Integral Of E To The Xy
Next Genwave
Mar 07, 2025 · 6 min read
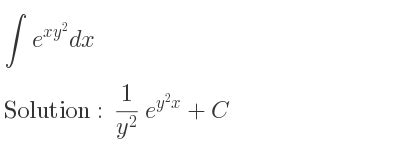
Table of Contents
The Integral of e^(xy): A Comprehensive Guide
The integral of e^(xy) is a fascinating mathematical concept that appears frequently in various fields, including physics, engineering, and probability. Unlike simpler exponential integrals, integrating e^(xy) requires a deeper understanding of integration techniques and often depends on the context of the problem. This comprehensive guide will explore the different approaches to integrating e^(xy), covering various scenarios and providing a thorough understanding of this crucial mathematical function.
Understanding the Challenges
The seemingly simple expression e^(xy) presents a unique challenge when it comes to integration. Unlike functions like e^x, which integrate directly to e^x + C, e^(xy) requires more sophisticated methods due to the presence of two variables, x and y. The approach to integration depends heavily on whether x and y are treated as independent variables, constants, or part of a larger expression within a double or multiple integral.
Case 1: Integrating with Respect to x (y treated as a constant)
The most straightforward scenario is when we're integrating e^(xy) with respect to x, treating y as a constant. In this case, the integration process is similar to integrating e^(ax), where 'a' is a constant.
The Solution:
∫e^(xy) dx = (1/y)e^(xy) + C
Where:
- y ≠ 0: The division by y is crucial and highlights the condition that y cannot be zero. If y were zero, the exponent would be 1, and the integral would simply be x + C.
- C: Represents the constant of integration. This is an essential element of indefinite integrals.
Example:
Let's say we want to evaluate the definite integral ∫e^(2x) dx from 0 to 1. Here, y effectively acts as a constant (2).
∫₀¹ e^(2x) dx = [(1/2)e^(2x)]₀¹ = (1/2)e² - (1/2)e⁰ = (1/2)(e² - 1)
Significance and Applications:
This integral is fundamental in many applications, particularly in solving differential equations involving exponential growth or decay. It also appears in probability theory and statistics when dealing with exponential distributions.
Case 2: Integrating with Respect to y (x treated as a constant)
Symmetrically, if we integrate e^(xy) with respect to y, treating x as a constant, we obtain a similar result.
The Solution:
∫e^(xy) dy = (1/x)e^(xy) + C
Where:
- x ≠ 0: Similar to the previous case, x cannot be zero to avoid division by zero.
- C: Represents the constant of integration.
Significance and Applications:
This integral mirrors the application of the previous case but with the roles of x and y reversed. It's crucial in solving partial differential equations and analyzing systems where exponential behavior is dependent on multiple variables.
Case 3: Double Integrals
When dealing with double integrals involving e^(xy), the integration process becomes more complex. The order of integration can significantly affect the difficulty of the problem. We'll consider two scenarios:
Scenario 3.1: Integrating First with Respect to x, Then y
Let's assume we have a double integral of the form:
∬<sub>R</sub> e^(xy) dA
where R is a region defined by specific limits of integration for x and y. If we first integrate with respect to x, treating y as a constant (as shown in Case 1), we will get:
∫<sub>a</sub><sup>b</sup> [ (1/y)e^(xy) ]<sub>x=c</sub><sup>x=d</sup> dy
where a, b, c, and d are the limits of integration. The resulting integral in y will then be solved using appropriate techniques.
Scenario 3.2: Integrating First with Respect to y, Then x
Similarly, if we integrate with respect to y first, treating x as a constant (as shown in Case 2), we get:
∫<sub>c</sub><sup>d</sup> [ (1/x)e^(xy) ]<sub>y=a</sub><sup>y=b</sup> dx
This again leads to a single integral that needs to be solved using appropriate methods. The choice of integration order is strategic and often depends on the complexity of the resultant integrals.
Example: Consider the double integral of e^(xy) over the rectangle R = {(x, y) | 0 ≤ x ≤ 1, 0 ≤ y ≤ 1}.
If we integrate with respect to x first:
∫₀¹ ∫₀¹ e^(xy) dx dy = ∫₀¹ [(1/y)e^(xy)]₀¹ dy = ∫₀¹ (e^y - 1)/y dy
This integral does not have a closed-form solution using elementary functions. We will need to resort to numerical methods or series expansion to approximate the value. This highlights a significant aspect of integrating e^(xy): the result isn't always expressible in terms of familiar functions.
Case 4: Transformations and Advanced Techniques
In more advanced scenarios, transformations like substitution or integration by parts might be required, particularly when e^(xy) appears as part of a more complex integrand.
Substitution:
Sometimes, a carefully chosen substitution can simplify the integral. This often requires recognizing patterns within the integrand and selecting a suitable substitution that eliminates the xy term or simplifies it to a more manageable form.
Integration by Parts:
If e^(xy) is part of a product within the integrand, integration by parts might be necessary. This technique involves selecting u and dv, and applying the formula: ∫u dv = uv - ∫v du
These advanced techniques often necessitate a deep understanding of calculus and require practice to master.
Case 5: Dealing with Infinite Limits
Integrating e^(xy) over infinite intervals requires careful consideration of convergence. Improper integrals with infinite limits demand the use of limits to assess whether the integral converges to a finite value or diverges.
Numerical Methods
Many integrals involving e^(xy) lack closed-form solutions. In these instances, numerical methods such as Simpson's rule, the trapezoidal rule, or more advanced techniques like Gaussian quadrature are used to approximate the value of the integral to a desired level of accuracy. Software packages like MATLAB, Mathematica, or Python's SciPy library provide powerful tools for implementing these numerical methods.
Applications Across Disciplines
The integral of e^(xy) finds its application in various fields:
- Physics: In areas like electromagnetism and quantum mechanics, solving differential equations often involves this integral.
- Engineering: This integral is fundamental in solving heat transfer problems, fluid dynamics, and other areas involving exponential behavior.
- Probability and Statistics: The integral appears in the context of bivariate exponential distributions and other probability models.
- Economics: Models of economic growth and decay can utilize this integral.
- Image Processing: In certain image processing tasks, transformations involving exponential functions might necessitate the evaluation of this integral.
Conclusion
The seemingly simple integral of e^(xy) presents a rich set of challenges and applications. Its solution heavily depends on the context, the treatment of variables (as constants or independent variables), and the presence of other functions within the integrand. Whether we're dealing with simple definite integrals, complex double integrals, or tackling problems with infinite limits, a solid understanding of integration techniques and sometimes the use of numerical approximation is crucial. Mastering this integral allows for a deeper engagement with mathematical modeling and problem-solving in numerous disciplines, highlighting its importance across various scientific and engineering fields. The journey from a seemingly straightforward exponential integral to the complex world of double integrals and numerical approximations underscores the continuous learning and adaptation required in mathematics and its applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Least Common Denominator Calculator With Variables
Mar 09, 2025
-
X 3 X 2 16x 16
Mar 09, 2025
-
How To Find Class Midpoints In Statistics
Mar 09, 2025
-
2 1 4 As An Improper Fraction
Mar 09, 2025
-
What Is 1 5th Of 15
Mar 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Integral Of E To The Xy . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
