2 1 2 As An Improper Fraction
Next Genwave
Mar 09, 2025 · 5 min read
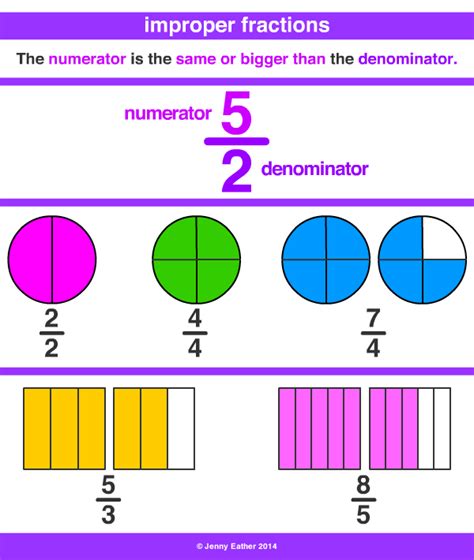
Table of Contents
2 1/2 as an Improper Fraction: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding fractions is a cornerstone of mathematical literacy. Whether you're a student tackling fractions for the first time or a seasoned professional needing a refresher, mastering the conversion between mixed numbers and improper fractions is crucial. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of converting the mixed number 2 1/2 into an improper fraction, exploring the underlying concepts and providing practical examples to solidify your understanding. We'll also examine why this conversion is important and how it applies to various mathematical scenarios.
Understanding Mixed Numbers and Improper Fractions
Before we dive into the conversion, let's clarify the terms:
-
Mixed Number: A mixed number combines a whole number and a fraction. For instance, 2 1/2 is a mixed number; it represents two whole units and one-half of another unit.
-
Improper Fraction: An improper fraction has a numerator (the top number) that is greater than or equal to its denominator (the bottom number). For example, 5/2 is an improper fraction because the numerator (5) is larger than the denominator (2). Improper fractions represent a value greater than or equal to one.
The ability to seamlessly convert between mixed numbers and improper fractions is essential for performing various mathematical operations, such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division of fractions.
Converting 2 1/2 to an Improper Fraction: Step-by-Step
The conversion process is straightforward and involves two simple steps:
Step 1: Multiply the whole number by the denominator.
In our example, the whole number is 2, and the denominator of the fraction is 2. Therefore, we multiply 2 x 2 = 4.
Step 2: Add the result to the numerator.
The numerator of our fraction is 1. We add the result from Step 1 (4) to the numerator (1): 4 + 1 = 5.
Step 3: Keep the denominator the same.
The denominator remains unchanged. In this case, the denominator is 2.
Therefore, 2 1/2 as an improper fraction is 5/2.
Visual Representation of the Conversion
To further solidify your understanding, let's visualize this conversion. Imagine you have two whole pizzas and half a pizza. Each pizza is divided into two equal slices. You have two whole pizzas, which equates to four slices (2 pizzas x 2 slices/pizza = 4 slices), plus the additional half-slice. In total, you have five slices (4 + 1 = 5) out of a possible two slices per pizza, thus giving you 5/2.
Why is this Conversion Important?
The conversion of mixed numbers to improper fractions is vital for various mathematical reasons:
-
Simplifying Calculations: Adding, subtracting, multiplying, and dividing fractions is significantly easier when all fractions are in the same format – either all mixed numbers or all improper fractions. Improper fractions are often preferred for multiplication and division of fractions.
-
Solving Equations: Many algebraic equations involve fractions. Converting mixed numbers to improper fractions ensures consistency and allows for easier manipulation of the equation.
-
Real-world Applications: Fractions are used extensively in various real-world applications, such as cooking, construction, engineering, and finance. The ability to convert between mixed numbers and improper fractions is crucial for accurately representing and manipulating quantities in these fields.
Practical Examples
Let's explore some practical examples to reinforce the conversion process:
Example 1: Converting 3 2/5 to an improper fraction:
- Multiply the whole number by the denominator: 3 x 5 = 15
- Add the result to the numerator: 15 + 2 = 17
- Keep the denominator the same: 5
Therefore, 3 2/5 as an improper fraction is 17/5.
Example 2: Converting 1 1/4 to an improper fraction:
- Multiply the whole number by the denominator: 1 x 4 = 4
- Add the result to the numerator: 4 + 1 = 5
- Keep the denominator the same: 4
Therefore, 1 1/4 as an improper fraction is 5/4.
Example 3: A Real-World Scenario
Imagine you're baking a cake and the recipe calls for 2 1/4 cups of flour. To accurately measure the flour using a measuring cup that is divided into quarters, it is more practical to work with the improper fraction equivalent, which is 9/4. This allows for easier understanding of how many quarter cups of flour you need.
Converting Improper Fractions back to Mixed Numbers
While converting mixed numbers to improper fractions is essential, you'll also need to perform the reverse conversion. The process is as follows:
- Divide the numerator by the denominator. This gives you the whole number part of the mixed number.
- The remainder becomes the numerator of the fraction.
- The denominator remains the same.
Let's use 5/2 as an example:
- Divide 5 by 2: 5 ÷ 2 = 2 with a remainder of 1.
- The remainder (1) becomes the numerator.
- The denominator remains 2.
Therefore, 5/2 as a mixed number is 2 1/2.
Advanced Applications: Operations with Improper Fractions
Once you're comfortable converting between mixed numbers and improper fractions, you can tackle more complex mathematical operations. Let's examine addition, subtraction, multiplication and division with improper fractions:
Addition and Subtraction: When adding or subtracting fractions, ensure they share a common denominator. If they don't, find the least common multiple (LCM) and adjust the fractions accordingly.
Multiplication: Multiply the numerators together and the denominators together. Simplify the resulting fraction if necessary.
Division: Invert the second fraction (reciprocal) and multiply.
Conclusion: Mastering Fractions for Success
Understanding the conversion between mixed numbers and improper fractions is a fundamental skill in mathematics. This guide has provided a comprehensive overview of the process, emphasizing the importance of this conversion and providing practical examples to solidify your understanding. Remember that mastering this concept will enhance your ability to solve various mathematical problems and tackle real-world applications effectively. By consistently practicing the techniques outlined above, you'll build confidence and proficiency in handling fractions with ease. This knowledge will serve as a strong foundation for more advanced mathematical concepts.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
X 3 2x 2 5x 10
Mar 09, 2025
-
Write 37 50 As A Decimal Number
Mar 09, 2025
-
3 Times 3 Times 3 Times 3
Mar 09, 2025
-
3x 2y 8 Slope Intercept Form
Mar 09, 2025
-
Perfect Square Root Pair Factors Of 405
Mar 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 2 1 2 As An Improper Fraction . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
