What Is The Square Root Of 54
Next Genwave
Mar 06, 2025 · 6 min read
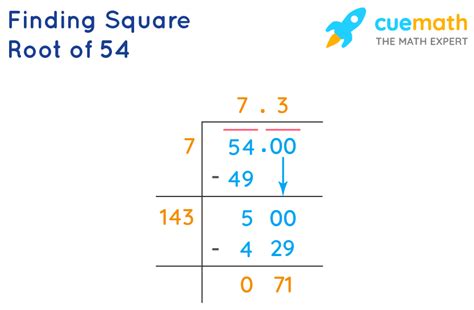
Table of Contents
What is the Square Root of 54? A Deep Dive into Square Roots and Their Applications
The question, "What is the square root of 54?" might seem simple at first glance. However, exploring this seemingly straightforward mathematical concept opens the door to a fascinating world of numbers, their properties, and their practical applications in various fields. This article will delve into the intricacies of finding the square root of 54, exploring both the exact and approximate solutions, and then discussing the broader context of square roots and their significance in mathematics and beyond.
Understanding Square Roots
Before we tackle the square root of 54, let's solidify our understanding of what a square root actually is. The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself (squared), gives the original number. For example, the square root of 9 is 3 because 3 × 3 = 9. This is denoted mathematically as √9 = 3.
The square root of a number can be either a whole number (like 3 in our example), a fraction, or an irrational number. An irrational number is a number that cannot be expressed as a simple fraction and its decimal representation goes on forever without repeating. This is crucial for understanding the square root of 54.
Calculating the Square Root of 54
54 is not a perfect square; there isn't a whole number that, when multiplied by itself, equals 54. Therefore, the square root of 54 is an irrational number. We can find an approximate value using various methods:
1. Using a Calculator
The simplest way to find an approximate value is using a calculator. Most calculators have a square root function (√). Inputting √54 will give you an approximate decimal value of 7.348469228. This is an approximation because the actual value has infinitely many digits after the decimal point.
2. Prime Factorization Method
A more insightful approach involves prime factorization. We break down 54 into its prime factors:
54 = 2 × 27 = 2 × 3 × 9 = 2 × 3 × 3 × 3 = 2 × 3³
This factorization doesn't simplify the square root directly because we don't have pairs of identical prime factors to extract from the root. However, it helps us understand the structure of the number. We can rewrite the square root as:
√54 = √(2 × 3²) × √3 = 3√(2 × 3) = 3√6
This shows that the square root of 54 can be expressed as 3√6. This is the exact form, avoiding the inaccuracies of decimal approximation. The value of √6 is still irrational, but this representation is considered more precise mathematically.
3. Approximation using Perfect Squares
We can estimate the square root of 54 by comparing it to nearby perfect squares. We know that 7² = 49 and 8² = 64. Since 54 is between 49 and 64, the square root of 54 must be between 7 and 8. This provides a rough estimate, but it lacks precision.
The Significance of Irrational Numbers
The fact that the square root of 54 is an irrational number highlights a significant aspect of mathematics. Irrational numbers, like √2, √3, π (pi), and e (Euler's number), demonstrate that not all numbers can be neatly expressed as fractions. Their discovery challenged ancient Greek mathematicians' assumptions about numbers and led to advancements in mathematical theory.
These numbers are not merely abstract concepts; they have real-world applications. For example, π is crucial for calculating the circumference and area of circles, while e is fundamental in calculus and exponential growth models. Similarly, irrational square roots appear frequently in geometry and physics, especially in problems involving distances, areas, and volumes.
Applications of Square Roots
Square roots have widespread applications across diverse fields:
1. Geometry and Trigonometry
Square roots are essential in geometry for calculating distances, areas, and volumes. The Pythagorean theorem, a cornerstone of geometry, uses square roots to determine the length of the hypotenuse of a right-angled triangle (a² + b² = c²). Many geometric calculations involve finding the square root of expressions representing areas, volumes, or distances.
Trigonometry, closely related to geometry, also employs square roots extensively. Many trigonometric functions involve the use of square roots in their calculations.
2. Physics and Engineering
In physics, square roots appear frequently in formulas related to motion, energy, and electricity. For example, calculating the velocity of an object under constant acceleration involves taking the square root. Similarly, in electrical engineering, calculating impedance, a measure of opposition to the flow of alternating current, requires the use of square roots.
3. Statistics and Probability
Square roots are fundamental in statistical analysis, particularly in calculating standard deviation and variance. These measures quantify the dispersion or spread of a dataset, providing valuable insights into the data's distribution.
4. Computer Graphics and Game Development
In computer graphics and game development, square roots are used extensively for calculating distances between points, determining the direction of movement, and implementing collision detection. These calculations are essential for creating realistic simulations and rendering 3D environments.
5. Finance and Economics
Square roots play a role in financial calculations, such as calculating the standard deviation of investment returns, a key metric in portfolio risk management.
Advanced Concepts Related to Square Roots
Exploring further into square roots reveals more complex concepts:
-
Complex Numbers: When we consider the square root of negative numbers, we enter the realm of complex numbers. The square root of -1 is defined as the imaginary unit, i. Complex numbers have a wide range of applications in various scientific and engineering fields, including electrical engineering and quantum mechanics.
-
Nth Roots: The concept of square roots extends to higher-order roots. The nth root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself n times, equals the original number. For example, the cube root (3rd root) of 8 is 2 (2 × 2 × 2 = 8).
-
Solving Quadratic Equations: The quadratic formula, used to solve quadratic equations (ax² + bx + c = 0), involves square roots. This formula is essential for solving numerous mathematical and physical problems.
Conclusion
The square root of 54, seemingly a simple mathematical problem, serves as a gateway to understanding fundamental mathematical concepts and their broad applications. Its irrational nature highlights the richness and complexity of the number system. From calculating areas in geometry to solving equations in physics and managing risk in finance, the square root, in its various forms, plays a crucial and often hidden role in numerous aspects of our world. Understanding its significance provides a deeper appreciation for the elegance and utility of mathematics in our daily lives and across various disciplines. The exact value, expressed as 3√6, offers mathematical precision, while the approximate decimal value provides practical utility in everyday computations. The journey from the simple question "What is the square root of 54?" to the exploration of irrational numbers, complex numbers, and their far-reaching implications shows the power of mathematical inquiry and its influence on our understanding of the world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Solve The Equation For X 5x 2 4x 6
Mar 07, 2025
-
Integral Of E To The Xy
Mar 07, 2025
-
Domain And Range For Y 1 X
Mar 07, 2025
-
53 6 As A Mixed Number
Mar 07, 2025
-
4 1 7 As An Improper Fraction
Mar 07, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Square Root Of 54 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
