Round 9.6 To The Nearest Whole Number.
Next Genwave
Mar 06, 2025 · 5 min read
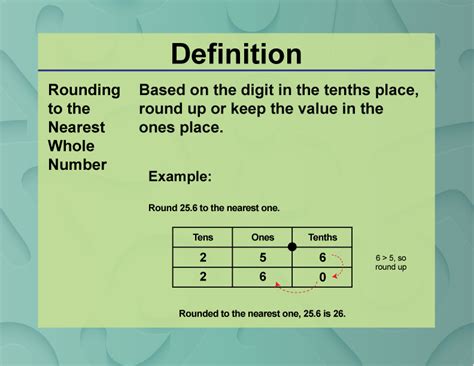
Table of Contents
Rounding 9.6 to the Nearest Whole Number: A Comprehensive Guide
Rounding numbers is a fundamental skill in mathematics with applications spanning various fields, from everyday calculations to complex scientific analyses. This article delves into the process of rounding 9.6 to the nearest whole number, providing a step-by-step explanation, exploring the underlying principles, and illustrating its practical relevance. We'll also examine related concepts and address common misconceptions to ensure a thorough understanding.
Understanding the Concept of Rounding
Rounding involves approximating a number to a specified degree of accuracy. Instead of using the exact value, we replace it with a simpler, rounded value that's close enough for the intended purpose. The level of accuracy is determined by the place value to which we're rounding—in this case, the nearest whole number (also known as the ones place).
The core principle of rounding rests on identifying the digit in the place value we're targeting and then looking at the digit immediately to its right. This right-hand digit acts as the "decider" – influencing whether we round up or down.
Rounding 9.6: A Step-by-Step Approach
Let's break down the process of rounding 9.6 to the nearest whole number:
-
Identify the target place value: We're rounding to the nearest whole number, meaning our target is the ones place (the digit to the left of the decimal point). In 9.6, this is the '9'.
-
Examine the digit to the right: The digit to the right of the '9' is '6'.
-
Apply the rounding rule: The standard rounding rule states:
- If the digit to the right is 5 or greater, we round up (increase the target digit by 1).
- If the digit to the right is less than 5, we round down (leave the target digit unchanged).
-
Round 9.6: Since the digit to the right of the '9' (which is '6') is greater than or equal to 5, we round up. Therefore, 9.6 rounded to the nearest whole number is 10.
Visualizing the Rounding Process
Imagine a number line with whole numbers marked: ... 8, 9, 10, 11 ...
9.6 lies between 9 and 10. Since 9.6 is closer to 10 than to 9, it rounds up to 10. This visual representation reinforces the understanding of the rounding process.
Practical Applications of Rounding
Rounding is not merely an abstract mathematical exercise; it has widespread practical applications in:
-
Everyday life: Estimating costs, calculating tips, measuring quantities, and even telling time all involve rounding. For example, if a product costs $9.60, we might round it up to $10 for quick mental calculations.
-
Science and engineering: Rounding plays a critical role in data analysis, experimental measurements, and simulations. Measurements are often imprecise, and rounding allows for simpler representation and comparison of data.
-
Finance and accounting: Rounding is essential for financial reporting, calculating taxes, and managing budgets. Slight discrepancies arising from rounding are often acceptable within predefined tolerances.
-
Computer science: Floating-point numbers, used extensively in computer programming, often require rounding to avoid precision issues and to display results in a user-friendly manner.
Rounding to Different Place Values
While this article focuses on rounding to the nearest whole number, the principles extend to rounding to other place values, such as tenths, hundredths, thousands, etc. The same rule applies: look at the digit immediately to the right of the target place value to determine whether to round up or down.
For instance:
-
Rounding 9.62 to the nearest tenth: The digit in the tenths place is 6. The digit to its right (2) is less than 5, so we round down. The answer is 9.6.
-
Rounding 9.65 to the nearest tenth: The digit in the tenths place is 6. The digit to its right (5) is 5 or greater, so we round up. The answer is 9.7.
Addressing Common Misconceptions
Several common misconceptions surround the rounding process:
-
Rounding multiple times: It's crucial to perform rounding only once. Repeated rounding can lead to significant errors in the final result.
-
Rounding only up: Some people mistakenly believe that all numbers with a decimal part should be rounded up. This is incorrect; the decision to round up or down depends solely on the digit to the right of the target place value.
-
Ignoring the context: The appropriate level of rounding depends on the context. In some situations, precise values are crucial, while in others, approximations suffice.
Beyond Simple Rounding: Other Rounding Methods
While the standard rounding method (as explained above) is widely used, other rounding methods exist:
-
Rounding towards zero: This method always rounds towards zero, irrespective of the digit to the right. For example, 9.6 would round to 9, and -9.6 would round to -9.
-
Rounding away from zero: This method always rounds away from zero. For example, 9.6 would round to 10, and -9.6 would round to -10.
-
Rounding to even/odd: This method rounds to the nearest even or odd number, respectively. This helps to minimize bias over many rounding operations. For example, 9.5 would round to 10 (even), while 8.5 would round to 8 (even).
The choice of rounding method depends on the specific application and desired level of accuracy.
Conclusion: The Importance of Accurate Rounding
Mastering the art of rounding is essential for anyone working with numbers. From everyday calculations to complex scientific analyses, the ability to accurately round numbers ensures efficient and reliable results. Understanding the principles discussed in this article—including the step-by-step process, practical applications, and potential pitfalls—will help you confidently handle rounding in any situation. Remember to always consider the context and choose the appropriate rounding method to maintain accuracy and prevent errors. The seemingly simple act of rounding 9.6 to the nearest whole number highlights the profound importance of this fundamental mathematical skill.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Do You Graph Y 3x 1
Mar 06, 2025
-
What Percentage Is 11 Out Of 12
Mar 06, 2025
-
2x 3 X 2 X 2
Mar 06, 2025
-
2x 3y 12 In Slope Intercept Form
Mar 06, 2025
-
Fill In The Table Using The Function Rule
Mar 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Round 9.6 To The Nearest Whole Number. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
