S 2πrh 2πr 2 Solve For H
Next Genwave
Mar 10, 2025 · 5 min read
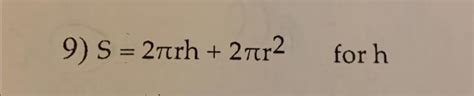
Table of Contents
Solving for h: A Comprehensive Guide to the Cylinder's Height Formula
The formula for the surface area of a cylinder, 2πrh + 2πr², is a cornerstone of geometry and has widespread applications in various fields, from engineering and architecture to packaging design and even baking. Understanding how to manipulate this formula to solve for different variables, particularly 'h' (height), is crucial for tackling real-world problems. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the process of solving for 'h' in the surface area formula of a cylinder, providing step-by-step instructions, illustrative examples, and practical applications.
Understanding the Cylinder Surface Area Formula
Before delving into the solution process, let's clarify the components of the formula: A = 2πrh + 2πr².
- A: Represents the total surface area of the cylinder. This includes the area of the curved lateral surface and the areas of the two circular bases.
- r: Represents the radius of the circular base of the cylinder. This is the distance from the center of the circle to any point on the circumference.
- h: Represents the height of the cylinder. This is the perpendicular distance between the two circular bases.
- π (pi): Represents the mathematical constant, approximately equal to 3.14159. It's the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter.
The formula itself is the sum of two parts:
- 2πrh: Represents the lateral surface area (the curved part) of the cylinder.
- 2πr²: Represents the combined area of the two circular bases.
Solving for h: A Step-by-Step Approach
To solve for 'h', we need to isolate 'h' on one side of the equation. Let's break down the process systematically:
1. Start with the formula:
A = 2πrh + 2πr²
2. Subtract 2πr² from both sides:
A - 2πr² = 2πrh
This step removes the term representing the area of the bases, leaving us closer to isolating 'h'.
3. Divide both sides by 2πr:
(A - 2πr²) / (2πr) = h
This step finally isolates 'h', giving us the solution.
Therefore, the formula to calculate the height (h) of a cylinder given its surface area (A) and radius (r) is:
h = (A - 2πr²) / (2πr)
Practical Applications and Examples
The ability to solve for 'h' using this formula is valuable in a variety of contexts. Let's look at a few examples:
Example 1: Finding the Height of a Can
Imagine you have a cylindrical can with a surface area of 100 square centimeters and a radius of 3 centimeters. To find its height, we apply the formula:
h = (100 - 2π(3)²) / (2π(3))
h ≈ (100 - 56.55) / 18.85
h ≈ 2.31 centimeters
Therefore, the height of the can is approximately 2.31 centimeters.
Example 2: Designing a Cylindrical Tank
An engineer needs to design a cylindrical water tank with a surface area of 500 square meters and a radius of 5 meters. The height is crucial for determining the tank's capacity. Using the formula:
h = (500 - 2π(5)²) / (2π(5))
h ≈ (500 - 157.08) / 31.42
h ≈ 10.88 meters
The required height of the water tank is approximately 10.88 meters.
Example 3: Calculating the Height of a Silo
A farmer needs to build a cylindrical silo with a known surface area and radius. Determining the silo's height is essential for planning the construction. This real-world problem is directly solved by applying the formula. The accuracy of this height calculation directly impacts material costs and the silo's functionality.
Troubleshooting and Common Mistakes
When solving for 'h', several common mistakes can arise:
-
Order of Operations: Remember to follow the order of operations (PEMDAS/BODMAS). Parentheses, exponents, multiplication and division (from left to right), and then addition and subtraction (from left to right). Incorrect order can lead to inaccurate results.
-
Unit Consistency: Ensure all units are consistent throughout the calculation. Using a mixture of centimeters and meters, for instance, will result in an incorrect answer. Convert all measurements to the same unit before applying the formula.
-
Calculator Errors: Double-check your calculations on a calculator. Even minor errors in inputting values can significantly impact the final result.
-
Understanding π: Remember that π is an irrational number, meaning it has an infinite number of decimal places. Using a sufficiently precise approximation (at least 3.14159) is necessary for accurate results, especially in calculations involving larger surface areas or radii.
Advanced Applications and Extensions
The ability to solve for 'h' in the cylinder surface area formula opens the door to more complex geometric problems. For example:
-
Combined Shapes: Problems involving cylinders combined with other shapes (cones, spheres) require breaking the problem down into individual components, solving for 'h' in the cylinder portion, and then combining the results.
-
Optimization Problems: In engineering and design, solving for 'h' is often part of an optimization problem, where the goal is to minimize the surface area for a given volume or vice-versa. Calculus techniques are often used to solve these problems.
-
Real-world Scenarios: From calculating the amount of paint needed for a cylindrical water tower to determining the optimal dimensions of a storage container, the formula's applications are widespread and impactful across various industries.
Conclusion: Mastering the Cylinder's Height Calculation
Solving for 'h' in the surface area formula of a cylinder is a fundamental skill in geometry and has far-reaching practical applications. By understanding the formula, following the step-by-step process, and avoiding common mistakes, you can confidently tackle a range of problems involving cylinders. The ability to perform these calculations is not only valuable for academic pursuits but also crucial for professionals in various fields requiring geometric problem-solving. This guide equips you with the knowledge and practical examples to confidently approach and solve problems involving the height calculation of cylinders. Remember to practice regularly to build your proficiency and comfort level with this important mathematical concept.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Factorise X 2 Y 2 2x 1
Mar 10, 2025
-
Whats The Square Root Of 28
Mar 10, 2025
-
24 To The Power Of 2
Mar 10, 2025
-
X 4 4x 2 4 0
Mar 10, 2025
-
X 3 2x 2 X 2 0
Mar 10, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about S 2πrh 2πr 2 Solve For H . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
