What's The Square Root Of 128
Next Genwave
Mar 06, 2025 · 4 min read
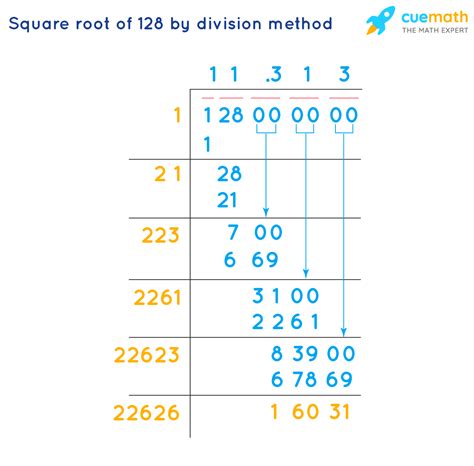
Table of Contents
What's the Square Root of 128? A Deep Dive into Square Roots and Simplification
Finding the square root of 128 might seem like a simple mathematical problem, but it offers a fantastic opportunity to explore fundamental concepts in algebra and number theory. This article will not only provide the answer but will delve into the process of simplifying square roots, exploring various methods and providing a solid understanding of the underlying principles. We'll also look at practical applications and further extend our knowledge beyond the simple calculation.
Understanding Square Roots
Before we tackle the square root of 128, let's establish a clear understanding of what a square root actually is. The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself (squared), gives the original number. For example, the square root of 9 is 3 because 3 x 3 = 9. This is often represented mathematically as √9 = 3.
Perfect Squares and Non-Perfect Squares
Some numbers have whole number square roots. These are known as perfect squares. Examples include 4 (√4 = 2), 25 (√25 = 5), and 100 (√100 = 10). However, many numbers, like 128, do not have whole number square roots. These are called non-perfect squares. Finding the square root of a non-perfect square often involves simplifying the root to its most concise form.
Calculating the Square Root of 128
The square root of 128 (√128) is not a whole number. To find its value, we can use a calculator, which will give you an approximate decimal value of 11.3137. However, this is not the most mathematically elegant solution. Simplifying the square root provides a more precise and informative answer.
Simplifying √128
Simplifying a square root involves finding the largest perfect square that is a factor of the number under the square root sign (the radicand). Let's break down 128 into its prime factors:
128 = 2 x 64 = 2 x 8 x 8 = 2 x 2³ x 2³ = 2⁸
Therefore, we can rewrite √128 as √(2⁸). Since √(a²) = a, we can simplify this further:
√(2⁸) = √(2⁴ x 2⁴) = √(2⁴) x √(2⁴) = 2⁴ = 16.
However there is another more common method that is used more often:
-
Find the Prime Factorization: As shown above, the prime factorization of 128 is 2⁸.
-
Identify Perfect Squares: We look for pairs of identical factors. We have eight 2's, so we can pair them up: (2 x 2) x (2 x 2) x (2 x 2) x (2 x 2). Each pair represents a perfect square (2² = 4).
-
Simplify: We can rewrite √128 as √(2² x 2² x 2² x 2²) = √(2²) x √(2²) x √(2²) x √(2²) = 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 = 16. Therefore √128 simplifies to 8√2.
So, the simplified form of √128 is 8√2. This is a more precise and informative representation than the decimal approximation.
Practical Applications of Square Roots
Square roots are not just abstract mathematical concepts; they have widespread applications in various fields:
Geometry
-
Calculating distances: The Pythagorean theorem, a cornerstone of geometry, uses square roots to determine distances in right-angled triangles. This is crucial in surveying, construction, and navigation.
-
Area and Volume: Finding the area of a square or the volume of a cube directly involves square roots if you know the area or volume and want to find the side length.
Physics
-
Velocity and acceleration: Many physics formulas involve square roots, particularly those relating to velocity, acceleration, and energy.
-
Electricity: Calculating impedance in electrical circuits often requires working with square roots.
Engineering
-
Structural design: Engineers use square roots in calculations related to stress, strain, and stability of structures.
-
Fluid dynamics: Square roots appear in equations dealing with fluid flow and pressure.
Extending Our Understanding: Higher Roots
The concept of square roots can be extended to higher roots, such as cube roots (∛), fourth roots (∜), and so on. An nth root of a number x is a value that, when raised to the power of n, equals x. For example, the cube root of 8 (∛8) is 2 because 2³ = 8. The methods for simplifying higher roots are similar to those used for square roots, involving prime factorization and identifying sets of identical factors.
Conclusion
Finding the square root of 128 is more than just a simple calculation; it's a gateway to a deeper understanding of number theory and its applications in various fields. Through simplifying the square root, we arrive at the precise and informative answer of 8√2. This exploration also highlights the importance of understanding perfect squares, prime factorization, and the broader concept of roots in mathematics. The practical applications of square roots, from geometry to engineering, underscore their relevance beyond the classroom, making them essential tools for problem-solving in numerous disciplines. Mastering the simplification of square roots is a valuable skill for anyone pursuing advanced studies in mathematics or related fields. Remember, the key to success lies in breaking down complex problems into smaller, manageable steps, as demonstrated in the simplification process of √128.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Factor X 3 X 2 X 1
Mar 06, 2025
-
What Is 1 3 Of 2
Mar 06, 2025
-
1 3 To The Power Of 2
Mar 06, 2025
-
What Is 6 8 As A Percent
Mar 06, 2025
-
6 Out Of 15 As A Percentage
Mar 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What's The Square Root Of 128 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
