6 4/7 As An Improper Fraction
Next Genwave
Mar 10, 2025 · 5 min read
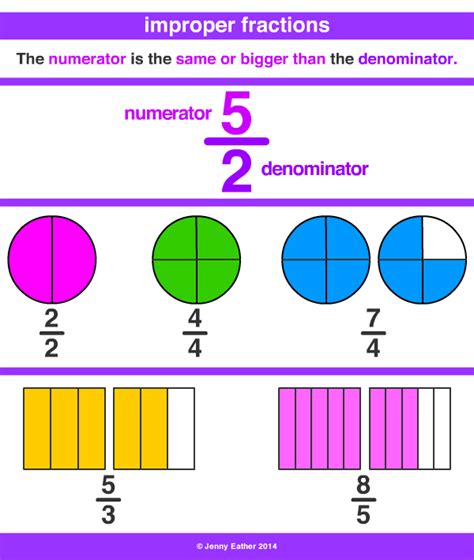
Table of Contents
6 4/7 as an Improper Fraction: A Comprehensive Guide
Converting mixed numbers to improper fractions is a fundamental skill in mathematics, crucial for various applications from basic arithmetic to advanced calculus. This comprehensive guide will delve into the process of converting the mixed number 6 4/7 into an improper fraction, exploring the underlying concepts and providing practical examples. We'll also examine why this conversion is important and how it's used in more complex mathematical operations.
Understanding Mixed Numbers and Improper Fractions
Before diving into the conversion, let's clarify the definitions:
-
Mixed Number: A mixed number combines a whole number and a proper fraction. A proper fraction has a numerator (top number) smaller than its denominator (bottom number). For example, 6 4/7 is a mixed number. It represents 6 whole units and 4/7 of another unit.
-
Improper Fraction: An improper fraction has a numerator that is greater than or equal to its denominator. For instance, 47/7 is an improper fraction. It represents more than one whole unit.
The conversion between these two forms is essential for performing various arithmetic operations, particularly addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division of fractions.
Converting 6 4/7 to an Improper Fraction: The Step-by-Step Process
The conversion of 6 4/7 to an improper fraction involves a simple two-step process:
Step 1: Multiply the whole number by the denominator.
In our example, the whole number is 6 and the denominator is 7. Multiplying these together gives us: 6 * 7 = 42
Step 2: Add the numerator to the result from Step 1.
The numerator of our fraction is 4. Adding this to the result from Step 1 (42) gives us: 42 + 4 = 46
Step 3: Keep the same denominator.
The denominator remains unchanged throughout the process. Therefore, the denominator remains 7.
Step 4: Combine the results to form the improper fraction.
Combining the results from Step 2 (46) and Step 3 (7), we arrive at our improper fraction: 46/7
Therefore, 6 4/7 is equivalent to 46/7.
Visual Representation: Understanding the Conversion
Imagine you have six whole pizzas and four-sevenths of another pizza. To represent this as an improper fraction, you need to determine the total number of slices, assuming each pizza is divided into seven equal slices.
You have six whole pizzas, each with 7 slices, totaling 6 * 7 = 42 slices. Adding the four slices from the partial pizza gives you a grand total of 42 + 4 = 46 slices. Since each pizza has 7 slices, you have 46/7 slices in total, representing the improper fraction.
The Importance of Converting to Improper Fractions
Converting mixed numbers to improper fractions is crucial for various reasons:
-
Simplifying Calculations: Adding, subtracting, multiplying, and dividing fractions is much easier when all numbers are in the same form. Working solely with improper fractions streamlines these calculations, preventing errors that can occur when mixing mixed numbers and improper fractions.
-
Solving Equations: Many algebraic equations involve fractions. Converting mixed numbers to improper fractions is a necessary step in simplifying and solving these equations effectively.
-
Working with Ratios and Proportions: Ratios and proportions often require working with fractions. Converting to improper fractions ensures consistent representation and simplifies calculations involving these mathematical concepts.
-
Geometry and Measurement: In geometry, many calculations involve fractions representing lengths, areas, and volumes. Converting mixed numbers to improper fractions helps ensure accuracy and consistency in these calculations.
Further Examples: Practicing the Conversion
Let's solidify our understanding with a few more examples:
-
Example 1: Converting 3 2/5 to an improper fraction:
- Multiply the whole number by the denominator: 3 * 5 = 15
- Add the numerator: 15 + 2 = 17
- Keep the same denominator: 5
- The improper fraction is 17/5
-
Example 2: Converting 1 1/2 to an improper fraction:
- Multiply the whole number by the denominator: 1 * 2 = 2
- Add the numerator: 2 + 1 = 3
- Keep the same denominator: 2
- The improper fraction is 3/2
-
Example 3: Converting 5 3/8 to an improper fraction:
- Multiply the whole number by the denominator: 5 * 8 = 40
- Add the numerator: 40 + 3 = 43
- Keep the same denominator: 8
- The improper fraction is 43/8
Converting Improper Fractions Back to Mixed Numbers
While converting mixed numbers to improper fractions is essential, you'll also need to be able to convert improper fractions back to mixed numbers. This is equally important for simplifying results and presenting answers in a more easily understandable format.
To convert an improper fraction to a mixed number, you perform division:
- Divide the numerator by the denominator. The quotient (the result of the division) becomes the whole number part of the mixed number.
- The remainder becomes the numerator of the proper fraction.
- The denominator remains the same.
For example, to convert 46/7 back to a mixed number:
- Divide 46 by 7: 46 ÷ 7 = 6 with a remainder of 4
- The quotient (6) is the whole number.
- The remainder (4) is the new numerator.
- The denominator remains 7.
- Therefore, 46/7 is equivalent to 6 4/7.
Real-World Applications of Fraction Conversions
The ability to convert between mixed numbers and improper fractions extends beyond theoretical mathematics. It's a practical skill with applications in many real-world scenarios:
-
Cooking and Baking: Recipes often use fractions for ingredient measurements. Converting between mixed numbers and improper fractions simplifies calculations when scaling recipes up or down.
-
Construction and Engineering: Precise measurements are crucial in construction and engineering. Converting fractions ensures accuracy and consistency in calculations involving lengths, areas, and volumes.
-
Finance and Budgeting: Managing finances involves working with percentages and fractions. Converting between mixed numbers and improper fractions can simplify calculations involving interest rates, discounts, and budgeting.
-
Data Analysis: Data analysis often involves working with fractions and percentages. Converting between mixed numbers and improper fractions is essential for consistent calculations and data interpretation.
Conclusion: Mastering Fraction Conversions for Mathematical Proficiency
Converting 6 4/7 to its improper fraction equivalent, 46/7, is a straightforward process involving multiplication and addition. This seemingly simple conversion is a crucial building block in mastering more complex mathematical concepts and solving real-world problems. Understanding the underlying principles and practicing the conversion process will enhance your overall mathematical proficiency and equip you with the skills needed to tackle various mathematical challenges confidently and efficiently. Remember the importance of mastering both conversions—from mixed numbers to improper fractions and vice-versa—for a complete understanding of fraction manipulation.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
S 2prh 2pr 2 Solve For H
Mar 10, 2025
-
What Is The Value Of 11 2
Mar 10, 2025
-
What Is The Cube Root Of 1000
Mar 10, 2025
-
Combine Like Terms To Create An Equivalent Expression 5 8c 4 2 3 1 1 4c
Mar 10, 2025
-
41 6 As A Mixed Number
Mar 10, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 6 4/7 As An Improper Fraction . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
