Slope Of 3 On A Graph
Next Genwave
Mar 09, 2025 · 6 min read
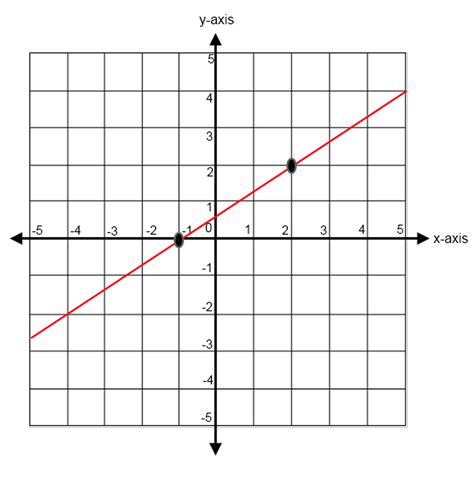
Table of Contents
Understanding the Slope of 3 on a Graph: A Comprehensive Guide
The concept of slope is fundamental to understanding linear relationships in mathematics and numerous real-world applications. In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve deep into the meaning and implications of a slope of 3 on a graph, exploring its visual representation, calculations, interpretations, and practical examples. We will also touch upon related concepts and how they connect to the core idea of a slope with a value of 3.
What Does a Slope of 3 Mean?
A slope of 3 on a graph signifies that for every 1 unit increase in the x-value (horizontal axis), the y-value (vertical axis) increases by 3 units. This represents a positive and relatively steep incline on the coordinate plane. The slope is a measure of the steepness and direction of a line. A larger positive slope indicates a steeper upward incline.
Key takeaway: The number 3 in the slope represents the rate of change. It quantifies how much the dependent variable (y) changes for a unit change in the independent variable (x).
Visualizing a Slope of 3
Imagine a line on a graph. If this line has a slope of 3, it means that if you move one unit to the right (along the x-axis), you'll move three units upward (along the y-axis) to reach another point on the same line. This consistent ratio of 3:1 (rise over run) defines the line's slope.
The steeper the line, the larger the slope. Conversely, a shallower line will have a smaller slope. A horizontal line has a slope of 0, while a vertical line has an undefined slope.
Calculating the Slope of 3
The slope (often denoted by 'm') of a line can be calculated using two points on the line (x1, y1) and (x2, y2) using the formula:
m = (y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1)
To obtain a slope of 3, the difference in y-values must be three times the difference in x-values. Let's illustrate this with examples:
-
Example 1: Points (1, 4) and (2, 7). m = (7 - 4) / (2 - 1) = 3/1 = 3
-
Example 2: Points (0, 0) and (1, 3). m = (3 - 0) / (1 - 0) = 3/1 = 3
-
Example 3: Points (-1, -1) and (0, 2). m = (2 - (-1)) / (0 - (-1)) = 3/1 = 3
In each of these examples, the calculated slope is 3, demonstrating how different sets of points can define the same line with a slope of 3.
Equation of a Line with a Slope of 3
The equation of a straight line can be written in the slope-intercept form:
y = mx + c
Where:
- 'm' is the slope
- 'c' is the y-intercept (the point where the line crosses the y-axis)
For a line with a slope of 3, the equation becomes:
y = 3x + c
The value of 'c' will depend on the specific line. For instance:
- y = 3x + 2: This line has a slope of 3 and intersects the y-axis at the point (0, 2).
- y = 3x - 5: This line also has a slope of 3 but intersects the y-axis at (0, -5).
Both lines are parallel because they share the same slope (3), indicating they will never intersect.
Real-World Applications of a Slope of 3
The concept of slope isn't confined to abstract mathematical exercises. It finds practical application in numerous real-world scenarios:
1. Physics and Engineering:
- Inclined Planes: A slope of 3 in physics could represent an inclined plane where for every 1 meter of horizontal distance, the vertical rise is 3 meters. This is crucial in calculating forces, work, and energy related to objects moving on the incline.
- Velocity and Acceleration: In analyzing motion, a slope of 3 on a velocity-time graph indicates a constant acceleration of 3 units (e.g., 3 m/s²).
2. Economics and Finance:
- Growth Rates: A slope of 3 in a graph showing economic growth over time signifies a consistent annual growth rate of 3 units (e.g., 3%).
- Stock Prices: While not always linear, a stock's price trend over a specific period might be approximated by a line with a positive slope, indicating price appreciation. A slope of 3 might suggest significant growth.
3. Everyday Life:
- Ramp Design: Architects and engineers use slope calculations extensively when designing ramps to ensure accessibility and safety. A slope of 3 might be too steep for wheelchair access, requiring a gentler incline.
- Road Gradient: The steepness of a road is described by its slope or gradient. A slope of 3 represents a very steep incline, usually found on mountainous roads.
Comparing Slopes: 3 vs. Other Values
Understanding the significance of a slope of 3 involves comparing it to slopes with other values:
- Slope of 0: A horizontal line, indicating no change in y for any change in x. This represents a constant value.
- Slope of 1: A line where the y-value increases by 1 unit for every 1 unit increase in x. This is a 45-degree angle on the coordinate plane.
- Slope of -3: A line with a negative slope, indicating a decrease in y-value by 3 units for every 1 unit increase in x. This shows a downward incline.
- Slope greater than 3: Represents a steeper incline compared to a slope of 3.
- Slope between 0 and 1: Represents a shallower incline compared to a slope of 3.
Advanced Concepts and Further Exploration
While this guide focuses on a slope of 3, several interconnected concepts deepen our understanding:
- Linear Equations: Mastering the slope-intercept form (y = mx + c) and the point-slope form (y - y1 = m(x - x1)) is crucial for handling various linear equation problems.
- Parallel and Perpendicular Lines: Lines with the same slope are parallel, while lines with slopes that are negative reciprocals of each other are perpendicular.
- Non-Linear Relationships: While this guide focuses on linear relationships, many real-world phenomena exhibit non-linear behavior, requiring more advanced mathematical techniques for analysis.
Conclusion
A slope of 3 on a graph represents a consistent rate of change, a positive and relatively steep upward incline. Understanding this fundamental concept allows us to interpret linear relationships effectively in various fields, from physics and engineering to economics and everyday life. By grasping the calculation, visualization, and real-world applications of slope, we can gain valuable insights into the quantitative relationships that govern our world. The ability to analyze and interpret slopes forms a crucial foundation for further explorations in mathematics, science, and other disciplines.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Solve P 144p Y For P
Mar 10, 2025
-
1 3 To The Power Of 3
Mar 10, 2025
-
Simplify The Square Root Of 10
Mar 10, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Slope Of 3 On A Graph . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
