A Pi R 2 Solve For R
Next Genwave
Mar 09, 2025 · 5 min read
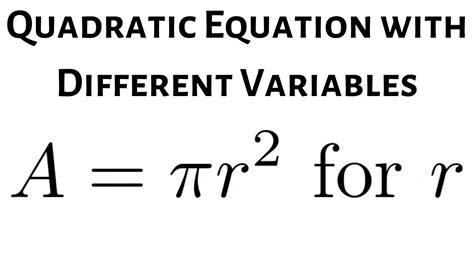
Table of Contents
Solving for r: A Comprehensive Guide to the Area of a Circle Formula
The area of a circle, a fundamental concept in geometry, is expressed by the formula A = πr². While seemingly simple, understanding this formula and, more importantly, how to manipulate it to solve for the radius (r) is crucial for various mathematical applications and real-world problem-solving. This comprehensive guide will walk you through various methods of solving for 'r' in A = πr², addressing different scenarios and complexities.
Understanding the Formula: A = πr²
Before delving into solving for 'r', let's solidify our understanding of the formula A = πr².
-
A: Represents the area of the circle. This is the space enclosed within the circle's circumference. The unit for area is always squared (e.g., square centimeters, square meters).
-
π (Pi): A mathematical constant, approximately equal to 3.14159. Pi represents the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter. It's an irrational number, meaning its decimal representation goes on forever without repeating. For most calculations, using 3.14 or the π button on your calculator is sufficient.
-
r: Represents the radius of the circle. This is the distance from the center of the circle to any point on its circumference.
The formula A = πr² essentially states that the area of a circle is directly proportional to the square of its radius. This means that if you double the radius, the area increases fourfold (2² = 4).
Solving for r: The Step-by-Step Process
To solve for 'r', we need to isolate 'r' on one side of the equation. This involves a series of algebraic manipulations. Here's the step-by-step process:
-
Start with the formula: A = πr²
-
Divide both sides by π: This removes π from the right side, leaving only r². The equation becomes: A/π = r²
-
Take the square root of both sides: This cancels out the square on 'r', leaving 'r' isolated. The equation now becomes: √(A/π) = r
-
Simplify (if possible): Depending on the value of 'A', you might be able to simplify the expression further. For example, if A is a perfect square and a multiple of π, simplification might be straightforward.
Therefore, the solution for 'r' is: r = √(A/π)
Practical Applications and Worked Examples
Let's solidify our understanding with some worked examples:
Example 1: Finding the radius given the area
A circle has an area of 78.54 square centimeters. Find its radius.
-
Substitute the given value of A: 78.54 = πr²
-
Divide by π: 78.54/π = r² (Using π ≈ 3.14) ≈ 25 = r²
-
Take the square root: √25 = r
-
Solution: r = 5 centimeters
Example 2: A more complex scenario
A circular garden has an area of 150 square meters. You want to build a fence around it. What is the length of the radius you need for your design calculations?
-
Substitute the given area: 150 = πr²
-
Divide by π: 150/π ≈ r² (Using π ≈ 3.14) ≈ 47.74 ≈ r²
-
Take the square root: √47.74 ≈ r
-
Solution: r ≈ 6.91 meters. This is the radius you will need for your fence design. You might round this up to 7 meters for practical considerations.
Example 3: Dealing with units
A circular pool has an area of 113.1 square feet. What is the radius of the pool in feet and inches?
-
Substitute the given area: 113.1 = πr²
-
Divide by π: 113.1/π ≈ r² (Using π ≈ 3.14159) ≈ 36 ≈ r²
-
Take the square root: √36 = r
-
Solution: r = 6 feet. Since 1 foot = 12 inches, the radius is also 6 * 12 = 72 inches.
Advanced Considerations and Troubleshooting
While the basic process is straightforward, certain situations might present challenges:
-
Approximations: Since π is an irrational number, calculations often involve approximations. The precision of your answer depends on the precision of the π value you use. Using more decimal places of π increases accuracy.
-
Units: Always pay attention to units. The area is always in square units (e.g., square meters, square feet), while the radius is in linear units (meters, feet). Ensure consistency throughout your calculations.
-
Complex Areas: If you're dealing with an area that isn't directly given but calculated from other geometrical elements, ensure you have correctly calculated the area before attempting to solve for 'r'.
-
Using a Calculator: Modern scientific calculators have built-in functions for square roots and π, making calculations faster and more accurate. Learn how to use these functions effectively.
-
Solving for other variables: The formula can also be rearranged to solve for A (if 'r' is known) and vice versa.
Beyond the Basics: Applications in Real-World Scenarios
The ability to solve for 'r' in A = πr² has numerous practical applications beyond simple geometry problems:
-
Engineering: Calculating the radius of pipes, wheels, circular components in various machines.
-
Construction: Determining the radius of circular structures, foundations, or landscape features.
-
Architecture: Designing circular spaces, arches, or domes.
-
Physics: Calculating the radius of circular motion, orbits, or other physical phenomena.
-
Data Analysis: Visualizing data with circular graphs where the area represents a certain quantity. Calculating radius helps determine appropriate graph scales.
-
Manufacturing: Designing circular parts or components, assessing the material needed.
Conclusion: Mastering the Area of a Circle
Understanding the formula A = πr² and mastering the ability to solve for 'r' is a fundamental skill in mathematics and various related fields. By following the step-by-step process outlined in this guide and practicing with different examples, you will develop a strong grasp of this crucial concept. Remember to always pay close attention to units, utilize appropriate tools (like calculators), and approach more complex problems systematically. With practice, solving for the radius of a circle will become second nature, equipping you with the skills to tackle a wide range of mathematical and real-world challenges.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
17 Divided By 3 With Remainder
Mar 10, 2025
-
What Percent Of 300 Is 300
Mar 10, 2025
-
2 And 2 3 As An Improper Fraction
Mar 10, 2025
-
Cual Es La Raiz Cuadrada De 216
Mar 10, 2025
-
Use Logarithmic Differentiation To Find The Derivative Of Y
Mar 10, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about A Pi R 2 Solve For R . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
