Integral Of 1/square Root Of X
Next Genwave
Mar 06, 2025 · 5 min read
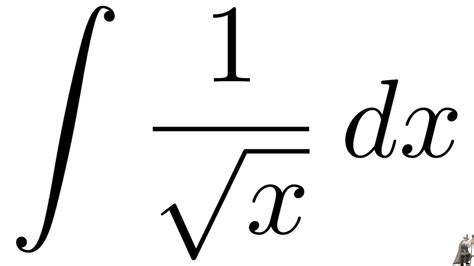
Table of Contents
Decoding the Integral of 1/√x: A Comprehensive Guide
The integral of 1/√x, often written as ∫(1/√x)dx, is a fundamental concept in calculus with far-reaching applications in various fields. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of solving this integral, exploring its theoretical underpinnings, practical applications, and related concepts. We'll also address common misconceptions and provide you with a solid understanding of this seemingly simple yet powerful mathematical operation.
Understanding the Problem: ∫(1/√x)dx
Before diving into the solution, let's understand the problem statement. We are asked to find the indefinite integral of the function f(x) = 1/√x. In simpler terms, we're looking for a function F(x) whose derivative is 1/√x. This involves reversing the process of differentiation. Remember that √x can be rewritten as x<sup>1/2</sup>, making our integrand 1/x<sup>1/2</sup> or x<sup>-1/2</sup>. This rewriting significantly simplifies our approach to integration.
The Power Rule of Integration: The Key to Solving the Integral
The key to solving this integral lies in the power rule of integration, a fundamental theorem in calculus. The power rule states that the integral of x<sup>n</sup> is (x<sup>n+1</sup>)/(n+1) + C, where 'n' is any real number except -1, and 'C' is the constant of integration.
Applying the Power Rule:
Since our integrand is x<sup>-1/2</sup>, we can apply the power rule directly:
∫x<sup>-1/2</sup> dx = (x<sup>-1/2 + 1</sup>)/(-1/2 + 1) + C
Simplifying the exponent:
-1/2 + 1 = 1/2
Substituting back into the equation:
∫x<sup>-1/2</sup> dx = (x<sup>1/2</sup>)/(1/2) + C
Finally, simplifying the fraction:
∫x<sup>-1/2</sup> dx = 2x<sup>1/2</sup> + C
Therefore, the integral of 1/√x is 2√x + C.
The Constant of Integration: An Important Detail
The constant of integration, 'C', is crucial. It represents an arbitrary constant that can take any value. This is because the derivative of a constant is always zero. Therefore, many functions can have the same derivative. For example, 2√x + 1, 2√x + 5, and 2√x - 10 all have the same derivative of 1/√x. The constant of integration accounts for this ambiguity. When dealing with definite integrals (integrals with limits), the constant cancels out, but it's vital to remember it in indefinite integrals.
Visualizing the Solution: Graphing the Function and its Integral
Graphing the function f(x) = 1/√x and its integral F(x) = 2√x + C can enhance understanding. The graph of f(x) shows a curve that approaches infinity as x approaches zero and gradually decreases as x increases. The graph of F(x) will be a family of curves, each differing by the value of C. Each curve represents a possible antiderivative of f(x). Observing the relationship between the function and its integral visually helps to solidify the concept.
Applications of the Integral of 1/√x
The integral 2√x + C, while seemingly simple, finds application in diverse fields:
1. Physics: Calculating Distance from Velocity
In physics, if you know the velocity function of an object, you can find its displacement by integrating the velocity function with respect to time. If the velocity function is proportional to 1/√t, the integral of 1/√x will be directly applicable in calculating the distance covered.
2. Statistics and Probability: Probability Density Functions
In probability and statistics, the integral of probability density functions is used to calculate probabilities. Several probability distributions might have probability density functions involving terms similar to 1/√x, making the integral crucial for calculating probabilities and expectations.
3. Economics: Marginal Cost and Total Cost
In economics, the marginal cost function represents the additional cost of producing one more unit of a good. If the marginal cost is proportional to 1/√x, integrating it with respect to quantity (x) gives the total cost function.
4. Engineering: Calculating Area Under a Curve
In engineering, the integral is used to calculate the area under a curve. If the curve is described by the function 1/√x, the integral provides the area. This application is useful in numerous engineering disciplines, from calculating fluid flow to determining stress distributions.
Addressing Common Misconceptions
Several common misconceptions surround the integral of 1/√x. Let's clarify them:
1. The Domain of the Function
The function f(x) = 1/√x is only defined for positive values of x (x > 0). The square root of a negative number is not a real number. This must be considered when evaluating definite integrals.
2. The Indefinite Nature of the Integral
Remember that the integral 2√x + C is an indefinite integral. It represents a family of functions, each differing only by the constant of integration, ‘C’. This constant is crucial and should never be omitted.
Further Exploration: Definite Integrals and Numerical Methods
The concept extends to definite integrals, where we evaluate the integral between specific limits. For instance, evaluating ∫(1/√x)dx from 1 to 4 involves substituting the limits into the antiderivative 2√x + C and calculating the difference. The constant ‘C’ cancels out in this process.
For more complex functions or when analytical solutions are unavailable, numerical integration techniques such as the trapezoidal rule or Simpson's rule can approximate the definite integral.
Conclusion: Mastering the Integral of 1/√x
The seemingly simple integral of 1/√x, or ∫x<sup>-1/2</sup>dx = 2x<sup>1/2</sup> + C, plays a critical role in various fields. This guide provides a thorough exploration of its solution, applications, and related concepts. Mastering this integral is fundamental for anyone pursuing higher-level mathematics, science, or engineering studies. Understanding the power rule, the significance of the constant of integration, and the various applications discussed here will enhance your problem-solving skills significantly. Always remember to consider the domain of the function and choose the appropriate integration technique based on the context of the problem. This understanding will solidify your foundation in calculus and its practical applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 2 3 2 3
Mar 08, 2025
-
Evauluate The Epression 2neponet 2 When N Is 5
Mar 08, 2025
-
What Percentage Of 40 Is 22
Mar 08, 2025
-
75 Is What Percent Of 150
Mar 08, 2025
-
2 3 4 In Decimal Form
Mar 08, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Integral Of 1/square Root Of X . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
