1 7/8 As An Improper Fraction
Next Genwave
Mar 09, 2025 · 5 min read
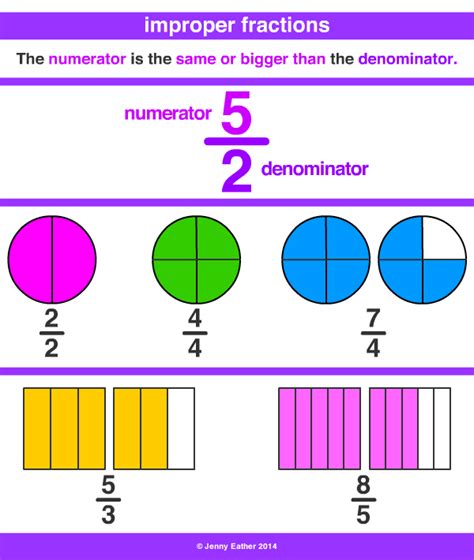
Table of Contents
1 7/8 as an Improper Fraction: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding fractions is a fundamental skill in mathematics, crucial for various applications from everyday calculations to complex scientific problems. This article delves deep into the conversion of mixed numbers, like 1 7/8, into improper fractions. We'll explore the process, its applications, and provide numerous examples to solidify your understanding. We'll also touch upon the importance of this conversion in higher-level math and practical situations.
What is a Mixed Number?
A mixed number combines a whole number and a proper fraction. A proper fraction has a numerator (top number) smaller than the denominator (bottom number). For example, 1 7/8 is a mixed number: 1 represents the whole number, and 7/8 is the proper fraction.
What is an Improper Fraction?
An improper fraction has a numerator that is greater than or equal to its denominator. For instance, 15/8 is an improper fraction because the numerator (15) is larger than the denominator (8). Improper fractions represent values greater than or equal to one.
Converting 1 7/8 to an Improper Fraction: The Step-by-Step Process
The conversion of a mixed number to an improper fraction involves a simple two-step process:
Step 1: Multiply the whole number by the denominator.
In our example, 1 7/8, we multiply the whole number (1) by the denominator (8): 1 * 8 = 8
Step 2: Add the result to the numerator.
Now, add the result from Step 1 (8) to the numerator (7): 8 + 7 = 15
Step 3: Keep the denominator the same.
The denominator remains unchanged. Therefore, the improper fraction equivalent of 1 7/8 is 15/8.
Let's visualize this: imagine a pizza cut into 8 slices. 1 7/8 pizzas means you have one whole pizza (8 slices) and 7 more slices from another pizza. In total, you have 15 slices (15/8).
Why is this Conversion Important?
Converting mixed numbers to improper fractions is crucial for several reasons:
-
Simplification of Calculations: Many mathematical operations, especially multiplication and division of fractions, are significantly easier to perform with improper fractions. Trying to multiply mixed numbers directly can be cumbersome and error-prone.
-
Algebra and Higher-Level Math: In algebra and calculus, working with improper fractions is often necessary for simplifying expressions and solving equations. Mixed numbers are less frequently used in these contexts.
-
Real-World Applications: Consider scenarios involving measurements or quantities. If a recipe calls for 1 7/8 cups of flour, expressing this as 15/8 simplifies calculations if you need to double or halve the recipe.
-
Consistent Representation: Using improper fractions ensures consistency in mathematical representations, avoiding ambiguity that might arise with mixed numbers.
More Examples of Mixed Number to Improper Fraction Conversions
Let's practice with a few more examples:
-
2 3/4:
- Step 1: 2 * 4 = 8
- Step 2: 8 + 3 = 11
- Result: 11/4
-
3 1/2:
- Step 1: 3 * 2 = 6
- Step 2: 6 + 1 = 7
- Result: 7/2
-
5 2/3:
- Step 1: 5 * 3 = 15
- Step 2: 15 + 2 = 17
- Result: 17/3
-
10 1/6:
- Step 1: 10 * 6 = 60
- Step 2: 60 + 1 = 61
- Result: 61/6
Converting Improper Fractions Back to Mixed Numbers
It's equally important to understand the reverse process: converting an improper fraction back to a mixed number. This involves dividing the numerator by the denominator.
For example, to convert 15/8 back to a mixed number:
-
Divide the numerator (15) by the denominator (8): 15 ÷ 8 = 1 with a remainder of 7.
-
The quotient (1) becomes the whole number.
-
The remainder (7) becomes the numerator of the proper fraction.
-
The denominator remains the same (8).
Therefore, 15/8 = 1 7/8.
Practical Applications in Everyday Life
The conversion between mixed numbers and improper fractions isn't just a theoretical exercise. It finds practical applications in various aspects of daily life:
-
Cooking and Baking: Recipes often use mixed numbers for ingredient quantities. Converting to improper fractions simplifies calculations when adjusting recipe sizes.
-
Construction and Engineering: Precise measurements are critical in these fields. Improper fractions provide a more accurate representation for calculations involving fractions of inches or centimeters.
-
Sewing and Tailoring: Accurate fabric measurements are essential. Using improper fractions allows for precise calculations when dealing with fractional measurements.
-
Finance and Budgeting: Calculating portions of budgets or shares often involves fractions. Improper fractions offer a more streamlined approach to these calculations.
Advanced Concepts and Further Exploration
While the basic conversion process is straightforward, understanding its application within broader mathematical concepts is beneficial:
-
Adding and Subtracting Fractions: Converting mixed numbers to improper fractions facilitates easier addition and subtraction of fractions with different denominators.
-
Multiplying and Dividing Fractions: Improper fractions simplify these operations significantly, often leading to cleaner and more easily manageable results.
-
Solving Equations: In algebra and beyond, working with improper fractions streamlines the process of solving equations that involve fractions.
Conclusion
Converting 1 7/8 (and other mixed numbers) to its improper fraction equivalent (15/8) is a fundamental skill with widespread applications across various fields. Mastering this conversion not only strengthens your foundational understanding of fractions but also equips you with essential tools for tackling more advanced mathematical concepts and practical real-world problems. Remember the simple two-step process – multiply, then add – and practice regularly to solidify your understanding. The ability to seamlessly switch between mixed numbers and improper fractions is a valuable asset in your mathematical toolkit.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Percent Is 32 Of 40
Mar 09, 2025
-
3x Y 4 In Slope Intercept Form
Mar 09, 2025
-
X 4y 8 In Slope Intercept Form
Mar 09, 2025
-
How Many Electrons Does Bromine Have
Mar 09, 2025
-
5 Km Equals How Many Meters
Mar 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 1 7/8 As An Improper Fraction . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
