X 2 Y 2 9 Graph
Next Genwave
Mar 09, 2025 · 5 min read
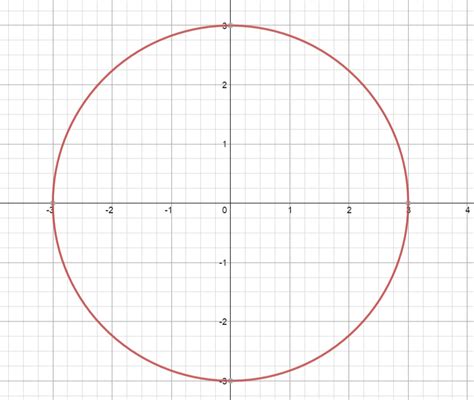
Table of Contents
Decoding the x² + y² = 9 Graph: A Comprehensive Guide
The equation x² + y² = 9 represents a fundamental concept in mathematics: the circle. Understanding its graphical representation, properties, and applications is crucial for anyone studying algebra, geometry, or calculus. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of the x² + y² = 9 graph, exploring its characteristics, transformations, and real-world applications. We’ll also touch upon related concepts to provide a holistic understanding.
Understanding the Equation: x² + y² = 9
The equation x² + y² = 9 is a specific instance of the general equation of a circle: (x - h)² + (y - k)² = r², where (h, k) represents the center of the circle and r represents its radius. In our case, x² + y² = 9, we can rewrite it as (x - 0)² + (y - 0)² = 3², revealing that:
- Center: The center of the circle is at the origin (0, 0).
- Radius: The radius of the circle is 3 units.
This simple equation elegantly describes a circle with a fixed radius centered at the heart of the Cartesian coordinate system.
Graphing the x² + y² = 9 Circle
Plotting this circle is straightforward. Starting at the origin (0,0), we measure 3 units along the positive x-axis, negative x-axis, positive y-axis, and negative y-axis to find four points on the circle: (3, 0), (-3, 0), (0, 3), and (0, -3). These points represent the intersections of the circle with the x and y axes. To complete the circle, we can either use a compass or plot more points by solving the equation for y:
y = ±√(9 - x²)
This equation gives us two values of y for each value of x within the range -3 ≤ x ≤ 3. Plotting these points and connecting them smoothly will yield a perfect circle.
Key Features to Highlight on the Graph:
- Center (0,0): Clearly mark the origin as the center of the circle.
- Radius (3): Indicate the radius by drawing a line segment from the center to any point on the circle.
- x-intercepts (3, 0) and (-3, 0): Mark these points where the circle intersects the x-axis.
- y-intercepts (0, 3) and (0, -3): Mark these points where the circle intersects the y-axis.
- Smooth Curve: Ensure the circle is drawn smoothly and evenly, representing a continuous curve.
Transformations of the Circle Equation
Understanding how changes to the equation affect the graph is crucial. Let's explore some common transformations:
1. Shifting the Center:
Adding or subtracting values within the parentheses changes the center of the circle. For example:
- (x - 2)² + (y + 1)² = 9: This shifts the center to (2, -1), moving the circle two units to the right and one unit down. The radius remains 3.
- (x + 4)² + (y - 3)² = 9: This shifts the center to (-4, 3), moving the circle four units to the left and three units up. The radius is still 3.
2. Changing the Radius:
Changing the number on the right-hand side of the equation changes the radius. For example:
- x² + y² = 16: This represents a circle with a center at (0,0) and a radius of 4 (√16 = 4).
- x² + y² = 4: This represents a circle with a center at (0,0) and a radius of 2 (√4 = 2).
3. Combining Transformations:
We can combine shifts and radius changes. For example:
- (x + 1)² + (y - 2)² = 25: This represents a circle with a center at (-1, 2) and a radius of 5 (√25 = 5).
Applications of the Circle Equation
The seemingly simple equation x² + y² = 9 and its variations have broad applications across various fields:
1. Geometry and Trigonometry:
The circle is a fundamental geometric shape, and its equation provides a precise mathematical description. It's used extensively in trigonometry, particularly in understanding angles, arcs, and sectors.
2. Physics and Engineering:
Circular motion is prevalent in physics and engineering. The equation is used to model circular orbits (planets around stars, satellites around Earth), the rotation of machinery parts, and the path of projectiles.
3. Computer Graphics and Game Development:
Circles are used extensively in computer graphics and game development to represent objects, create visual effects, and model collisions. The equation facilitates efficient calculations for drawing circles and determining if points lie within a circular area.
4. Navigation and Surveying:
The circle is used in navigation systems and surveying to model locations and distances. For example, GPS technology uses circles to represent the area where a satellite's signal is received.
5. Data Analysis and Statistics:
In statistics, the circle can be used to represent data distributions, particularly when dealing with circular or periodic data.
Exploring Related Concepts
Understanding the x² + y² = 9 graph requires familiarity with related mathematical concepts:
- The Distance Formula: The equation of a circle is directly derived from the distance formula, which calculates the distance between two points in a Cartesian plane.
- Pythagorean Theorem: The Pythagorean theorem forms the basis for the distance formula and hence the circle equation.
- Coordinate Geometry: Graphing the circle requires a strong understanding of the Cartesian coordinate system and how to plot points based on their x and y coordinates.
- Trigonometric Functions: Trigonometric functions (sine, cosine, tangent) are intimately related to circles and can be used to describe points on the circle's circumference.
Advanced Topics and Extensions
For those seeking a deeper understanding, we can explore advanced topics:
- Parametric Equations of a Circle: Representing the circle using parametric equations (x = rcos(t), y = rsin(t)) provides a different perspective and is useful in animations and simulations.
- Polar Coordinates: Describing the circle in polar coordinates (r = constant) simplifies the equation and offers a more intuitive approach for certain applications.
- Three-Dimensional Extensions: The concept of a circle extends to three dimensions, where we have spheres, described by equations like (x - h)² + (y - k)² + (z - l)² = r².
Conclusion: Mastering the x² + y² = 9 Graph
The seemingly simple equation x² + y² = 9 represents a fundamental geometric object—the circle—with far-reaching applications. By understanding its properties, transformations, and related concepts, we gain a powerful tool for modeling numerous phenomena in mathematics, science, and technology. This comprehensive guide has explored the equation’s intricacies, enabling readers to confidently graph, analyze, and apply this crucial mathematical concept. Remember that practice is key to mastering this and any mathematical concept. By working through various examples and exploring different transformations, you can solidify your understanding and unlock the full potential of the x² + y² = 9 graph.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How To Find Limit When H Is 0
Mar 10, 2025
-
1 1 7 As An Improper Fraction
Mar 10, 2025
-
Write 21 50 As A Decimal Number
Mar 10, 2025
-
8 48 Rounded To The Nearest Tenth
Mar 10, 2025
-
3 125 Rounded To The Nearest Tenth
Mar 10, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about X 2 Y 2 9 Graph . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
