What Is Oxygen's Number Of Protons
Next Genwave
Mar 09, 2025 · 6 min read
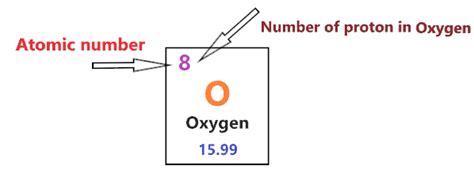
Table of Contents
What is Oxygen's Number of Protons? A Deep Dive into Atomic Structure and Isotopes
Oxygen, the life-giving element crucial for respiration in most living organisms, holds a fascinating place in the periodic table. Understanding its atomic structure, particularly its number of protons, is fundamental to grasping its chemical properties and behavior. This article delves deep into the question, "What is oxygen's number of protons?", exploring the concept of atomic number, isotopes, and the implications of oxygen's proton count in various scientific fields.
Understanding Atomic Number and Protons
Before we answer the central question, let's establish a clear understanding of atomic number and its relationship to protons. The atomic number of an element is defined as the number of protons found in the nucleus of a single atom of that element. This number is unique to each element and is what distinguishes it from all other elements. Protons, along with neutrons, reside in the atom's nucleus, forming its core. Protons carry a positive electrical charge, while neutrons are electrically neutral. Electrons, negatively charged particles, orbit the nucleus in shells or energy levels.
The Significance of Atomic Number
The atomic number is a cornerstone of chemistry and physics. It dictates an element's position on the periodic table, influencing its chemical properties and reactivity. Elements with similar atomic numbers often share similar chemical behaviors due to the arrangement of their electrons, determined by the number of protons in their nucleus. This principle underpins the organization and predictability of the periodic table, a crucial tool for understanding chemical reactions and the behavior of matter.
Oxygen's Atomic Number: The Definitive Answer
Now, let's directly address the main question: What is oxygen's number of protons? The answer is eight. Oxygen's atomic number is 8, which means every oxygen atom contains eight protons in its nucleus. This fundamental fact is crucial for understanding oxygen's chemical behavior and its role in countless biological and industrial processes.
Isotopes: Variations in Neutron Count
While the number of protons defines an element, the number of neutrons can vary. Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes. Oxygen has several naturally occurring isotopes, each with the same number of protons (eight) but a varying number of neutrons.
Common Oxygen Isotopes:
- Oxygen-16 (¹⁶O): This is the most abundant isotope of oxygen, comprising about 99.76% of naturally occurring oxygen. It has eight protons and eight neutrons.
- Oxygen-17 (¹⁷O): This isotope has eight protons and nine neutrons, making up a small fraction of naturally occurring oxygen.
- Oxygen-18 (¹⁸O): This isotope, with eight protons and ten neutrons, is also present in smaller amounts in nature.
The different isotopes of oxygen have slightly different masses due to the variation in neutron count. However, their chemical properties remain largely consistent because the number of protons and electrons, which determine chemical reactivity, remains the same.
The Role of Oxygen's Eight Protons in Chemical Bonding
Oxygen's eight protons significantly influence its chemical behavior. The electron configuration resulting from these eight protons leads to oxygen's high electronegativity. Electronegativity is the tendency of an atom to attract electrons towards itself in a chemical bond. Oxygen's high electronegativity makes it highly reactive and capable of forming strong bonds with other atoms.
Formation of Covalent Bonds:
Oxygen frequently forms covalent bonds, sharing electrons with other atoms to achieve a stable electron configuration. This is prominently seen in water (H₂O), where oxygen shares electrons with two hydrogen atoms. The strong covalent bonds in water contribute to its unique properties, crucial for life as we know it.
Oxidation and Reduction Reactions:
Oxygen's role in oxidation-reduction (redox) reactions is vital in many biological and industrial processes. Oxygen's high electronegativity allows it to readily accept electrons from other atoms, oxidizing them and reducing itself in the process. This electron transfer is fundamental to respiration, combustion, and many other chemical reactions.
Oxygen in Biological Systems: Respiration and Metabolism
Oxygen's eight protons and its consequent chemical properties are central to life itself. Cellular respiration, the process by which living organisms convert energy from food, relies heavily on oxygen as the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain. This process generates the energy needed for various cellular functions, highlighting the fundamental role of oxygen in sustaining life.
Oxygen's Impact on Human Health:
The presence and availability of oxygen are crucial for human health. Oxygen deprivation, or hypoxia, can lead to serious health complications and even death. Conversely, exposure to excessive amounts of oxygen, especially under high pressure, can also have harmful effects. Understanding oxygen's chemical properties, driven by its eight protons, is essential for understanding its impact on health and developing effective medical interventions.
Oxygen in Industrial Applications: Combustion and Beyond
Oxygen's reactivity, dictated by its eight protons, has widespread industrial applications. Combustion, the rapid chemical combination of a substance with oxygen, producing heat and light, is a crucial process in many industries. The burning of fossil fuels, for instance, relies on oxygen for energy generation. The understanding of oxygen's behavior in combustion processes is essential for designing efficient and safe energy systems.
Oxygen in Welding and Cutting:
Oxygen's high reactivity is also utilized in welding and cutting processes. The use of oxygen-fuel mixtures enables high temperatures, essential for melting and joining metals. Understanding oxygen's properties, especially those determined by its eight protons, is crucial in optimizing these industrial processes.
Oxygen's Isotopic Ratios and Scientific Applications
The different isotopes of oxygen, particularly ¹⁶O, ¹⁷O, and ¹⁸O, have found significant applications in various scientific fields. Their relative abundances can provide insights into various environmental and geological processes.
Paleoclimatology and Ice Core Analysis:
The ratios of oxygen isotopes in ice cores provide valuable information about past climates. The relative abundance of ¹⁸O compared to ¹⁶O reflects temperature variations over time, offering critical insights into past climate change.
Hydrology and Water Tracing:
Isotopic ratios of oxygen are also used to trace water movement and sources. The differing isotopic compositions of water from different sources allow researchers to track water flow patterns and understand hydrological processes.
Conclusion: The Importance of Oxygen's Eight Protons
Oxygen's eight protons are the foundation of its unique chemical properties. This atomic number defines its position in the periodic table, dictates its reactivity, and influences its role in countless natural and industrial processes. From sustaining life through respiration to enabling industrial processes like combustion, oxygen's influence is pervasive and essential. Understanding the significance of oxygen's eight protons underscores the importance of basic atomic structure in comprehending the world around us. The continued study of oxygen, its isotopes, and its interactions with other elements remains crucial for advancing scientific understanding and technological development in various fields, from medicine to environmental science and beyond. The seemingly simple fact that oxygen has eight protons unlocks a world of complexity and importance, highlighting the fundamental role of atomic structure in shaping our universe.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Write 37 50 As A Decimal Number
Mar 09, 2025
-
3 Times 3 Times 3 Times 3
Mar 09, 2025
-
3x 2y 8 Slope Intercept Form
Mar 09, 2025
-
Perfect Square Root Pair Factors Of 405
Mar 09, 2025
-
Whats The Square Root Of 30
Mar 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is Oxygen's Number Of Protons . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
