4.5 Divided By Sin 42 Degrees
Next Genwave
Mar 07, 2025 · 5 min read
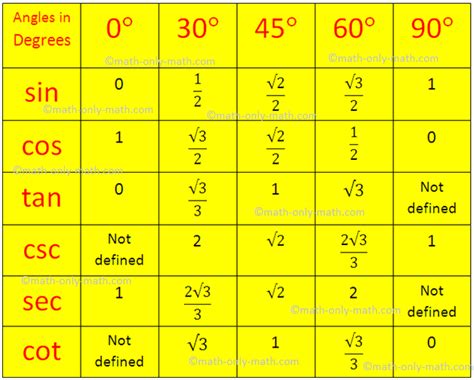
Table of Contents
4.5 Divided by Sin 42 Degrees: A Deep Dive into Trigonometry and its Applications
This article explores the trigonometric calculation of 4.5 divided by the sine of 42 degrees (4.5/sin 42°), delving into the underlying mathematical principles, practical applications, and potential pitfalls. We'll examine the solution, discuss the significance of trigonometric functions, and explore real-world scenarios where this type of calculation is crucial.
Understanding the Calculation: 4.5 / sin 42°
The expression 4.5 / sin 42° is a straightforward trigonometric calculation. It involves dividing a constant value (4.5) by the sine of a specific angle (42 degrees). To solve this, you need a calculator capable of handling trigonometric functions. Most scientific calculators and even many standard calculators have this functionality.
The Steps:
-
Ensure your calculator is in degree mode: This is crucial. If your calculator is in radian mode, the result will be significantly different and incorrect.
-
Find the sine of 42 degrees: Input "sin 42" into your calculator. You should get a value approximately equal to 0.6691.
-
Perform the division: Divide 4.5 by the value obtained in step 2 (4.5 / 0.6691).
-
The Result: The result of 4.5 / sin 42° is approximately 6.725.
The Significance of Sine in Trigonometry
The sine function (sin) is one of the fundamental trigonometric functions. It's defined within the context of a right-angled triangle as the ratio of the length of the side opposite a particular angle to the length of the hypotenuse (the longest side).
Key Properties of Sine:
-
Range: The sine of an angle always falls within the range of -1 to +1. This means that -1 ≤ sin(θ) ≤ 1, where θ represents the angle.
-
Periodicity: The sine function is periodic, meaning its values repeat in a cyclical pattern. The period of the sine function is 2π radians (or 360 degrees).
-
Relationship to other trigonometric functions: Sine is intrinsically linked to cosine and tangent functions through various trigonometric identities. For example, sin²θ + cos²θ = 1.
-
Applications: Sine, cosine and tangent functions are fundamental in many fields, including:
- Navigation: Calculating distances and bearings.
- Physics: Modeling wave phenomena (sound, light, etc.), projectile motion, and oscillatory systems.
- Engineering: Structural analysis, surveying, and design of mechanical systems.
- Computer Graphics: Creating realistic images and animations.
- Astronomy: Calculating celestial positions and distances.
Real-World Applications of 4.5 / sin 42° Type Calculations
While the specific calculation 4.5 / sin 42° might not appear frequently in its exact form in real-world problems, the underlying principle – dividing a known quantity by the sine of an angle – is common in various scenarios. Let's explore some examples:
1. Finding the Hypotenuse of a Right-Angled Triangle:
Imagine a right-angled triangle where you know the length of one side (opposite to a given angle) and the angle itself. Let's say the length of the opposite side is 4.5 units, and the angle is 42 degrees. To find the length of the hypotenuse (h), you'd use the sine function:
sin(42°) = opposite / hypotenuse
Rearranging the formula:
hypotenuse = opposite / sin(42°) = 4.5 / sin(42°) ≈ 6.725 units
2. Solving Problems in Physics (Projectile Motion):
In projectile motion, the sine function is crucial for calculating vertical components of velocity and displacement. For instance, if a projectile is launched with an initial velocity of 4.5 m/s at an angle of 42 degrees above the horizontal, the vertical component of the initial velocity (v<sub>y</sub>) would be:
v<sub>y</sub> = initial velocity * sin(42°) = 4.5 * sin(42°) ≈ 3.01 m/s
Calculating the total initial velocity from the vertical component would involve a similar calculation to our example, using a known vertical component and the angle:
initial velocity = v<sub>y</sub> / sin(42°)
3. Determining Heights and Distances in Surveying:
Surveyors often use trigonometric functions to measure heights and distances indirectly. If a surveyor knows the distance to an object and the angle of elevation, they can calculate the height of the object using the sine function. This involves a calculation similar to finding the hypotenuse of a right-angled triangle.
4. Applications in Engineering:
In engineering, especially in structural and mechanical engineering, this type of calculation is applied extensively in force calculations and stress analysis. This often involves decomposing forces into their components, using the sine function to calculate the vertical component of force.
Potential Pitfalls and Considerations
While the calculation itself is relatively straightforward, there are a few potential pitfalls to be aware of:
-
Units: Ensure consistency in units. If you're working with angles in degrees, your calculator must be in degree mode. Using radians instead will lead to an incorrect result.
-
Significant Figures: Pay attention to the number of significant figures used in your calculations. The accuracy of the final answer depends on the accuracy of the input values.
-
Rounding Errors: Rounding intermediate results can introduce errors. It's best to retain as many decimal places as possible throughout the calculation and only round the final answer.
-
Inverse Sine Function (arcsin): Don't confuse the sine function with its inverse, arcsin or sin<sup>-1</sup>. The inverse sine gives you the angle corresponding to a given sine value. The calculation 4.5 / sin 42° uses the sine function directly, not its inverse.
Conclusion: The Broader Context of Trigonometric Calculations
The seemingly simple calculation of 4.5 / sin 42° offers a window into the power and versatility of trigonometry. While the specific numbers may vary, the underlying principles of working with trigonometric functions – like sine, cosine, and tangent – are essential for solving a vast range of problems in numerous fields. Understanding these principles, along with careful attention to detail and potential pitfalls, is key to accurate and effective application of trigonometry in any context. The ability to perform calculations like this one is a fundamental skill for anyone working with mathematics, physics, engineering, or any field involving geometric relationships. This calculation exemplifies the practical and powerful application of trigonometry in solving real-world problems.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Fraction Is Equals To 9 16
Mar 09, 2025
-
Graph The Line 3x Y 3
Mar 09, 2025
-
81 To The Power Of 1 2
Mar 09, 2025
-
1 7 8 As An Improper Fraction
Mar 09, 2025
-
4x 4 35x 2 9 0
Mar 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 4.5 Divided By Sin 42 Degrees . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
