4x To The Power Of 2
Next Genwave
Mar 06, 2025 · 6 min read
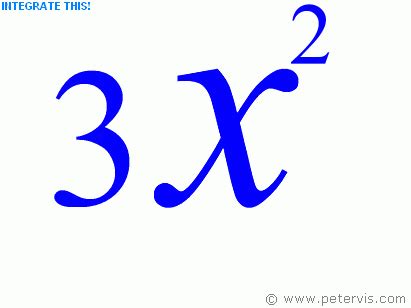
Table of Contents
4x to the Power of 2: A Comprehensive Exploration
The seemingly simple expression "4x to the power of 2" (often written as (4x)² or 4x²) opens doors to a wide array of mathematical concepts and applications. This article will delve into a comprehensive exploration of this expression, covering its simplification, its role in various mathematical contexts, and its practical applications in different fields.
Understanding the Fundamentals: Order of Operations
Before we embark on a deeper analysis, it's crucial to understand the fundamental principles of order of operations, often remembered by the acronym PEMDAS/BODMAS (Parentheses/Brackets, Exponents/Orders, Multiplication and Division, Addition and Subtraction). This dictates the sequence in which mathematical operations should be performed. In the case of 4x², the exponent (power of 2) takes precedence over multiplication.
This means that we first square the expression within the parentheses (or, equivalently, apply the exponent to the term) before performing any multiplications. Therefore, (4x)² is not the same as 4 * x². This is a common mistake to avoid.
Simplifying 4x²
The simplification of 4x² involves applying the exponent to both the coefficient (4) and the variable (x). Here's the breakdown:
(4x)² = 4² * x² = 16x²
Therefore, 4x to the power of 2 simplifies to 16x². This is a crucial step in many algebraic manipulations and problem-solving scenarios.
Applications in Algebra
The expression 4x² frequently appears in various algebraic contexts, including:
Quadratic Equations
Quadratic equations are equations of the form ax² + bx + c = 0, where a, b, and c are constants and a ≠ 0. The term 4x² can be a component of such equations, requiring its proper manipulation during the process of solving for x (finding the roots of the equation). Methods such as factoring, completing the square, or using the quadratic formula are often employed.
Polynomial Expressions
4x² is a term in a polynomial expression. Polynomials are sums of terms involving variables raised to non-negative integer powers. Understanding how to manipulate terms like 4x² is fundamental to adding, subtracting, multiplying, and dividing polynomials.
Graphing Parabolas
In coordinate geometry, the equation y = 4x² represents a parabola. Understanding this expression is crucial for graphing the parabola, finding its vertex, axis of symmetry, and intercepts. The coefficient 4 affects the parabola's shape – a larger coefficient results in a narrower parabola.
Applications in Calculus
The expression 4x² plays a significant role in calculus, particularly in differentiation and integration:
Differentiation
The derivative of 4x² with respect to x is found using the power rule of differentiation. The power rule states that the derivative of xⁿ is nxⁿ⁻¹. Applying this rule, we get:
d(4x²)/dx = 8x
This derivative represents the instantaneous rate of change of the function 4x² at any given point x.
Integration
The indefinite integral of 4x² with respect to x is found using the power rule of integration, which is the reverse process of differentiation. The power rule of integration states that the integral of xⁿ is (xⁿ⁺¹)/(n+1) + C, where C is the constant of integration. Applying this rule, we get:
∫4x² dx = (4x³)/3 + C
This integral represents the area under the curve of the function 4x² from a given point to x.
Applications in Physics and Engineering
The expression 4x² and its related concepts find practical applications in various fields of physics and engineering:
Kinematics
In kinematics (the study of motion), equations of motion often involve quadratic expressions. For instance, the equation for the distance traveled by an object under constant acceleration can involve a term similar to 4x², depending on the specific problem and the chosen coordinate system.
Dynamics
In dynamics (the study of forces and motion), the concept of acceleration is frequently encountered. As we saw earlier, the derivative of 4x² represents the rate of change (acceleration) which can describe aspects of acceleration. Understanding how to work with such expressions is vital for solving dynamic problems.
Projectile Motion
Projectile motion analysis often involves parabolic trajectories described by quadratic equations. The vertical displacement of a projectile might be modeled by an expression with a term similar to 4x², especially if air resistance is neglected.
Electrical Engineering
In electrical engineering, quadratic expressions can describe the relationship between voltage and current in certain circuit elements. For example, the power dissipated in a resistor is given by P = I²R (where I is current and R is resistance), highlighting the significance of squared terms. Although not directly 4x², the principle of squaring a variable to obtain a relevant physical quantity is widely applicable.
Civil Engineering
The structural design of buildings and bridges involves consideration of stress and strain, which may be expressed by quadratic relationships. Analyzing the load-bearing capacity of structures might involve solving quadratic equations.
Mechanical Engineering
In mechanical engineering, understanding the behavior of springs, pendulums, and other mechanical systems might involve quadratic equations. Analyzing the oscillation of these systems often employs principles involving derivatives and integrals of quadratic functions.
Advanced Applications and Extensions
The concept of 4x² can be further explored in more advanced mathematical contexts:
Multivariable Calculus
In multivariable calculus, functions of multiple variables are analyzed. Expressions analogous to 4x² can appear in such functions, requiring partial differentiation and integration techniques. For instance, a function like f(x, y) = 4x²y involves the term 4x².
Linear Algebra
In linear algebra, quadratic forms are expressions involving variables raised to the power of 2. Understanding the properties of quadratic forms is important for analyzing systems of linear equations and other linear algebraic problems. Again, though not directly 4x², the underlying principle of quadratic terms is significant.
Complex Numbers
The concept of squaring can be extended to complex numbers. The expression (4z)², where z is a complex number, can be simplified using the properties of complex numbers and the rules of exponents.
Numerical Analysis
Numerical methods are used to approximate solutions to mathematical problems. When dealing with equations involving quadratic expressions, numerical methods such as the Newton-Raphson method might be employed.
Conclusion
The expression 4x² may appear simple at first glance, but its significance extends far beyond its elementary form. It serves as a fundamental building block in various mathematical and scientific disciplines. Understanding its simplification, its applications in algebra, calculus, and various fields of science and engineering, is crucial for anyone pursuing studies or careers in quantitative fields. From solving quadratic equations to understanding projectile motion and analyzing electrical circuits, mastering the concept of 4x² empowers one to tackle complex problems and further their understanding of the world around them. Its seemingly simple nature belies its deep and far-reaching impact.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How To Factor X 3 2
Mar 06, 2025
-
Y 5x 7 3x 2y 12
Mar 06, 2025
-
9 2 3 As An Improper Fraction
Mar 06, 2025
-
How To Factor 2x 2 2
Mar 06, 2025
-
1 2 9 As An Improper Fraction
Mar 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 4x To The Power Of 2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
