What Is 1 3 Minus 1 2
Next Genwave
Mar 09, 2025 · 5 min read
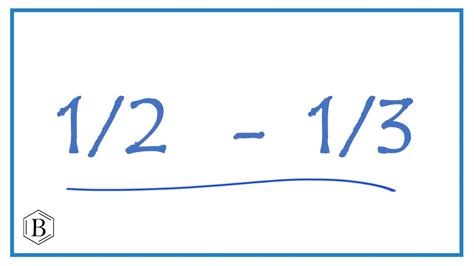
Table of Contents
What is 1/3 Minus 1/2? A Deep Dive into Fraction Subtraction
This seemingly simple question, "What is 1/3 minus 1/2?", opens a door to a fundamental concept in mathematics: fraction subtraction. While the arithmetic might appear straightforward, understanding the underlying principles is crucial for mastering more complex mathematical operations. This comprehensive guide will not only answer the question but also explore the intricacies of fraction subtraction, providing you with a solid foundation for future mathematical endeavors.
Understanding Fractions: The Building Blocks
Before tackling the subtraction, let's solidify our understanding of fractions. A fraction represents a part of a whole. It's composed of two key components:
- Numerator: The top number, indicating the number of parts we have.
- Denominator: The bottom number, indicating the total number of equal parts the whole is divided into.
For example, in the fraction 1/2, the numerator (1) represents one part, and the denominator (2) signifies that the whole is divided into two equal parts. Similarly, 1/3 represents one part out of a whole divided into three equal parts.
Finding a Common Denominator: The Key to Fraction Subtraction
The crucial step in subtracting (or adding) fractions is finding a common denominator. This is a number that is a multiple of both denominators. Without a common denominator, we cannot directly compare or combine the fractions. Think of it like trying to compare apples and oranges – you need a common unit of measurement.
In our problem, 1/3 - 1/2, the denominators are 3 and 2. To find the least common denominator (LCD), we need to find the smallest number that is divisible by both 3 and 2. This is achieved by finding the least common multiple (LCM) of 3 and 2.
Several methods exist to find the LCM:
- Listing Multiples: List the multiples of each number until you find a common one. Multiples of 3: 3, 6, 9, 12... Multiples of 2: 2, 4, 6, 8... The LCM is 6.
- Prime Factorization: Break down each number into its prime factors. 3 = 3 and 2 = 2. The LCM is the product of the highest powers of all prime factors present: 2 x 3 = 6.
Therefore, the least common denominator for 1/3 and 1/2 is 6.
Converting Fractions to Equivalent Fractions
Now that we have the common denominator (6), we need to convert both fractions, 1/3 and 1/2, into equivalent fractions with a denominator of 6. This means we need to find fractions that have the same value but a different representation. We achieve this by multiplying both the numerator and denominator of each fraction by the appropriate number.
-
For 1/3: To get a denominator of 6, we need to multiply the denominator (3) by 2. To maintain the value of the fraction, we must also multiply the numerator (1) by 2: (1 x 2) / (3 x 2) = 2/6
-
For 1/2: To get a denominator of 6, we need to multiply the denominator (2) by 3. Again, we must also multiply the numerator (1) by 3: (1 x 3) / (2 x 3) = 3/6
Performing the Subtraction
Now that both fractions have a common denominator, we can perform the subtraction:
2/6 - 3/6 = -1/6
Therefore, 1/3 minus 1/2 equals -1/6.
Simplifying the Result (if necessary)
In this case, the resulting fraction (-1/6) is already in its simplest form. A fraction is simplified when the greatest common divisor (GCD) of the numerator and denominator is 1. If the GCD were greater than 1, we would divide both the numerator and denominator by the GCD to simplify.
Visualizing Fraction Subtraction: A Geometric Approach
Understanding fractions can be significantly enhanced through visualization. Imagine a circle divided into six equal parts. 2/6 represents two of these six parts, while 3/6 represents three of them. Subtracting 3/6 from 2/6 means removing three parts from the two already present, resulting in a deficit of one part out of six, hence -1/6. This visual representation makes the abstract concept of negative fractions more concrete.
Applications of Fraction Subtraction in Real Life
Fraction subtraction isn't confined to textbooks; it finds practical applications in various real-world scenarios:
- Cooking and Baking: Adjusting recipes, measuring ingredients, and understanding portion sizes.
- Construction and Engineering: Calculating material quantities, measuring distances, and creating precise designs.
- Finance and Budgeting: Managing expenses, tracking savings, and calculating loan repayments.
- Data Analysis: Working with proportions and percentages, representing and interpreting data sets.
Beyond the Basics: Extending Fraction Subtraction
This foundational understanding empowers you to tackle more complex fraction subtraction problems:
-
Subtracting mixed numbers: Mixed numbers (e.g., 1 1/2) combine whole numbers and fractions. To subtract them, convert them into improper fractions (where the numerator is greater than or equal to the denominator) before applying the standard subtraction process. For example: 1 1/2 = 3/2
-
Subtracting fractions with different denominators: Always find the least common denominator before subtracting.
-
Subtracting multiple fractions: Apply the same principles of finding the least common denominator and then performing the subtraction sequentially.
Mastering Fraction Subtraction: Practice and Resources
Consistent practice is key to mastering fraction subtraction. Start with simple problems and gradually progress to more challenging ones. Numerous online resources, including interactive exercises and tutorials, can aid in your learning journey. Don't be afraid to explore different approaches and visualization techniques to find the method that suits your learning style best.
Conclusion: A Foundation for Future Mathematical Success
The seemingly simple question, "What is 1/3 minus 1/2?", has unveiled a world of mathematical concepts, from understanding fractions and finding common denominators to visualizing operations and applying them to real-world problems. Mastering fraction subtraction is not just about solving equations; it's about developing a fundamental understanding of mathematical principles that will serve you well in more advanced mathematical studies and numerous practical applications throughout your life. The journey of mathematical learning is continuous, and this exploration of fraction subtraction marks an essential milestone on that journey. Embrace the challenge, practice consistently, and watch your mathematical confidence and skills grow.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
13x 11y 12 In Slope Intercept Form
Mar 09, 2025
-
What Is 2 1 As A Decimal
Mar 09, 2025
-
Ax By C Solve For Y
Mar 09, 2025
-
Find The Direction Angle Of V For The Following Vector
Mar 09, 2025
-
How Many Yards Are In 24 Ft
Mar 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is 1 3 Minus 1 2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
