What Is The Cube Root Of 1
Next Genwave
Mar 09, 2025 · 5 min read
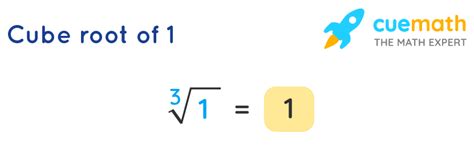
Table of Contents
What is the Cube Root of 1? A Deep Dive into the Fundamentals of Cube Roots and Complex Numbers
The seemingly simple question, "What is the cube root of 1?" opens a fascinating door into the world of mathematics, revealing intricacies far beyond the immediate answer. While the most obvious answer is 1 (since 1 x 1 x 1 = 1), a deeper exploration reveals a richer mathematical landscape involving complex numbers and their geometric representation. This article delves into the concept of cube roots, explores the different methods to calculate them, particularly focusing on the cube root of 1, and finally showcases the elegant connection between algebra and geometry.
Understanding Cube Roots
Before tackling the cube root of 1, let's establish a foundational understanding of cube roots in general. The cube root of a number, 'x', is a value, 'y', such that y³ = x. In simpler terms, it's the number that, when multiplied by itself three times, equals the original number. For example, the cube root of 8 is 2 because 2 x 2 x 2 = 8.
This concept is easily extended to negative numbers. The cube root of -8 is -2 because (-2) x (-2) x (-2) = -8. Unlike square roots, where the root of a negative number is imaginary, cube roots can handle negative inputs and yield real number outputs.
Finding the Cube Root of 1: The Obvious and the Unexpected
As mentioned earlier, the most immediate and intuitive cube root of 1 is 1. This is because 1³ = 1. However, the story doesn't end there. The fundamental theorem of algebra states that a polynomial of degree 'n' has exactly 'n' roots (solutions) in the complex number system. Since the equation x³ - 1 = 0 is a polynomial of degree 3, it must have three roots.
This means that there are two more cube roots of 1 besides the obvious one. To find them, we need to delve into the realm of complex numbers.
Complex Numbers: Expanding Mathematical Horizons
Complex numbers are numbers that can be expressed in the form a + bi, where 'a' and 'b' are real numbers, and 'i' is the imaginary unit, defined as the square root of -1 (i² = -1). The 'a' part is called the real part, and the 'bi' part is called the imaginary part.
Complex numbers are essential for solving equations that don't have real number solutions, like finding the other cube roots of 1.
Finding the Other Cube Roots of 1 Using De Moivre's Theorem
A powerful tool for finding the roots of complex numbers is De Moivre's Theorem. This theorem states that for any complex number in polar form, r(cos θ + i sin θ), its nth root can be expressed as:
√ⁿ[r(cos θ + i sin θ)] = ⁿ√r [cos((θ + 2kπ)/n) + i sin((θ + 2kπ)/n)]
where k = 0, 1, 2, ..., n-1.
Let's apply this to find the cube roots of 1. First, we express 1 in polar form:
1 = 1(cos 0 + i sin 0)
Now, we use De Moivre's Theorem with n = 3:
-
k = 0: ³√1 [cos(0/3) + i sin(0/3)] = 1(cos 0 + i sin 0) = 1 (This is our familiar root)
-
k = 1: ³√1 [cos(2π/3) + i sin(2π/3)] = cos(120°) + i sin(120°) = -1/2 + i√3/2
-
k = 2: ³√1 [cos(4π/3) + i sin(4π/3)] = cos(240°) + i sin(240°) = -1/2 - i√3/2
Therefore, the three cube roots of 1 are:
- 1
- -1/2 + i√3/2
- -1/2 - i√3/2
Geometric Interpretation: Roots of Unity on the Complex Plane
The beauty of complex numbers lies in their geometric representation on the complex plane (also known as the Argand plane). The three cube roots of 1 form an equilateral triangle inscribed in a unit circle centered at the origin. This geometric interpretation beautifully connects algebra and geometry, showcasing the elegance of complex numbers.
The vertices of this equilateral triangle represent the three roots: 1, -1/2 + i√3/2, and -1/2 - i√3/2. This geometric pattern extends to higher-order roots of unity, forming regular polygons inscribed in the unit circle.
Applications of Cube Roots and Complex Numbers
The concept of cube roots and complex numbers extends far beyond theoretical mathematics. They have profound applications in various fields, including:
-
Engineering: In electrical engineering, complex numbers are used to analyze alternating current circuits, where the cube root of unity plays a role in understanding three-phase power systems.
-
Physics: Quantum mechanics heavily relies on complex numbers to describe wave functions and the behavior of subatomic particles.
-
Signal Processing: Complex numbers are crucial in digital signal processing, particularly in Fourier analysis, which decomposes signals into their constituent frequencies.
-
Computer Graphics: Complex numbers find applications in computer graphics for transformations, rotations, and generating fractal patterns.
Solving Cubic Equations: The Connection to Cube Roots
The cube root of 1 is also crucial in solving cubic equations. Cubic equations are polynomial equations of degree 3, and their solution often involves the cube root of complex numbers. Solving a cubic equation involves reducing it to a simpler form, which might necessitate finding the cube roots of complex quantities. Understanding the cube root of 1 provides a fundamental building block for tackling such problems.
Conclusion: Beyond the Simple Answer
The question, "What is the cube root of 1?" initially appears straightforward. However, a comprehensive exploration unveils the rich mathematical landscape encompassing complex numbers, De Moivre's Theorem, and the elegant geometric representation of roots of unity on the complex plane. These concepts have far-reaching implications in numerous scientific and engineering disciplines, underscoring the importance of understanding the seemingly simple yet profoundly complex world of cube roots. The journey from the simple answer of 1 to the discovery of two additional complex roots highlights the beauty and depth of mathematical exploration. The connections between algebra and geometry, revealed through the visualization of roots on the complex plane, showcase the interconnectedness and elegance of mathematical concepts. This exploration goes beyond a simple calculation; it unveils a fundamental concept that underpins advanced mathematical theories and their practical applications in various fields.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
5 5 6 As An Improper Fraction
Mar 09, 2025
-
X 4 16x 2 X 2 18
Mar 09, 2025
-
What Is 3 1 2 In Decimal Form
Mar 09, 2025
-
What Percent Is 3 Of 15
Mar 09, 2025
-
24 Feet Equals How Many Yards
Mar 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Cube Root Of 1 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
