X 2 Y 2 4 Graph
Next Genwave
Mar 06, 2025 · 5 min read
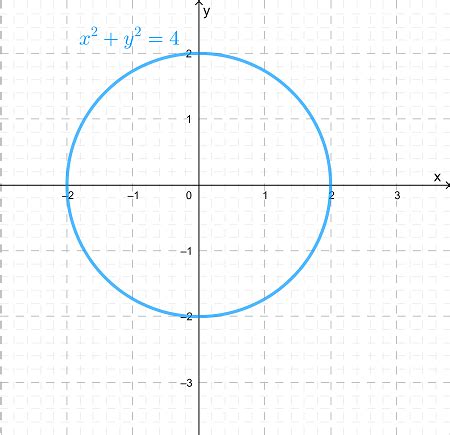
Table of Contents
X² + Y² = 4 Graph: A Comprehensive Exploration
The equation x² + y² = 4 represents a fundamental concept in mathematics and has significant applications across various fields. This article delves into a comprehensive exploration of this equation, examining its graphical representation, its derivation from the distance formula, its relationship to circles, and its practical applications. We'll also look at variations and transformations of this basic equation.
Understanding the Equation x² + y² = 4
At its core, x² + y² = 4 is an equation defining a circle in a two-dimensional Cartesian coordinate system. It's a specific instance of the general equation of a circle: (x - h)² + (y - k)² = r², where (h, k) represents the center of the circle and r represents its radius.
In our equation, x² + y² = 4, we can rewrite it as (x - 0)² + (y - 0)² = 2², revealing that:
- Center (h, k): The center of the circle is located at the origin (0, 0).
- Radius (r): The radius of the circle is 2 units.
This means the circle is centered at the origin and extends 2 units in every direction.
Deriving the Equation from the Distance Formula
The equation x² + y² = 4 can be elegantly derived from the distance formula. The distance formula calculates the distance between two points (x₁, y₁) and (x₂, y₂) in a Cartesian plane:
d = √[(x₂ - x₁)² + (y₂ - y₁)²]
Consider any point (x, y) on the circle. The distance between this point and the center of the circle (0, 0) is always equal to the radius, which is 2. Applying the distance formula:
2 = √[(x - 0)² + (y - 0)²]
Squaring both sides to eliminate the square root:
4 = (x - 0)² + (y - 0)²
This simplifies to:
x² + y² = 4
This derivation demonstrates the inherent relationship between the equation of a circle and the concept of distance.
Graphing x² + y² = 4
Graphing x² + y² = 4 is straightforward. Since we know the circle is centered at the origin (0, 0) with a radius of 2, we can plot points that satisfy the equation:
- (2, 0): 2² + 0² = 4
- (0, 2): 0² + 2² = 4
- (-2, 0): (-2)² + 0² = 4
- (0, -2): 0² + (-2)² = 4
- (√2, √2): (√2)² + (√2)² = 4
- (-√2, √2): (-√2)² + (√2)² = 4
- (√2, -√2): (√2)² + (-√2)² = 4
- (-√2, -√2): (-√2)² + (-√2)² = 4
By plotting these points and connecting them smoothly, you create the graph of the circle. The graph visually represents all points (x, y) that are exactly 2 units away from the origin. Using graphing software or a graphing calculator can make this process even easier.
Applications of x² + y² = 4 and Related Equations
The equation x² + y² = 4, and its variations, appear in numerous applications across various fields:
1. Physics and Engineering:
- Circular Motion: The equation describes the path of an object undergoing uniform circular motion. Consider a ball swinging on a string of length 2 units; its path would be described by this equation if the string's pivot point is the origin.
- Signal Processing: Circular functions, closely related to the circle's equation, are fundamental in representing and analyzing signals in various domains, including sound and electrical engineering.
- Optics: Understanding circular wavefronts and their propagation is crucial in optics and related fields.
2. Computer Graphics and Game Development:
- Object Representation: Circles and spheres (3D equivalents) are common shapes used in computer graphics and game development. The equation provides a mathematical basis for generating and manipulating these shapes.
- Collision Detection: Determining whether two objects collide often involves checking for intersections between their bounding circles or spheres, which can be defined by equations similar to x² + y² = 4.
3. Geography and Cartography:
- Mapping: While the Earth is a sphere, smaller regions can often be approximated as planar surfaces. Circular regions can then be effectively represented by equations like x² + y² = 4 in geographic information systems (GIS).
4. Mathematics:
- Trigonometry: The unit circle (x² + y² = 1) is crucial in understanding trigonometric functions and their relationships. The equation x² + y² = 4 is a scaled-up version of the unit circle.
- Calculus: The equation can be used to illustrate concepts like parametric equations, polar coordinates, and integration.
Variations and Transformations of the Equation
Understanding the basic equation allows us to easily grasp its variations and transformations:
1. Shifting the Center:
The equation (x - h)² + (y - k)² = 4 represents a circle with the same radius (2) but centered at (h, k). This shifts the circle horizontally by 'h' units and vertically by 'k' units.
2. Changing the Radius:
The equation x² + y² = r² represents a circle centered at the origin with radius 'r'. Changing 'r' alters the circle's size.
3. Combining Transformations:
We can combine shifting and radius changes: (x - h)² + (y - k)² = r² represents a circle centered at (h, k) with radius 'r'.
Exploring the Equation in Different Coordinate Systems
While we've primarily discussed the equation in Cartesian coordinates, it's also valuable to consider its representation in other coordinate systems:
1. Polar Coordinates:
In polar coordinates, the equation x² + y² = 4 transforms simply to r² = 4, or r = 2. This makes intuitive sense, as 'r' represents the radial distance from the origin. This representation emphasizes the radial symmetry of the circle.
2. Parametric Equations:
The circle can be represented parametrically using trigonometric functions:
- x = 2cos(t)
- y = 2sin(t)
where 't' is a parameter representing the angle. As 't' varies from 0 to 2π, the point (x, y) traces out the entire circle.
Conclusion
The seemingly simple equation x² + y² = 4 is a powerful tool with broad applications. Its graphical representation as a circle, its derivation from the distance formula, and its diverse applications in various fields underscore its importance in mathematics, physics, engineering, and computer science. Understanding this equation, its transformations, and its representation in different coordinate systems provides a solid foundation for more advanced mathematical concepts and practical problem-solving. The exploration of this equation extends beyond simple graphing; it's a gateway to understanding fundamental concepts in geometry, algebra, and their real-world applications. This comprehensive exploration should provide a solid understanding of this fundamental equation and its multifaceted nature.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Graph The Line With Slope And Intercept
Mar 06, 2025
-
What Is The Reciprocal Of 8 9
Mar 06, 2025
-
Degree And Leading Coefficient Of A Polynomial
Mar 06, 2025
-
Graph Of X 2 X 1
Mar 06, 2025
-
How Do You Graph Y 4x 2
Mar 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about X 2 Y 2 4 Graph . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
