X 3 2x 2 5x 10
Next Genwave
Mar 09, 2025 · 5 min read
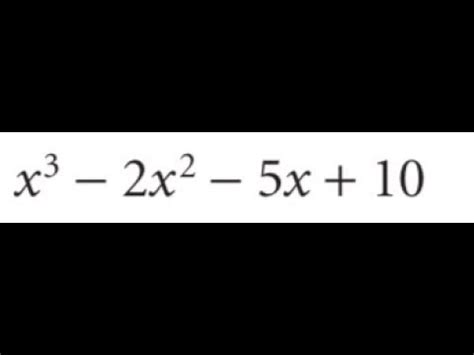
Table of Contents
Deconstructing and Exploring the Mathematical Expression: x³ + 2x² + 5x + 10
This article delves deep into the mathematical expression x³ + 2x² + 5x + 10, exploring its various facets, from basic algebraic manipulation to advanced techniques like factoring and finding roots. We will uncover its inherent properties, discuss methods to solve related equations, and touch upon its applications in different fields. Our goal is to provide a comprehensive understanding of this seemingly simple expression, revealing its rich mathematical complexity.
Understanding the Components: A Polynomial Overview
The expression x³ + 2x² + 5x + 10 is a polynomial – a mathematical expression involving a sum of powers in one or more variables multiplied by coefficients. Specifically, it's a cubic polynomial because the highest power of the variable x is 3. Let's break down its components:
- x³: This term represents x raised to the power of 3 (x * x * x). It's the cubic term.
- 2x²: This term is the quadratic term, representing 2 multiplied by x squared (2 * x * x).
- 5x: This is the linear term, simply 5 multiplied by x.
- 10: This is the constant term, an independent value not multiplied by any power of x.
Understanding these individual components is crucial for manipulating and solving equations involving this polynomial.
Factoring the Polynomial: Unveiling Hidden Structures
Factoring a polynomial involves expressing it as a product of simpler polynomials. This process can reveal hidden relationships and make solving equations significantly easier. For our expression, x³ + 2x² + 5x + 10, we can employ the factoring by grouping method:
- Group terms: We group the terms into pairs: (x³ + 2x²) + (5x + 10).
- Factor out common terms: From the first group, we can factor out x²: x²(x + 2). From the second group, we can factor out 5: 5(x + 2).
- Combine: Notice that both terms now share a common factor (x + 2). We can factor this out: (x + 2)(x² + 5).
Therefore, the factored form of x³ + 2x² + 5x + 10 is (x + 2)(x² + 5). This factored form reveals a significant structural insight into the polynomial.
Solving the Equation: Finding the Roots
Finding the roots (or zeros) of a polynomial means finding the values of x that make the polynomial equal to zero. In other words, we solve the equation:
x³ + 2x² + 5x + 10 = 0
Using the factored form, this equation becomes:
(x + 2)(x² + 5) = 0
This equation is satisfied if either (x + 2) = 0 or (x² + 5) = 0.
-
Solving (x + 2) = 0: This gives us x = -2 as one root.
-
Solving (x² + 5) = 0: This gives us x² = -5. Taking the square root of both sides, we get x = ±√(-5). Since the square root of a negative number involves imaginary numbers, the roots are x = ±i√5, where i is the imaginary unit (√-1).
Therefore, the roots of the polynomial x³ + 2x² + 5x + 10 are -2, i√5, and -i√5. These roots represent the x-intercepts of the graph of the polynomial function.
Graphical Representation: Visualizing the Polynomial
Visualizing the polynomial as a graph helps to understand its behavior and relationships between its roots. The graph of a cubic polynomial typically has either one or three real roots, and it can have various shapes depending on its coefficients. In this case, the graph would intersect the x-axis at x = -2, and the imaginary roots would not be visible on a standard Cartesian plane representing real numbers. The graph would show a curve that passes through (-2,0) and exhibits other features dictated by the polynomial’s behavior.
Applications in Various Fields
Polynomial equations, particularly cubic polynomials, have wide-ranging applications in various fields:
-
Engineering: Cubic polynomials are used in modelling various physical phenomena, such as the trajectory of projectiles, the deflection of beams under load, and the flow of fluids.
-
Physics: They find applications in solving problems related to kinematics, dynamics, and electromagnetism.
-
Computer Science: Cubic splines, which are piecewise cubic polynomials, are utilized in computer graphics for smooth curve interpolation and surface modelling.
-
Economics: Cubic polynomials can be used to model cost functions, production functions, and demand curves.
-
Chemistry: They can be used to model reaction rates and equilibrium concentrations.
Advanced Techniques: Numerical Methods
For more complex polynomials where factoring isn't straightforward, numerical methods are employed to approximate the roots. These methods, used extensively in computer programs, include:
- Newton-Raphson Method: An iterative method that refines an initial guess to find a root.
- Bisection Method: A method that repeatedly bisects an interval containing a root until the desired accuracy is achieved.
- Secant Method: A method that uses the slope of a secant line to approximate the root.
These numerical methods are essential for solving polynomial equations that lack easy analytical solutions.
Extending the Exploration: Related Concepts
The exploration of x³ + 2x² + 5x + 10 opens doors to several related mathematical concepts:
- Polynomial Division: Dividing this polynomial by a linear factor (like x+2) can reveal the quotient and remainder, providing further insights into its structure.
- Partial Fraction Decomposition: This technique, used in calculus, is relevant when dealing with rational functions (ratios of polynomials).
- Derivatives and Integrals: Calculus allows for finding the rate of change (derivative) and the area under the curve (integral) of the polynomial function, revealing further properties.
Conclusion: A Deeper Appreciation
This in-depth exploration of the cubic polynomial x³ + 2x² + 5x + 10 reveals a surprisingly rich mathematical landscape. From basic algebraic manipulation to advanced techniques like factoring, finding roots, and graphical representation, we've uncovered its inherent structure and diverse applications. Understanding this seemingly simple expression provides a strong foundation for tackling more complex mathematical problems and appreciating the power of polynomials in diverse scientific and engineering disciplines. The journey through this exploration highlights the beauty and utility of mathematics in explaining and modelling the world around us. The seemingly simple equation has much more depth and complexity than initially apparent, showcasing the fascinating world of polynomial algebra.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
45 Is What Percent Of 72
Mar 09, 2025
-
5 5 6 As An Improper Fraction
Mar 09, 2025
-
X 4 16x 2 X 2 18
Mar 09, 2025
-
What Is 3 1 2 In Decimal Form
Mar 09, 2025
-
What Percent Is 3 Of 15
Mar 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about X 3 2x 2 5x 10 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
