What Is The Factorization Of 49
Next Genwave
Mar 09, 2025 · 5 min read
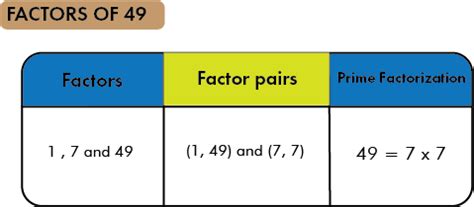
Table of Contents
What is the Factorization of 49? A Deep Dive into Prime Numbers and Beyond
The seemingly simple question, "What is the factorization of 49?" opens the door to a fascinating exploration of number theory, prime numbers, and the fundamental building blocks of mathematics. While the answer itself is straightforward, understanding the why behind the answer reveals a rich tapestry of mathematical concepts. This article will not only answer the question directly but also delve into the broader context of prime factorization, its applications, and its significance in mathematics.
The Prime Factorization of 49: A Quick Answer
The prime factorization of 49 is 7 x 7, or 7².
This means that 49 can be expressed as the product of only two prime numbers: 7 and 7. A prime number is a whole number greater than 1 that has only two divisors: 1 and itself. Since 7 is only divisible by 1 and 7, it's a prime number.
Understanding Prime Factorization
Prime factorization, also known as prime decomposition, is the process of finding the prime numbers that, when multiplied together, result in a given number. Every whole number greater than 1 can be uniquely expressed as a product of prime numbers. This unique representation is known as the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic. This theorem forms a cornerstone of number theory and has far-reaching implications in various fields.
Why is Prime Factorization Important?
Prime factorization is crucial for several reasons:
-
Foundation of Number Theory: It provides a fundamental building block for understanding the properties and relationships between numbers. Many advanced mathematical concepts rely on the principles of prime factorization.
-
Cryptography: Prime factorization is at the heart of many modern encryption methods, including RSA cryptography, which is widely used to secure online transactions and communications. The difficulty of factoring large numbers into their prime components is what makes these encryption methods secure.
-
Simplifying Calculations: Prime factorization can simplify complex calculations. For example, finding the greatest common divisor (GCD) or the least common multiple (LCM) of two numbers is much easier when you know their prime factorizations.
-
Solving Diophantine Equations: Prime factorization plays a crucial role in solving Diophantine equations, which are algebraic equations where only integer solutions are sought.
Methods for Finding Prime Factorization
Several methods can be used to find the prime factorization of a number. Let's explore some common approaches, illustrating them with examples besides 49:
1. Factor Tree Method
The factor tree method is a visual approach that breaks down a number into its factors until all factors are prime numbers.
Let's find the prime factorization of 120 using a factor tree:
120
/ \
2 60
/ \
2 30
/ \
2 15
/ \
3 5
Therefore, the prime factorization of 120 is 2 x 2 x 2 x 3 x 5, or 2³ x 3 x 5.
2. Division Method
The division method involves repeatedly dividing the number by the smallest prime number possible until the result is 1.
Let's find the prime factorization of 36 using the division method:
36 ÷ 2 = 18
18 ÷ 2 = 9
9 ÷ 3 = 3
3 ÷ 3 = 1
Therefore, the prime factorization of 36 is 2 x 2 x 3 x 3, or 2² x 3².
3. Trial Division
Trial division is a straightforward method, especially effective for smaller numbers. You systematically try dividing the number by prime numbers, starting with the smallest prime number, 2. If the division results in a whole number, you continue with the quotient. If not, you move on to the next prime number.
Let's find the prime factorization of 70 using trial division:
- 70 ÷ 2 = 35
- 35 ÷ 5 = 7
- 7 is a prime number.
Therefore, the prime factorization of 70 is 2 x 5 x 7.
The Uniqueness of Prime Factorization: The Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic
The Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic states that every integer greater than 1 can be represented uniquely as a product of prime numbers, disregarding the order of the factors. This uniqueness is critical. It means that no matter which method you use to find the prime factorization of a number, you will always arrive at the same result (up to the order of the factors). This seemingly simple statement has profound implications for the structure of numbers and is a cornerstone of many advanced mathematical theories.
Beyond the Basics: Applications of Prime Factorization
The applications of prime factorization extend far beyond simple number theory. Here are some noteworthy examples:
-
Cryptography: As mentioned earlier, RSA cryptography relies heavily on the difficulty of factoring large numbers into their prime components. The security of online transactions and data communication depends on this computational challenge. Breaking RSA encryption requires factoring extremely large numbers, a task currently considered computationally infeasible for sufficiently large numbers.
-
Coding Theory: Prime numbers are crucial in designing error-correcting codes used in data transmission and storage. These codes help to ensure that data remains accurate even when it's transmitted over noisy channels or stored in unreliable media.
-
Computer Science: Prime factorization algorithms are used in various aspects of computer science, such as hash functions, random number generators, and database indexing.
-
Number Theory Research: The search for larger prime numbers and the study of their distribution is a continuing area of research in number theory. The discovery of Mersenne primes, which are prime numbers of the form 2<sup>p</sup> - 1, often leads to breakthroughs in computational mathematics.
Conclusion: The Significance of 49 and its Factorization
While the prime factorization of 49 (7 x 7) might appear simple at first glance, it serves as a gateway to a deeper understanding of fundamental mathematical concepts. The principle of prime factorization, its uniqueness as stated by the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic, and its far-reaching applications across various fields highlight its significance. The seemingly simple question of factoring 49 unveils a world of mathematical richness, showcasing the beauty and power of number theory and its influence on our technological world. Understanding prime factorization is not just about calculating; it's about grasping the underlying structure and elegance of numbers themselves. From basic arithmetic to advanced cryptography, the concept remains a cornerstone of mathematical understanding and technological advancement.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
16 To The Power Of 3 4
Mar 10, 2025
-
What Percent Of 60 Is 57
Mar 10, 2025
-
How Many Yards Are In 36 Feet
Mar 10, 2025
-
13 Out Of 25 Is What Percent
Mar 10, 2025
-
0 25 Rounded To The Nearest Hundredth
Mar 10, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Factorization Of 49 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
