Tan X Cos X Sin X
Next Genwave
Mar 07, 2025 · 6 min read
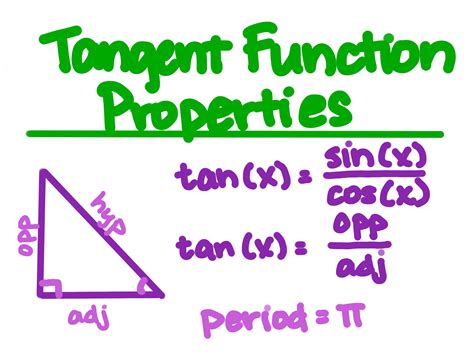
Table of Contents
Exploring the Trigonometric Identity: tan x cos x sin x
The seemingly simple expression tan x cos x sin x holds a wealth of mathematical richness, offering a fascinating journey into the world of trigonometry. This exploration will delve into its simplification, its graphical representation, its applications, and its connections to other trigonometric concepts. Understanding this expression unlocks a deeper appreciation of the interrelationships within trigonometry and enhances problem-solving capabilities.
Simplifying tan x cos x sin x
Our starting point is the fundamental trigonometric identities. Recall that the tangent function, tan x, is defined as the ratio of sine to cosine: tan x = sin x / cos x. Substituting this definition into our expression, we get:
tan x cos x sin x = (sin x / cos x) * cos x * sin x
Notice that cos x appears in both the numerator and the denominator. Assuming cos x ≠ 0 (to avoid division by zero), we can cancel these terms:
tan x cos x sin x = sin x * sin x = sin²x
Therefore, the expression tan x cos x sin x simplifies to sin²x. This simplification is crucial for various mathematical operations and applications, making it easier to analyze and manipulate within more complex equations.
The Significance of the Simplification
The simplification highlights the interconnectedness of trigonometric functions. It showcases how seemingly complex expressions can be reduced to simpler forms through the application of fundamental identities. This reduction simplifies calculations and often reveals underlying patterns and relationships that may not be immediately obvious. The simplified form, sin²x, is much easier to work with in calculus, differential equations, and other areas of mathematics and physics.
Graphical Representation and Analysis
Understanding the graphical representation of sin²x provides valuable insight into the behavior of the original expression. The graph of y = sin²x is a periodic function with a period of π. Unlike the sine function which oscillates between -1 and 1, sin²x oscillates between 0 and 1. This is because the square of any real number is always non-negative.
Key Features of the Graph:
- Period: The graph repeats itself every π units along the x-axis.
- Amplitude: The maximum value is 1, and the minimum value is 0.
- Symmetry: The graph is symmetric about the vertical lines x = nπ/2, where n is an integer.
- Zeros: The graph intersects the x-axis at x = nπ, where n is an integer.
- Maxima: The graph reaches its maximum value of 1 at x = (2n+1)π/2, where n is an integer.
By visualizing the graph, we can quickly determine the values of the expression for different values of x and understand its behavior over its entire domain. This visual representation aids in solving problems related to the expression and helps in understanding its periodic nature.
Applications of sin²x
The simplified expression, sin²x, finds numerous applications in various fields, including:
1. Physics:
- Wave phenomena:
sin²xplays a crucial role in describing the intensity of waves, such as light or sound waves. The square of the sine function represents the power or energy associated with the wave. - Oscillatory motion: Many physical systems exhibit oscillatory motion, such as a pendulum or a mass on a spring. The motion can often be described using trigonometric functions, with
sin²xrepresenting the displacement or energy of the system. - AC Circuits: In alternating current (AC) circuits,
sin²xdescribes the instantaneous power in the circuit.
2. Calculus:
- Integration and Differentiation: The simplicity of
sin²xmakes it relatively easy to integrate and differentiate. This is useful in solving various problems related to areas, volumes, and rates of change. For example, the integral ofsin²xcan be found using trigonometric identities or integration by parts. - Power Series Expansions:
sin²xcan be expressed as a power series, enabling approximation and numerical computations.
3. Computer Graphics and Animation:
- Modeling curves and surfaces: Trigonometric functions, including
sin²x, are extensively used in computer graphics to create smooth curves and surfaces. The function’s periodic and symmetrical nature makes it particularly useful for generating repeating patterns and textures.
Connection to Other Trigonometric Identities
sin²x is intrinsically linked to other fundamental trigonometric identities. Most notably:
-
Pythagorean Identity: The Pythagorean identity,
sin²x + cos²x = 1, is crucial in trigonometry. It provides a direct relationship betweensin²xandcos²x. We can expresscos²xas1 - sin²xorsin²xas1 - cos²x. This allows for substitutions and manipulations within complex equations. -
Double Angle Formulas: The double angle formula for cosine,
cos(2x) = 1 - 2sin²x, provides a direct link betweensin²xand the cosine of a double angle. This identity is frequently used in solving trigonometric equations and simplifying expressions. Conversely, we can expresssin²xas(1 - cos(2x))/2. This form is often preferred for integration, as it eliminates the square. -
Half Angle Formulas: Similarly, half-angle formulas provide relationships between
sin²xand trigonometric functions of half the angle (x/2).
Advanced Applications and Further Exploration
The seemingly simple expression tan x cos x sin x, and its simplified form sin²x, underpins many advanced mathematical concepts and applications.
1. Fourier Analysis:
Fourier analysis involves decomposing complex periodic functions into simpler sinusoidal components. sin²x, being a periodic function itself, plays a role in this decomposition. Its properties are crucial for understanding the frequency spectrum of complex signals in various fields such as signal processing and audio engineering.
2. Probability and Statistics:
In probability and statistics, the distribution of certain random variables can be modeled using trigonometric functions. sin²x can arise in the context of probability density functions.
3. Differential Equations:
Many differential equations, particularly those describing oscillatory systems, involve trigonometric functions. The function sin²x, and its derivatives, can be solutions to or components of solutions for these equations.
Conclusion
The exploration of tan x cos x sin x has revealed its surprisingly rich mathematical content. Its simplification to sin²x unlocks a deeper understanding of trigonometric identities and their interrelationships. The graphical representation aids in visualization and problem-solving. Furthermore, sin²x finds widespread applications in physics, calculus, computer graphics, and various other fields. Its connection to other trigonometric identities underscores its fundamental role in mathematics. This exploration should encourage a more profound appreciation for the elegance and power of trigonometry and its utility in various scientific and engineering disciplines. Further exploration into the advanced applications mentioned above will undoubtedly reveal even more fascinating aspects of this seemingly simple trigonometric expression.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 4 20 As A Percent
Mar 09, 2025
-
What Is A Half Of 150
Mar 09, 2025
-
What Percent Is 13 Out Of 15
Mar 09, 2025
-
What Percent Of 25 Is 14
Mar 09, 2025
-
Percentage Of 26 Out Of 30
Mar 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Tan X Cos X Sin X . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
