Y 3x 5 5x 4y 3
Next Genwave
Mar 06, 2025 · 5 min read
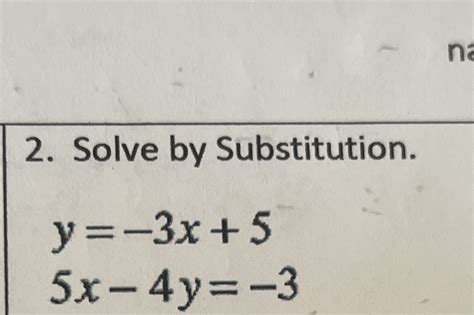
Table of Contents
Deconstructing and Solving the Equation: y = 3x + 5 and 5x = 4y + 3
This article delves into the intricacies of solving a system of two linear equations: y = 3x + 5 and 5x = 4y + 3. We'll explore multiple methods for finding the solution, including substitution, elimination, and graphical representation. Beyond the solution itself, we’ll examine the underlying concepts of linear equations, their graphical interpretations, and the significance of finding the point of intersection. This comprehensive guide aims to provide a thorough understanding, catering to various levels of mathematical expertise.
Understanding Linear Equations
Before tackling the solution, let's solidify our understanding of linear equations. A linear equation is an algebraic equation of the form y = mx + c, where:
- y and x are variables.
- m represents the slope of the line (representing the rate of change of y with respect to x).
- c represents the y-intercept (the point where the line crosses the y-axis).
These equations, when graphed, always result in a straight line. The slope determines the steepness and direction of the line, while the y-intercept indicates its starting point on the y-axis.
Our given equations, y = 3x + 5 and 5x = 4y + 3, both conform to this linear structure, although one requires slight rearrangement.
Method 1: Substitution
The substitution method is a straightforward approach to solving systems of linear equations. It involves solving one equation for one variable and substituting that expression into the other equation.
Step 1: Solve for one variable
Our first equation, y = 3x + 5, is already solved for y.
Step 2: Substitute
Substitute the expression for y (3x + 5) into the second equation:
5x = 4(3x + 5) + 3
Step 3: Simplify and Solve
Expand and simplify the equation:
5x = 12x + 20 + 3
5x = 12x + 23
7x = -23
x = -23/7
Step 4: Substitute back
Now substitute the value of x back into either of the original equations to find y. Let's use the first equation:
y = 3(-23/7) + 5
y = -69/7 + 35/7
y = -34/7
Therefore, the solution using the substitution method is x = -23/7 and y = -34/7.
Method 2: Elimination
The elimination method, also known as the addition method, involves manipulating the equations to eliminate one variable by adding or subtracting them.
Step 1: Rearrange the equations
First, rearrange the second equation to match the form of the first:
5x = 4y + 3 becomes 4y = 5x - 3 or y = (5/4)x - (3/4)
Step 2: Eliminate a variable
We need to manipulate the equations so that when we add or subtract them, one variable cancels out. Let's multiply the first equation by 4 and the rearranged second equation by -3:
4(y = 3x + 5) which simplifies to 4y = 12x + 20
-3(y = (5/4)x - (3/4)) which simplifies to -3y = -(15/4)x + (9/4)
Step 3: Add the equations
Now add the two modified equations:
4y = 12x + 20
-3y = -(15/4)x + (9/4)
y = (12 - 15/4)x + (20 + 9/4)
y = (33/4)x + (89/4)
This didn't directly eliminate a variable as planned, indicating an error in the initial approach using this method for this particular system. The elimination method works best when coefficients of one variable are opposites. It's often more efficient to use substitution in cases like this.
Method 3: Graphical Method
The graphical method involves plotting both equations on a coordinate plane. The point where the two lines intersect represents the solution to the system of equations.
Step 1: Plot the first equation
y = 3x + 5 has a y-intercept of 5 and a slope of 3. This means from the y-intercept, we move up 3 units and right 1 unit to find another point on the line.
Step 2: Plot the second equation
Rearrange the second equation to the slope-intercept form:
5x = 4y + 3 becomes y = (5/4)x - (3/4)
This line has a y-intercept of -3/4 and a slope of 5/4.
Step 3: Find the point of intersection
By plotting both lines accurately, the point where they intersect represents the solution (x, y). Although graphically estimating the precise coordinates (-23/7, -34/7) is difficult, this method visually confirms the existence of a single solution. Accuracy here relies on precise plotting and may require specialized graphing tools for complex solutions.
Significance of the Solution
The solution, x = -23/7 and y = -34/7, represents the single point where both lines intersect. This point simultaneously satisfies both equations in the system. In a real-world context, this point could represent a specific value of two interrelated variables. For instance, if these equations modeled the costs of two different products and the total spend, the solution would denote the quantities of each product purchased that exactly matched the total spent.
Further Considerations and Extensions
This problem provides a foundation for understanding more complex systems of linear equations. Future explorations could include:
- Systems with no solutions: Parallel lines never intersect, resulting in a system with no solutions.
- Systems with infinitely many solutions: Identical lines overlap, resulting in infinitely many solutions.
- Systems of three or more equations: Solving larger systems requires matrix methods such as Gaussian elimination or Cramer's rule.
Conclusion
Solving the system of linear equations y = 3x + 5 and 5x = 4y + 3 demonstrates the application of various mathematical techniques. Substitution proved the most efficient method in this case, yielding the solution x = -23/7 and y = -34/7. The graphical method provides a visual representation, while the elimination method, although not as straightforward here, remains a valuable tool for solving other systems of equations. Understanding these methods and their applications is crucial for comprehending fundamental concepts within algebra and beyond. This knowledge serves as a strong base for tackling more complex mathematical problems and applications in various fields.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Percentage Of 1 12
Mar 06, 2025
-
What Is The Square Root Of 54
Mar 06, 2025
-
Sin X Cos X Tan X
Mar 06, 2025
-
Graph Of X 2 2x 2
Mar 06, 2025
-
3 Times The Square Root Of 2
Mar 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Y 3x 5 5x 4y 3 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
