X 2 X 6 X 3
Next Genwave
Mar 06, 2025 · 6 min read
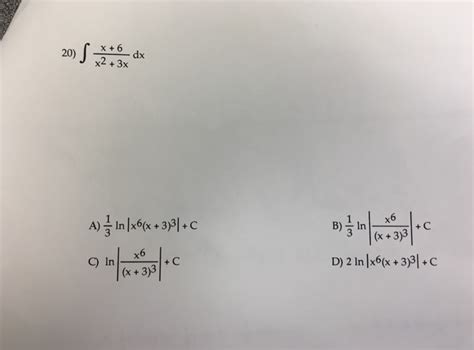
Table of Contents
Decoding the Enigma: Exploring the Mathematical and Practical Implications of "x 2 x 6 x 3"
The seemingly simple expression "x 2 x 6 x 3" presents a fascinating challenge, inviting exploration across diverse mathematical and practical fields. While the core operation is straightforward multiplication, the ambiguity surrounding the variable 'x' opens doors to a range of interpretations and applications. This article delves deep into the meaning, implications, and potential applications of this expression, demonstrating its relevance across various disciplines.
Understanding the Fundamentals: Multiplication and the Variable 'x'
At its most basic level, "x 2 x 6 x 3" represents a multiplication problem. The numbers 2, 6, and 3 are constants, while 'x' acts as a variable, representing an unknown quantity or a placeholder for a value that can change. The order of operations dictates that multiplication is performed from left to right. Thus, the expression can be simplified to:
- (x * 2) * 6 * 3 = 36x
This simplified form highlights the crucial role of 'x'. The final result is directly proportional to the value of 'x'. If 'x' is 1, the result is 36. If 'x' is 10, the result is 360. This simple relationship underscores the power of variables in mathematical modeling and problem-solving.
Exploring Applications in Different Fields
The seemingly simple expression "x 2 x 6 x 3" finds surprising applicability across various fields. Let's examine some key areas:
1. Algebra and Equation Solving:
In algebra, this expression forms the basis of various equations. For example:
-
36x = 72 In this equation, we need to solve for 'x'. Dividing both sides by 36 gives us x = 2.
-
36x + 10 = 100 This equation requires an additional step. First, subtract 10 from both sides (36x = 90), then divide by 36 to get x = 2.5.
Such equations are fundamental to solving real-world problems, ranging from calculating distances and speeds to determining financial projections.
2. Geometry and Volume Calculations:
Imagine a rectangular prism (a box). Let's say the width is represented by 'x', the length is 2 units, the height is 6 units, and the depth is 3 units. The volume of this prism can be expressed as:
- Volume = x * 2 * 6 * 3 = 36x
This formula demonstrates how our expression can be used to calculate the volume of a prism based on the unknown width 'x'. By knowing the volume, we can solve for 'x'. For example, if the volume is 72 cubic units, then x=2 units. This simple application extends to numerous geometric problems involving shapes with variable dimensions.
3. Physics and Engineering:
In physics and engineering, this expression might represent a simplified model of a physical phenomenon. Consider a scenario where 'x' represents the force applied to an object, and the numbers represent factors such as leverage, friction, or efficiency. The final result (36x) might represent the work done or the acceleration achieved.
4. Business and Finance:
In business, 'x' could represent a unit cost, while the numbers 2, 6, and 3 represent different factors affecting the total cost. For example, 2 could be the number of materials used, 6 could be the labor cost per unit, and 3 could be the transportation cost. The resulting expression 36x will show the total cost associated with 'x' units. This application can extend to calculating profits, estimating sales revenue, and determining pricing strategies.
5. Computer Science and Programming:
In computer programming, this expression is a trivial calculation. It can be easily implemented in any programming language, using the variable 'x' as an input to the function. This is a fundamental building block in complex algorithms and data processing tasks.
Extending the Scope: Exploring Variations and Complexities
The expression "x 2 x 6 x 3" can be extended and modified to represent more complex scenarios. For example:
- (x + 2) * 6 * 3: Here, 'x' is added to 2 before the multiplication. This signifies a scenario where an initial value is added before the other factors are applied.
- x * (2 + 6 + 3): This simplifies to 11x, indicating a scenario where the factors are summed before being multiplied by 'x'.
- x^2 * 2 * 6 * 3 = 36x^2: This involves squaring 'x', adding an exponential term which significantly alters the relationship between the value of 'x' and the final result. This variation can represent more intricate models involving squared relationships, like those found in physics (e.g., Newton's second law, where force is proportional to acceleration).
- (x * 2) * (6 * 3): This uses parentheses to group operations, potentially suggesting a specific order of actions or a hierarchical relationship between the factors.
These variations illustrate the versatility of the underlying expression and demonstrate how a simple formula can be adapted to represent increasingly complex relationships.
Practical Applications and Real-World Examples
Let's look at some specific real-world examples to illustrate the versatility of the expression:
- Construction: A contractor needs to calculate the cost of building a wall. The width of the wall is 'x', the height is 6 feet, the length is 3 feet, and the cost per square foot is $2. The expression 36x represents the total cost of building the wall in dollars, allowing the contractor to easily estimate costs for walls of varying widths.
- Manufacturing: A factory produces widgets. 'x' represents the number of widgets produced in a day. The production process involves 2 steps, each costing $6, and final packaging costs $3 per widget. The expression 36x represents the total production cost for 'x' widgets.
- Agriculture: A farmer wants to estimate the yield from a field. 'x' represents the average yield per square meter, the field's length is 6 meters, the width is 3 meters, and there are 2 similar fields. The expression 36x represents the total yield from both fields.
Conclusion: Unveiling the Power of Simple Expressions
The seemingly simple expression "x 2 x 6 x 3" reveals a wealth of mathematical and practical implications. Its fundamental nature as a multiplication problem, combined with the inclusion of a variable, allows it to model and solve problems across diverse fields. By exploring its variations and applying it to real-world examples, we see its power in representing and solving a wide range of quantitative relationships. This exploration highlights the importance of understanding even the most basic mathematical concepts and the power they hold in unlocking solutions to complex problems. Furthermore, the analysis underscores the essential role of mathematical modeling in understanding and solving problems in various disciplines. The seemingly simple equation 36x serves as a potent reminder of the power and flexibility hidden within even the most fundamental mathematical concepts. Understanding such expressions allows us to build more sophisticated models and unlock a deeper understanding of the world around us.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Square Root Of 3 Times Square Root Of 3
Mar 06, 2025
-
8 Of 15 Is What Percentage
Mar 06, 2025
-
What Is 8 11 As A Decimal
Mar 06, 2025
-
Convert 8 3 4 To A Decimal
Mar 06, 2025
-
16 To The Power Of 2
Mar 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about X 2 X 6 X 3 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
