Square Root Of 162 In Radical Form
Next Genwave
Mar 10, 2025 · 5 min read
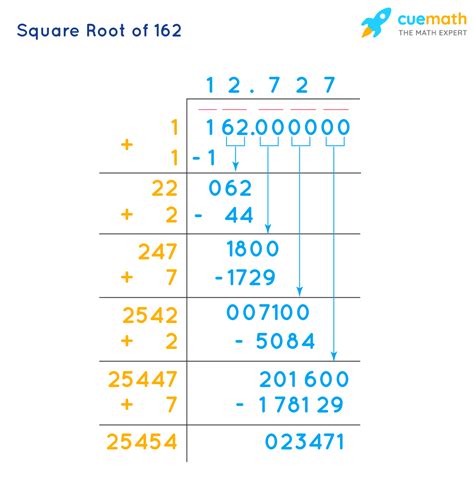
Table of Contents
Understanding the Square Root of 162 in Radical Form
The square root of 162, denoted as √162, represents a number that, when multiplied by itself, equals 162. While a calculator can provide a decimal approximation, expressing √162 in its simplest radical form is a crucial skill in algebra and higher-level mathematics. This article will delve deep into the process, exploring different methods, explaining the underlying concepts, and providing numerous examples to solidify your understanding. We'll also touch upon related concepts to broaden your mathematical knowledge.
What is a Radical?
Before we embark on simplifying √162, let's clarify the term "radical." In mathematics, a radical expression involves a root (like the square root, cube root, etc.) of a number. The symbol '√' denotes the radical, and the number inside the radical symbol is called the radicand. In our case, 162 is the radicand. Simplifying a radical involves expressing it in its most concise and efficient form, free of perfect square factors within the radicand.
Prime Factorization: The Key to Simplifying Radicals
The foundation of simplifying radicals lies in prime factorization. Prime factorization is the process of breaking down a number into its prime factors – numbers divisible only by 1 and themselves (e.g., 2, 3, 5, 7, 11...). This process is crucial because it allows us to identify perfect squares hidden within the radicand.
Let's find the prime factorization of 162:
162 = 2 × 81 81 = 9 × 9 9 = 3 × 3
Therefore, the prime factorization of 162 is 2 × 3 × 3 × 3 × 3 = 2 × 3<sup>4</sup>.
Simplifying √162
Now, we can use the prime factorization to simplify √162:
√162 = √(2 × 3<sup>4</sup>)
Since √(a × b) = √a × √b, we can rewrite the expression as:
√162 = √2 × √(3<sup>4</sup>)
We know that √(3<sup>4</sup>) = 3<sup>4/2</sup> = 3<sup>2</sup> = 9. Therefore:
√162 = 9√2
Therefore, the simplest radical form of √162 is 9√2. This means that 9√2, when multiplied by itself, equals 162.
Alternative Methods for Simplifying Radicals
While prime factorization is the most fundamental and widely applicable method, let's explore some alternative approaches:
Method 1: Identifying Perfect Square Factors
Instead of complete prime factorization, you can directly look for perfect square factors within the radicand. Notice that 162 is divisible by 81 (a perfect square, 9 x 9).
√162 = √(81 × 2) = √81 × √2 = 9√2
This method is faster if you can readily identify perfect square factors.
Method 2: Repeated Division by Perfect Squares
This method involves repeatedly dividing the radicand by perfect squares until you're left with a number that doesn't contain any more perfect square factors.
- Start with √162.
- Divide 162 by 9 (a perfect square): 162 ÷ 9 = 18.
- Now we have √(9 × 18). This simplifies to 3√18.
- 18 is divisible by 9 again: √(9 × 2) which simplifies to 3√2.
- Therefore, we have 3√2 multiplied by the earlier 3, giving us 9√2.
Understanding the Concept of Radical Simplification
Simplifying radicals is not just about finding the answer; it's about expressing the number in its most efficient and manageable form. In algebraic manipulations and advanced mathematical calculations, simplified radical forms are much easier to work with than unwieldy decimal approximations. For example, it's significantly easier to add 9√2 + 2√2 = 11√2 than to add their decimal approximations and then convert back to a radical.
Practical Applications of Radical Simplification
Simplifying radicals isn't just a theoretical exercise; it has numerous real-world applications, particularly in fields like:
- Geometry: Calculating lengths of diagonals, areas of triangles, and volumes of shapes often involve square roots and radical simplification.
- Physics: Formulas in physics, especially those related to motion, energy, and electricity, often involve square roots.
- Engineering: Civil, mechanical, and electrical engineers use radicals in design calculations.
- Computer Graphics: Radical expressions are used in algorithms for computer graphics and 3D modeling.
Advanced Concepts: Higher Order Roots
While this article focuses on square roots, the principles of prime factorization and simplifying radicals extend to higher-order roots (cube roots, fourth roots, etc.). For example:
-
Cube root of 64: The cube root of 64 (∛64) involves finding a number that, when multiplied by itself three times, equals 64. Since 4 × 4 × 4 = 64, the cube root of 64 is 4.
-
Simplifying ∛108: To simplify ∛108, we perform prime factorization: 108 = 2<sup>2</sup> × 3<sup>3</sup>. We can then write this as ∛(2<sup>2</sup> × 3<sup>3</sup>) = 3∛4.
Solving Equations Involving Radicals
Radicals often appear in algebraic equations. Solving these equations may involve squaring or cubing both sides of the equation to eliminate the radical. Remember, it’s crucial to always check your solutions to ensure they are valid (i.e., they don't lead to a negative number under a square root).
Conclusion: Mastering Radical Simplification
Mastering the simplification of radicals is a fundamental skill in mathematics. By understanding the concepts of prime factorization and applying the techniques outlined in this article, you can efficiently simplify radical expressions and tackle more complex mathematical problems. The ability to work fluently with radicals will serve you well in various academic disciplines and practical applications. Practice consistently, and you'll become proficient in this essential mathematical skill. Remember to break down complex problems into smaller, manageable steps, and always double-check your work. The more you practice, the easier and more intuitive the process will become.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Find The Exact Value Of Tan
Mar 10, 2025
-
Square Root Of X 3 2
Mar 10, 2025
-
N 4 9 5n
Mar 10, 2025
-
What Is The Square Root Of 99
Mar 10, 2025
-
How Do I Graph X 1
Mar 10, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Square Root Of 162 In Radical Form . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
