8 1/2 As An Improper Fraction
Next Genwave
Mar 10, 2025 · 5 min read
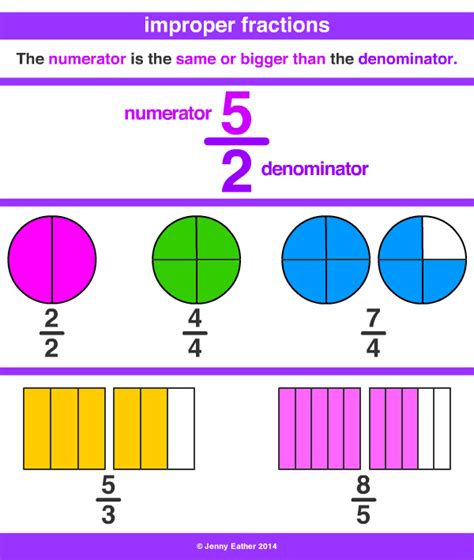
Table of Contents
8 1/2 as an Improper Fraction: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding fractions, both proper and improper, is a fundamental skill in mathematics. This guide delves deep into converting mixed numbers, like 8 1/2, into improper fractions. We'll explore the process, its applications, and even touch upon advanced concepts. This comprehensive resource aims to solidify your understanding of this crucial mathematical concept, improving your problem-solving capabilities and boosting your overall math proficiency.
What is an Improper Fraction?
Before we dive into converting 8 1/2, let's establish a clear understanding of what an improper fraction actually is. An improper fraction is a fraction where the numerator (the top number) is greater than or equal to the denominator (the bottom number). For example, 7/4, 9/5, and even 5/5 are all improper fractions. They represent a value greater than or equal to one.
Contrast this with a proper fraction, where the numerator is smaller than the denominator (e.g., 1/4, 3/8, 2/5). Proper fractions represent values less than one. Mixed numbers, like 8 1/2, are a combination of a whole number and a proper fraction.
Converting 8 1/2 to an Improper Fraction: The Step-by-Step Process
Converting a mixed number like 8 1/2 into an improper fraction involves a simple yet crucial two-step process. Let's break it down:
Step 1: Multiply the whole number by the denominator.
In our example, 8 1/2, the whole number is 8, and the denominator is 2. Multiply these together: 8 * 2 = 16.
Step 2: Add the numerator to the result from Step 1.
The numerator in 8 1/2 is 1. Add this to the result from Step 1: 16 + 1 = 17.
Step 3: Keep the denominator the same.
The denominator remains unchanged throughout this process. The denominator in 8 1/2 is 2, and it will remain 2 in our improper fraction.
The Final Result:
Therefore, 8 1/2 expressed as an improper fraction is 17/2. This signifies that 8 1/2 represents seventeen halves.
Visualizing the Conversion
It can be helpful to visualize this conversion. Imagine eight whole pizzas, each cut into two equal slices. That's 8 * 2 = 16 slices. Then, you add one more half-pizza slice, giving you a total of 16 + 1 = 17 slices. Each slice represents 1/2 of a pizza, so you have 17/2.
Why is Converting to Improper Fractions Important?
The ability to convert mixed numbers to improper fractions is crucial for several mathematical operations, including:
-
Addition and Subtraction of Fractions: Adding or subtracting mixed numbers directly can be cumbersome. Converting them to improper fractions first simplifies the process significantly, allowing for straightforward addition or subtraction of the numerators while keeping the denominator constant.
-
Multiplication and Division of Fractions: Similar to addition and subtraction, multiplying and dividing mixed numbers is easier when they are first converted to improper fractions. This streamlines the calculations, minimizing errors and improving efficiency.
-
Solving Equations: Many algebraic equations involve fractions. Converting mixed numbers to improper fractions facilitates solving these equations, making the algebraic manipulations cleaner and more manageable.
-
Working with Ratios and Proportions: In situations involving ratios and proportions, expressing values as improper fractions ensures consistency and simplifies calculations.
Advanced Applications and Real-World Examples
The conversion of mixed numbers to improper fractions transcends basic arithmetic. It's applied extensively in various fields:
-
Engineering and Construction: Precise measurements and calculations are essential in engineering and construction. Converting mixed numbers to improper fractions helps ensure accuracy in blueprint readings, material calculations, and structural design.
-
Cooking and Baking: Recipes often use fractions. Converting mixed numbers to improper fractions simplifies scaling recipes up or down, maintaining the correct proportions of ingredients.
-
Computer Programming: Many programming languages utilize fractions and their representations in various algorithms and calculations. Understanding improper fractions is crucial for handling these numerical manipulations efficiently and accurately.
-
Financial Calculations: Financial models and calculations often involve fractions and percentages. Converting mixed numbers to improper fractions simplifies complex financial operations, improving the precision and reliability of the calculations.
Practicing Conversion: Examples
Let's practice converting a few more mixed numbers into improper fractions to solidify your understanding:
-
5 2/3: (5 * 3) + 2 = 17. The denominator remains 3. Therefore, 5 2/3 = 17/3.
-
3 1/4: (3 * 4) + 1 = 13. The denominator remains 4. Therefore, 3 1/4 = 13/4.
-
12 5/8: (12 * 8) + 5 = 101. The denominator remains 8. Therefore, 12 5/8 = 101/8.
-
1 7/10: (1 * 10) + 7 = 17. The denominator remains 10. Therefore, 1 7/10 = 17/10.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
While the conversion process is straightforward, some common mistakes can arise:
-
Forgetting to add the numerator: Remember that the numerator needs to be added to the product of the whole number and denominator. This is a critical step.
-
Changing the denominator: The denominator always remains the same throughout the conversion process.
-
Incorrect multiplication or addition: Carefully double-check your multiplication and addition steps to prevent arithmetic errors.
Conclusion: Mastering Improper Fractions
The ability to seamlessly convert mixed numbers to improper fractions is a cornerstone of mathematical proficiency. It streamlines calculations, enhances accuracy, and unlocks the ability to tackle more complex mathematical problems across various disciplines. Through consistent practice and a thorough understanding of the process, you can confidently master this essential skill and confidently navigate the world of fractions. By understanding the ‘why’ behind the conversion, beyond just the ‘how’, you'll solidify your comprehension and build a strong foundation for further mathematical exploration. Remember to practice regularly – the more you work with improper fractions, the easier and more intuitive the process will become.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
17 Rounded To The Nearest Tenth
Mar 10, 2025
-
1 3 2m M 3 2
Mar 10, 2025
-
X 2 X 1 0 Solve For X
Mar 10, 2025
-
Square Root Of 162 In Radical Form
Mar 10, 2025
-
Find The 8th Term Of The Geometric Sequence
Mar 10, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 8 1/2 As An Improper Fraction . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
