What's The Square Root Of 28
Next Genwave
Mar 10, 2025 · 5 min read
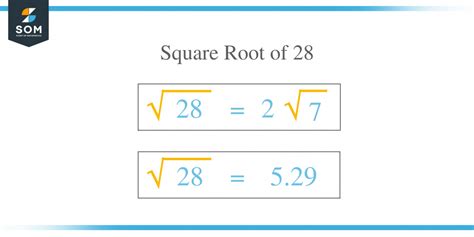
Table of Contents
What's the Square Root of 28? A Deep Dive into Square Roots and Approximation Techniques
The seemingly simple question, "What's the square root of 28?" opens a door to a fascinating exploration of mathematical concepts, approximation techniques, and the power of numerical methods. While a calculator readily provides a decimal approximation, understanding the underlying principles offers a far richer understanding of mathematics. This article will delve into the calculation of the square root of 28, exploring both exact and approximate solutions, and examining the broader context of square roots within mathematics.
Understanding Square Roots
Before tackling the square root of 28 specifically, let's establish a fundamental understanding of what a square root represents. The square root of a number, denoted as √x, is a value that, when multiplied by itself (squared), equals the original number, x. In simpler terms, it's the inverse operation of squaring a number. For example:
- √9 = 3 because 3 x 3 = 9
- √16 = 4 because 4 x 4 = 16
However, not all numbers have perfect square roots – integers that result in whole numbers when squared. Numbers like 28 fall into this category. They have irrational square roots, meaning their decimal representation goes on forever without repeating.
Calculating the Square Root of 28: The Exact Value
The exact value of √28 cannot be expressed as a simple fraction or a terminating decimal. It's an irrational number. However, we can simplify it using the properties of square roots:
√28 = √(4 x 7) = √4 x √7 = 2√7
This simplified form, 2√7, represents the exact square root of 28. It expresses the square root in terms of the square root of a prime number (7), which cannot be further simplified.
Approximating the Square Root of 28: Various Methods
Since the exact value is irrational, we often rely on approximations. Several methods can provide increasingly accurate approximations:
1. Using a Calculator: The Easiest Approach
The most straightforward method is to use a calculator. Simply input √28, and you'll get a decimal approximation, typically around 5.2915. While this is convenient, it doesn't provide insight into the underlying mathematical process.
2. The Babylonian Method (or Heron's Method): An Iterative Approach
The Babylonian method is an ancient and efficient iterative algorithm for approximating square roots. It involves repeatedly refining an initial guess until the desired accuracy is achieved. The formula is:
x<sub>n+1</sub> = ½ (x<sub>n</sub> + a/x<sub>n</sub>)
Where:
- x<sub>n</sub> is the current approximation
- x<sub>n+1</sub> is the next approximation
- a is the number whose square root is being calculated (28 in our case)
Let's demonstrate with an initial guess of 5:
- x<sub>1</sub> = 5
- x<sub>2</sub> = ½ (5 + 28/5) = 5.3
- x<sub>3</sub> = ½ (5.3 + 28/5.3) ≈ 5.2915
With each iteration, the approximation gets closer to the actual value. This method converges rapidly, offering a good approximation with relatively few iterations.
3. Linear Interpolation: A Simpler Approximation
Linear interpolation uses the known square roots of nearby perfect squares to estimate the square root of 28. Since 28 lies between 25 (√25 = 5) and 36 (√36 = 6), we can linearly interpolate:
- The difference between 36 and 25 is 11.
- The difference between 28 and 25 is 3.
- The fraction representing the position of 28 between 25 and 36 is 3/11.
Therefore, an approximation is: 5 + (3/11) x (6-5) ≈ 5.27
This method is less accurate than the Babylonian method but provides a quick, rough estimate.
4. Using the Taylor Series Expansion: A More Advanced Approach
For a higher level of accuracy and a deeper mathematical understanding, the Taylor Series expansion can be employed. This involves representing the square root function as an infinite sum of terms. While complex, it offers remarkable accuracy with a sufficient number of terms. This method requires a strong background in calculus.
The Significance of Irrational Numbers and Square Roots
The fact that the square root of 28 is irrational highlights the richness and complexity of the number system. Irrational numbers, like √28, cannot be expressed as a simple fraction, underscoring the limitations of rational numbers in representing all mathematical quantities. This discovery has significant implications across various fields:
- Geometry: Irrational numbers frequently appear in geometrical calculations, particularly concerning distances and areas of shapes. The Pythagorean theorem, for instance, often leads to irrational solutions.
- Physics: Many physical phenomena are modeled using equations that involve irrational numbers.
- Engineering: Precision engineering and design frequently require calculations with high degrees of accuracy, necessitating the use of approximations for irrational numbers.
- Computer Science: Representing and computing with irrational numbers presents challenges in computer science, requiring the use of floating-point arithmetic and approximation techniques.
Conclusion: Beyond the Calculation
The seemingly simple task of finding the square root of 28 leads us down a path of exploring various mathematical concepts and techniques. While a calculator readily provides an approximate decimal value, understanding the exact form (2√7) and the different methods of approximation provides a far more profound comprehension of the underlying mathematical principles. The journey also highlights the significance of irrational numbers and their prevalence across numerous scientific and engineering disciplines. The ability to both calculate and understand the nature of these numbers is essential for anyone seeking a deep appreciation of mathematics. Further exploration into numerical analysis and advanced mathematical methods would reveal even more sophisticated techniques for approximating irrational numbers to any desired degree of accuracy.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
W 3 3 8 1 5 6
Mar 10, 2025
-
21 Is What Percent Of 25
Mar 10, 2025
-
5 4x 7 4x 2 X
Mar 10, 2025
-
0 05 Rounded To The Nearest Tenth
Mar 10, 2025
-
What Is The Square Root Of 576
Mar 10, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What's The Square Root Of 28 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
