging applications and connections to other mathematical areas, this seemingly simple integral serves as a testament to the interconnected nature of mathematics and its power to illuminate numerous fields of study. Understanding this fundamental integral is crucial for anyone seeking a deeper appreciation for calculus and its profound implications. Further exploration into the advanced techniques and applications discussed herein will continue to enrich your mathematical understanding. The journey of mathematical discovery, propelled by seemingly simple problems like this, is never-ending, constantly revealing new depths and complexities.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 25 C In F
Mar 07, 2025
-
Rectangular Equation To Polar Form Calculator
Mar 07, 2025
-
Solve 2x Y 7 For Y
Mar 07, 2025
-
2 Out Of 12 Is What Percent
Mar 07, 2025
-
3 X 3 X 3 X 3 X 3
Mar 07, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Integral 1 X 2 1 2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
