What Is The Slope For Y 5
Next Genwave
Mar 10, 2025 · 5 min read
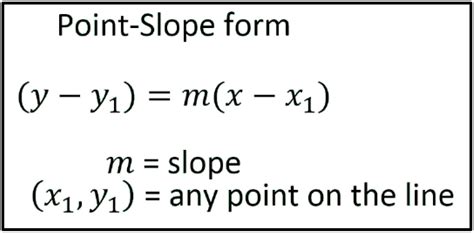
Table of Contents
Decoding the Slope: Understanding the Concept in the Context of y = 5
The question "What is the slope for y = 5?" might seem deceptively simple at first glance. However, understanding the answer requires a solid grasp of the fundamental concept of slope and its representation in different forms of linear equations. This article delves deep into this seemingly basic question, exploring the concept of slope, its various interpretations, and how it applies specifically to the equation y = 5. We'll also explore related concepts and provide practical examples to solidify your understanding.
What is Slope?
In mathematics, particularly in algebra and calculus, the slope (often denoted by m) of a line is a measure of its steepness. It represents the rate at which the y-value changes with respect to the x-value. More formally, it's the ratio of the vertical change (rise) to the horizontal change (run) between any two distinct points on the line.
The slope can be positive, negative, zero, or undefined, each indicating a different characteristic of the line:
-
Positive Slope: The line rises from left to right. The larger the positive slope, the steeper the incline.
-
Negative Slope: The line falls from left to right. The magnitude of the negative slope indicates the steepness of the decline.
-
Zero Slope: The line is horizontal. There is no vertical change for any horizontal change.
-
Undefined Slope: The line is vertical. The horizontal change is zero, resulting in an undefined ratio.
Calculating Slope: Different Methods
There are several ways to calculate the slope of a line, depending on the information available:
-
Using Two Points: If you have the coordinates of two points (x₁, y₁) and (x₂, y₂), the slope is calculated using the formula:
m = (y₂ - y₁) / (x₂ - x₁) -
Using the Equation of a Line: The equation of a line is often expressed in the slope-intercept form:
y = mx + bwhere m is the slope and b is the y-intercept (the point where the line crosses the y-axis). In this form, the slope is directly apparent as the coefficient of x.
-
Using the Graph of a Line: You can visually determine the slope from a graph by selecting two points on the line and calculating the rise over run.
The Case of y = 5: Understanding the Horizontal Line
The equation y = 5 represents a horizontal line. This line passes through all points with a y-coordinate of 5, regardless of the x-coordinate. For instance, points (1, 5), (0, 5), (-2, 5), and (100, 5) all lie on this line.
To understand the slope, let's consider two points on this line: (1, 5) and (3, 5). Applying the slope formula:
m = (5 - 5) / (3 - 1) = 0 / 2 = 0
The slope is 0. This confirms our intuitive understanding that a horizontal line has a slope of zero. There is no change in the y-value (rise = 0) as the x-value changes (run > 0).
Visualizing y = 5 and its Slope
Imagine plotting the equation y = 5 on a Cartesian coordinate system. You will see a perfectly straight line parallel to the x-axis and passing through the point (0, 5). The line extends infinitely in both the positive and negative x-directions, always maintaining a y-value of 5. This visual representation immediately indicates a horizontal line, which, as established above, has a slope of 0.
Comparing y = 5 with Other Linear Equations
Let's contrast y = 5 with other linear equations to highlight the significance of its zero slope:
-
y = 2x + 1: This equation represents a line with a slope of 2 (positive, indicating an upward incline) and a y-intercept of 1.
-
y = -x + 3: This line has a slope of -1 (negative, indicating a downward incline) and a y-intercept of 3.
-
x = 4: This equation represents a vertical line with an undefined slope. A vertical line has an infinite slope because the run (change in x) is zero, resulting in division by zero.
The equation y = 5 stands out because its slope is zero, distinguishing it from lines with positive, negative, or undefined slopes.
Applications of Zero Slope in Real-World Scenarios
The concept of zero slope isn't just a theoretical mathematical idea; it has practical applications in various real-world scenarios:
-
Horizontal Ground Level: In surveying or construction, a perfectly level ground surface can be represented by a line with a zero slope.
-
Constant Temperature: Imagine monitoring the temperature of a room over a period of time. If the temperature remains constant, the graph of temperature versus time will be a horizontal line with a zero slope.
-
Constant Speed at a Fixed Altitude: An airplane maintaining a constant altitude and speed during a flight segment can be represented by a horizontal line on a graph showing altitude versus time. The slope of zero indicates no change in altitude.
Advanced Concepts and Further Exploration
While the equation y = 5 and its zero slope seem straightforward, it's crucial to consider its relationship with broader mathematical concepts:
-
Calculus: In calculus, the slope is related to the derivative of a function. The derivative of a constant function (like y = 5) is always zero, reflecting the zero slope of the horizontal line.
-
Linear Algebra: In linear algebra, the concept of slope extends to higher dimensions, where the slope is represented by vectors or matrices.
-
Data Analysis: In data analysis, a zero slope in a regression line indicates no linear relationship between two variables.
Conclusion: The Significance of the Zero Slope in y = 5
The seemingly simple question of the slope for y = 5 leads to a deeper understanding of the fundamental concept of slope in linear equations. A zero slope for y = 5 signifies a horizontal line, indicating no change in the y-value as the x-value varies. This concept extends beyond theoretical mathematics, finding practical applications in various fields such as surveying, engineering, and data analysis. The exploration of y = 5 provides a solid foundation for understanding more complex linear equations and their slopes. Further investigation into calculus, linear algebra, and data analysis will deepen this understanding. Remember, mastering the basics is crucial to tackling more advanced mathematical concepts.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
21 Is What Percent Of 25
Mar 10, 2025
-
5 4x 7 4x 2 X
Mar 10, 2025
-
0 05 Rounded To The Nearest Tenth
Mar 10, 2025
-
What Is The Square Root Of 576
Mar 10, 2025
-
5x 2y 8 In Slope Intercept Form
Mar 10, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Slope For Y 5 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
